The 6.7 Cummins engine parts diagram is known for its durability, power, and efficiency. It has become increasingly popular in the heavy-duty truck market, especially in Ram trucks. For mechanics, understanding the various components of this engine is crucial for maintenance, repair, and performance optimization. A well-organized engine parts diagram serves as a useful reference tool for both novice and experienced mechanics. In this article, we will explore the essential components of the 6.7 Cummins engine parts diagram, their functions, and how they interact.
Overview of the 6.7 Cummins Engine
Engine Design and Purpose
The 6.7 Cummins engine is a turbocharged inline-six diesel engine. This configuration provides excellent torque and power delivery, making it suitable for heavy loads. With a displacement of 6.7 liters, this engine incorporates a range of advanced technologies to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. It is used in various applications, including pickup trucks, commercial vehicles, and industrial machines.
One of the standout features of the 6.7 Cummins engine is its robust architecture. The engine block is constructed from cast iron, providing strength and durability. Additionally, the engine includes innovations such as a variable geometry turbocharger and an enhanced fuel injection system to optimize performance. Understanding the key components and their layout allows mechanics to diagnose issues and make informed repairs.
Engine Performance Specifications
The 6.7 Cummins engine is available in various power levels, typically delivering between 350 and 400 horsepower, along with impressive torque figures. The engine’s torque output is vital for towing and hauling, making it a favorite among those who require heavy-duty performance. With its advanced design, the engine also meets stringent emissions regulations.
For mechanics, being familiar with these performance specifications is essential. Knowing the power output and torque ratings helps when discussing modifications or upgrades with clients. Additionally, understanding how each component contributes to overall performance enables mechanics to make effective recommendations for maintenance schedules and potential improvements.

Key Components of the 6.7 Cummins Engine
Engine Block and Cylinder Head
The engine block is the foundation of the 6.7 Cummins engine. It houses the cylinders, pistons, and crankshaft, providing structural support for other components. The block design includes several vital features, such as coolant passages and oil channels, allowing for efficient temperature regulation and lubrication.
The cylinder head, mounted on top of the engine block, contains the valvetrain. This includes intake and exhaust valves, valve springs, and camshafts. The cylinder head is crucial for controlling airflow into and out of the combustion chamber. A well-designed cylinder head improves engine efficiency, throttle response, and power output.
Pistons and Crankshaft
Pistons are cylindrical components that move within the engine’s cylinders. They are connected to the crankshaft via connecting rods. As the pistons move up and down, they create the necessary compression for combustion. High-quality materials are essential for pistons to withstand the intense pressures and temperatures present during operation.
The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which powers the vehicle. It is crucial for transmitting power to the transmission and ultimately driving the wheels. Understanding the relationship between these components is key for diagnosing issues like misfires or power loss.
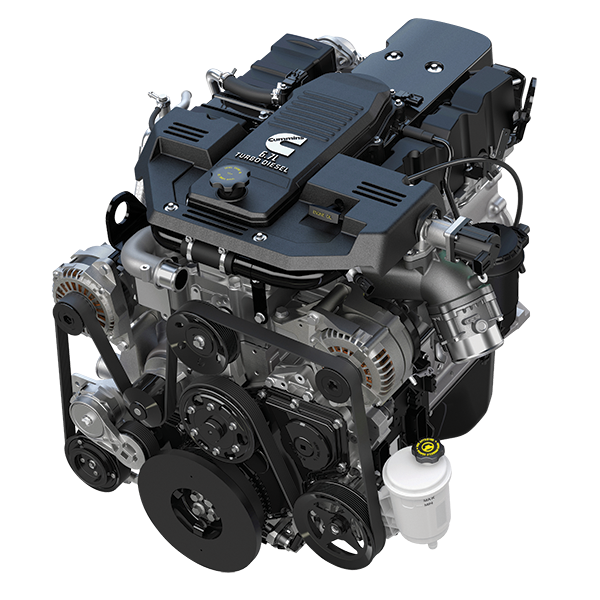

Fuel System Components
Fuel Injector and Injection Pump
The fuel system in the 6.7 Cummins engine plays a critical role in performance and efficiency. Fuel injectors spray fuel directly into the combustion chamber at precise timings to ensure complete combustion. Common rail direct injection (CRDI) technology is employed in the 6.7 Cummins, allowing for multiple injections per cycle for better fuel atomization.
The injection pump is responsible for delivering pressurized fuel to the injectors. Its performance directly affects engine responsiveness and fuel efficiency. Regular inspection and maintenance of the fuel system components are key to preventing performance issues and costly repairs.
Fuel Filter and Fuel Lines
The fuel filter removes contaminants and debris from diesel fuel before it reaches the injectors. A clogged fuel filter can lead to fuel starvation and engine hiccups. Mechanics should regularly check and replace fuel filters based on maintenance schedules to ensure optimal engine performance.
