Introduction
Ww2 motorcycle – World War II marked a significant era in the evolution of transportation, with motorcycles playing a pivotal role in military operations. Far from being mere modes of transport, these machines became instrumental in reconnaissance, communication, and rapid troop deployment. This period saw motorcycles adapted to meet the rigorous demands of warfare, leading to innovations that influenced motorcycle design long after the war ended. This article explores the critical role of motorcycles during WWII and their lasting impact on military strategy and engineering.
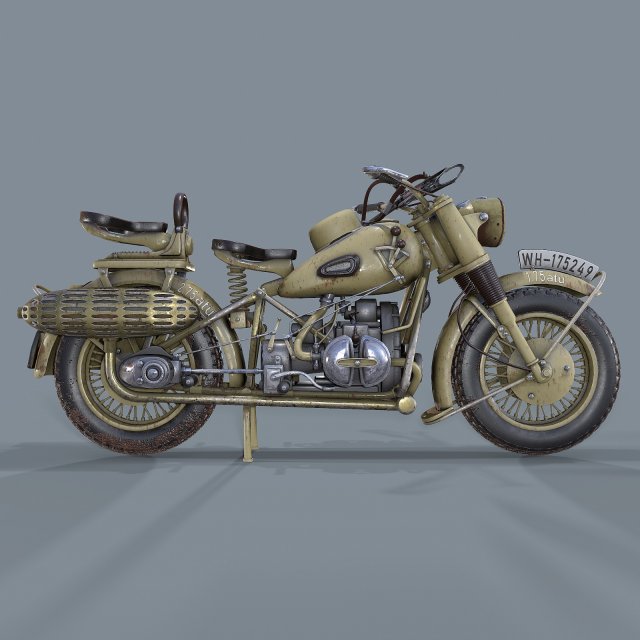

Early Adoption and Adaptation
Before WWII, motorcycles were already in use by various armies, but the conflict accelerated their development and deployment. Countries like Germany, Britain, the United States, and the Soviet Union recognized the potential of motorcycles for their agility, maneuverability, and ability to traverse challenging terrains where larger vehicles couldn’t operate effectively.
German Motorcycles: BMW R75 and Zündapp KS750
Germany stands out for its systematic integration of motorcycles into its military strategy. Two iconic models, the BMW R75 and the Zündapp KS750, were purpose-built for the war effort. Both featured sidecars with a driven wheel, enhancing their off-road capabilities and allowing them to tow light artillery or carry supplies. These bikes also had a unique design with interchangeable parts between the two models, simplifying maintenance and repair in the field.
British Motorcycles: Norton WD16H and BSA M20
The British relied heavily on motorcycles like the Norton WD16H and the BSA M20 for their flexibility and speed. These bikes were often used for messenger duties, rapidly conveying orders and intelligence across the battlefield. Their simplicity and ruggedness made them ideal for the harsh conditions of war.
Tactical Advantages
Motorcycles provided several tactical advantages during the war:
- Speed and Agility: They allowed troops to move swiftly through congested urban areas, dense forests, and rough terrain, providing a significant advantage in reconnaissance and rapid response.
- Communication: Motorcycle-mounted messengers were faster than traditional methods, ensuring urgent messages reached commanders promptly.
- Versatility: Motorcycles could be adapted for various roles, from carrying wounded soldiers to transporting equipment and laying communication wires.
Post-War Influences
The technological advancements and lessons learned from WWII had a profound influence on post-war motorcycle design:
- Engine Technology: Engines became more robust and efficient, influenced by the need for durability and performance under extreme conditions.
- Off-Road Capabilities: The development of motorcycles with enhanced off-road capabilities, such as better suspension and improved tire technology, was directly influenced by wartime demands.
- Adventure and Touring Bikes: The post-war era saw the rise of large displacement motorcycles, inspired by military models, which laid the foundation for today’s adventure and touring motorcycles.
Cultural Impact
WWII motorcycles also left a cultural footprint, becoming symbols of freedom, rebellion, and the spirit of adventure. Veterans returning home often continued riding, contributing to the rise of motorcycle clubs and subcultures. Moreover, movies and media romanticized these machines, further embedding them into popular culture.