Fuel lines transport the pressurized fuel from the tank to the engine. Proper routing and reliability of these lines are essential for preventing leaks and ensuring that the correct amount of fuel reaches the injectors. Understanding the layout of the fuel system is vital for troubleshooting fuel delivery issues.
Air Intake and Exhaust System
Turbocharger and Intake Manifold
The 6.7 Cummins engine features a variable geometry turbocharger (VGT) designed to maximize airflow and boost performance. The turbocharger compresses air entering the engine, increasing pressure and density for optimal combustion. Mechanics should familiarize themselves with the turbocharger’s components to ensure they operate effectively.
The intake manifold distributes the compressed air from the turbocharger to the engine’s cylinders. It must maintain optimal airflow and temperature levels to promote efficient combustion. Being aware of any restrictions or leaks in the intake system helps mechanics diagnose performance issues.
Exhaust Manifold and Emission Control Systems
The exhaust manifold collects exhaust gases from the engine and routes them to the exhaust system. It must be designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures. A properly functioning exhaust manifold is critical for performance and minimizing emissions.
The 6.7 Cummins engine is equipped with an advanced emissions control system, including a diesel particulate filter (DPF) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR). These systems help reduce harmful emissions, meeting stricter environmental standards. Mechanics should understand the maintenance and diagnostic procedures for these components, as they can significantly impact engine performance and longevity.
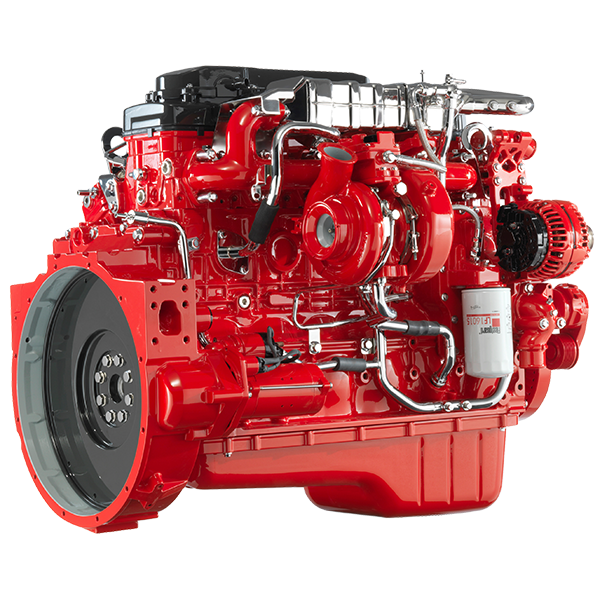
Cooling System Components
Radiator and Coolant System
Maintaining optimal engine temperature is crucial for performance and longevity. The radiator is responsible for dissipating heat from the engine coolant. Proper cooling ensures that the engine does not overheat, which can lead to severe damage.
The cooling system also includes components such as the water pump, thermostat, and coolant hoses. These components work together to circulate coolant throughout the engine. Mechanics must regularly inspect and service the cooling system to prevent leaks and overheating issues.
Thermostat and Coolant Reservoir
The thermostat regulates coolant flow based on engine temperature. It opens and closes to maintain the ideal operating temperature range, ensuring efficient engine performance. A malfunctioning thermostat can result in overheating or inadequate heating during cold weather.
The coolant reservoir stores excess coolant. It acts as a buffer to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction within the system. Regularly checking coolant levels in the reservoir is essential for maintaining proper coolant circulation and preventing air pockets.
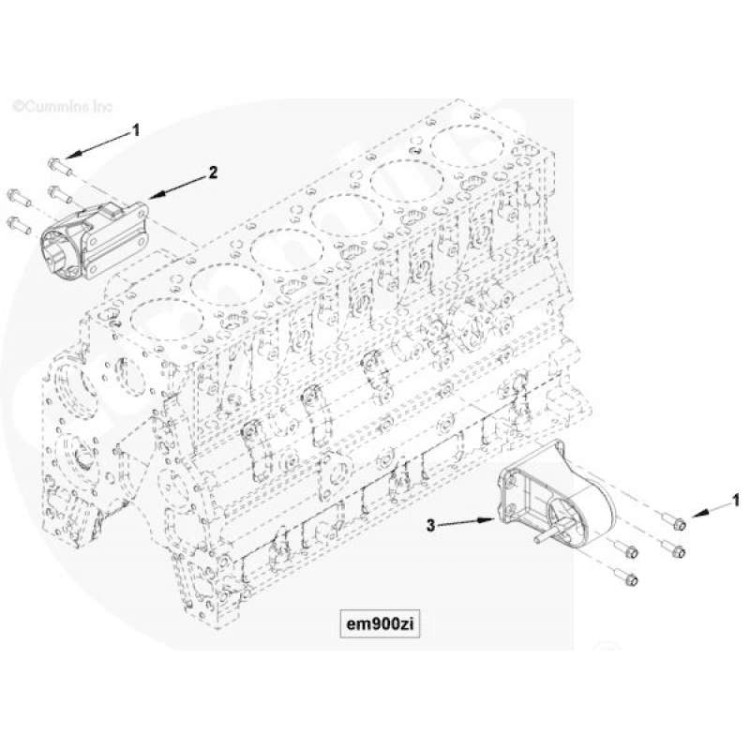
Electrical System and Sensors
Starter Motor and Alternator
The electrical system in the 6.7 Cummins engine includes key components such as the starter motor and alternator. The starter motor is responsible for igniting the engine, while the alternator generates electrical power to recharge the battery and run vehicle accessories.