Development and Adoption
Motorcycles had already proven their utility in World War I, prompting further development and adoption by various armed forces leading up to WWII. Manufacturers like BMW, Harley-Davidson, and Norton produced purpose-built motorcycles capable of navigating diverse terrains and carrying out specialized roles in combat.
Roles and Functions
- Reconnaissance and Communication:
- Motorcycles were invaluable for reconnaissance missions due to their speed, agility, and ability to traverse rough terrain where larger vehicles couldn’t go.
- They served as vital communication vehicles, delivering messages and orders swiftly between units on the battlefield.
- Logistics and Transport:
- Motorcycles were used to transport personnel, equipment, and supplies quickly and efficiently, especially in areas where traditional vehicles faced logistical challenges.
- They facilitated the rapid deployment of troops and provided logistical support during offensives and retreats.
- Combat Support:
- Armed motorcycles equipped with machine guns or anti-tank weapons were employed to provide mobile firepower and support infantry units.
- They were used for harassment tactics, disrupting enemy supply lines, and conducting raids behind enemy lines.
Military Strategy and Effectiveness
The use of motorcycles influenced military strategy in several key ways:
- Mobility and Speed: Motorcycles enhanced the mobility of military units, allowing for rapid maneuvers and flexible responses to changing battlefield conditions.
- Versatility: They provided versatility in roles ranging from reconnaissance and communication to combat support, making them indispensable assets on both the Eastern and Western fronts.
- Economic Use of Resources: Motorcycles offered a cost-effective alternative to larger vehicles, conserving fuel and other critical resources essential for sustaining prolonged military campaigns.
Impact on Vehicle Design
The experiences gained from WWII shaped the future design of military vehicles:
- Improvements in Durability: Manufacturers incorporated lessons learned from combat to enhance motorcycle durability, reliability, and survivability.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations such as better suspension systems, improved engines, and enhanced braking mechanisms were directly influenced by wartime requirements.
- Integration of Specialized Features: Designers integrated specialized features such as off-road capabilities, waterproofing, and increased payload capacity to meet military specifications.
Legacy and Post-War Influence
After WWII, motorcycles continued to evolve and diversify in military and civilian applications:
- Continued Military Use: Many nations continued to utilize motorcycles for military purposes, adapting them to modern warfare scenarios and peacekeeping operations.
- Civilian Market Expansion: The popularity of military-surplus motorcycles after WWII contributed to the growth of the civilian motorcycle market, leading to further innovations in motorcycle design and technology.
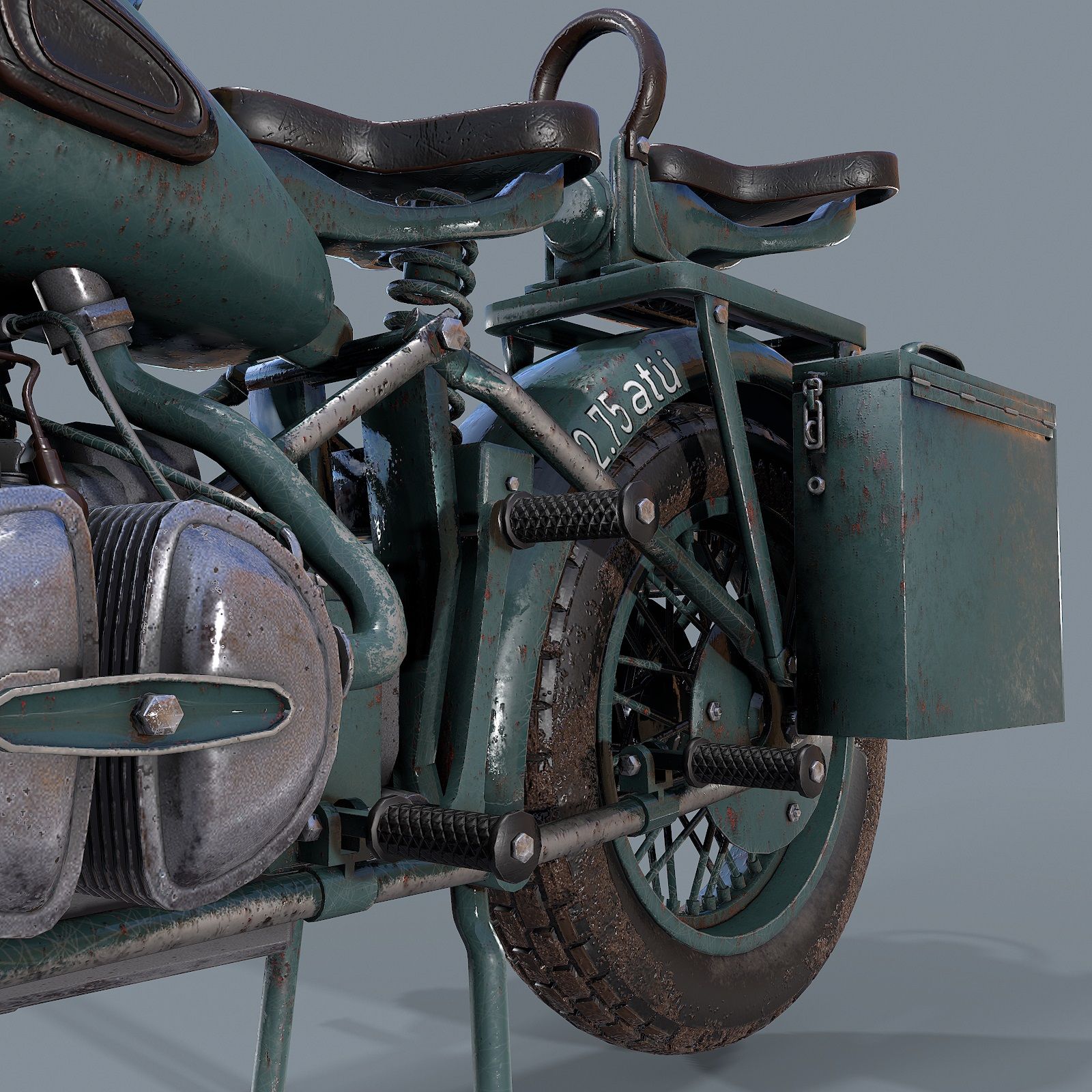