Regular maintenance of the electrical system helps prevent starting issues and electrical failures. Mechanics should be aware of the signs of a failing starter or alternator, including sluggish starting and dim headlights, which can indicate a problem.
Engine Control Module (ECM) and Sensors
The Engine Control Module (ECM) is responsible for monitoring and managing various engine functions. It collects data from sensors that measure parameters such as throttle position, coolant temperature, and exhaust gas composition. The ECM processes this data to optimize fuel injection and ignition timing, enhancing performance and efficiency.
Key sensors include the mass air flow (MAF) sensor, throttle position sensor (TPS), and crankshaft position sensor. Mechanics must understand how these sensors interact with the ECM to diagnose issues accurately. Performing regular scans and diagnostics can help identify problems before they escalate.
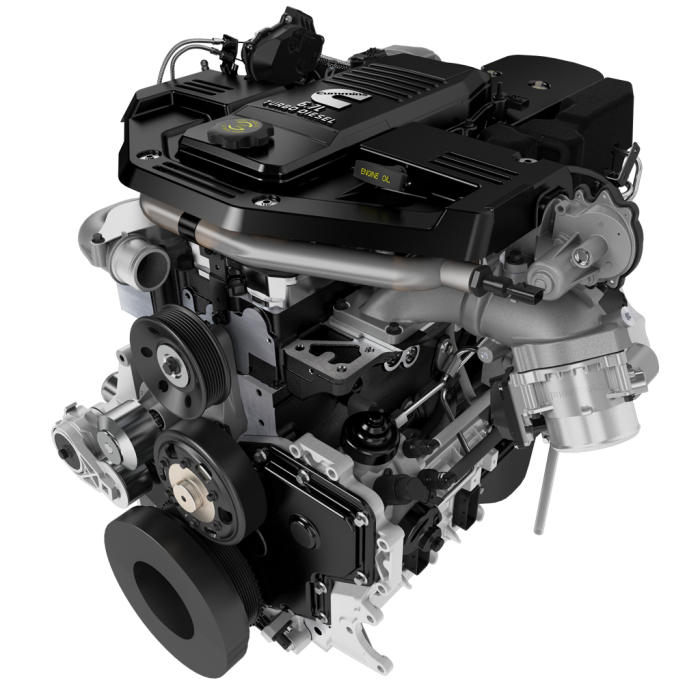
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Routine Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance of your 6.7 Cummins engine is crucial for optimal performance. Key practices include changing engine oil, inspecting filters, and checking fluid levels. Mechanics should follow the manufacturer’s service intervals for inspections and fluid changes.
Scheduled coolant flushes and fuel filter replacements also contribute to the engine’s longevity. Paying attention to any unusual sounds or performance changes can lead to early identification of potential issues. Educating yourself and your clients on proper maintenance will result in a more reliable engine and fewer costly repairs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common problems with the 6.7 Cummins engine may include starting difficulties, poor fuel economy, or reduced power output. Identifying the root causes of these issues often requires systematic troubleshooting. Mechanics should start by checking the electrical system, fuel delivery, and air intake components.
For performance issues, a diagnostic scan can reveal any trouble codes stored in the ECM, guiding the mechanic to the malfunctioning component. Additionally, be vigilant for any signs of leaks in the fuel or cooling systems. Early diagnostics and regular maintenance will help catch small issues before they become major problems.
The 6.7 Cummins Engine Simplified
In conclusion, the 6.7 Cummins engine parts diagram is a robust and reliable powerplant with various components working in harmony. Understanding its parts and their functions is essential for mechanics who wish to perform maintenance and repairs effectively. From the engine block to the electrical system, each component plays a vital role in the engine’s performance and longevity.
Using a detailed engine parts diagram can serve as an invaluable tool in visually understanding these components and their functions. With knowledge comes power for mechanics; the better equipped you are, the more confident you will be in diagnosing and fixing issues. By prioritizing routine maintenance and familiarizing yourself with the intricacies of the 6.7 Cummins engine parts diagram, you can ensure that it continues to perform at its best for years to come.

Leave a Reply