Civilian Applications Post-War – ww2 motorcycle
As the war came to an end, surplus military motorcycles were sold off, flooding the civilian market. This influx not only popularized motorcycling as a leisure activity but also inspired new generations of motorcycle manufacturers and customizers. Many riders began modifying these ex-military bikes to suit their individual tastes, giving birth to the customization culture that remains vibrant today.
Technological Spin-offs – ww2 motorcycle
WWII-era motorcycle innovations didn’t just influence subsequent motorcycle designs but also had spin-offs in other industries. For example, improvements in suspension systems and tire technology found their way into civilian vehicles, enhancing overall road safety and performance. Moreover, the development of compact, powerful engines for motorcycles led to similar advancements in portable generator sets and other compact machinery, demonstrating the far-reaching impact of wartime engineering.
Collectibility and Preservation
Today, original WWII motorcycles and their replicas are highly sought after by collectors and enthusiasts worldwide. These machines serve as tangible links to history, with each scar and modification telling a story of survival and bravery. Organizations and museums dedicated to preserving these vehicles ensure that the legacy of WWII motorcycles lives on, educating future generations about their crucial role in shaping not only military history but also technological and cultural advancements.
Training and Special Forces – ww2 motorcycle
In addition to their operational roles, motorcycles played a significant part in the training and conditioning of special forces units. For instance, the British Commandos and U.S. Army Rangers used motorcycles for physical training and to develop riding skills necessary for swift insertion and extraction missions behind enemy lines. These intense training regimens underscored the importance of motorcycle proficiency in unconventional warfare tactics.
International Contributions and Variations – ww2 motorcycle
While German and British motorcycles are often highlighted, other nations also made notable contributions to the motorcycle’s wartime role. For example, the Soviet Union produced the reliable and robust Ural M72, which was based on the BMW R71 design. And extensively used it for reconnaissance and communication tasks on the Eastern Front. Similarly, the United States employed Harley-Davidson WLA and Indian Scout models, which were modified for military service, demonstrating American engineering prowess and contributing to logistical and tactical successes.
Conclusion
WWII motorcycles were more than just vehicles; they were strategic assets that shaped military operations and engineering advancements. Their legacy can still be seen in modern motorcycle design, adventure riding, and the broader cultural fascination with these machines. The war demanded innovation and resilience. Qualities that were embodied in the motorcycles of the era and continue to inspire motorcycle enthusiasts and designers today.

Leave a Reply