Introduction to Piston Components
Piston components are integral to the performance of an internal combustion engine. Their design and quality affect an engine’s efficiency, power, and durability. Understanding these components helps in maintaining and improving engine functionality.
What Are Pistons?
Pistons are cylindrical mechanical devices inside the engine’s combustion chamber. They move up and down within the cylinder, converting the energy from fuel combustion into mechanical motion. This linear motion powers the crankshaft, which subsequently drives the wheels or other machinery. Pistons are typically made of strong and lightweight materials to withstand high pressures and temperatures during engine operation.
Importance of Pistons in Engine Functionality
Pistons play a vital role in the engine’s combustion cycle. They compress the air-fuel mixture, helping the mixture ignite fully and generate maximum energy. Pistons maintain pressure in the cylinder and ensure smooth operation. Any malfunction can reduce engine efficiency, increase fuel consumption, and even lead to engine failure. Choosing the right piston components ensures long-lasting engine performance.
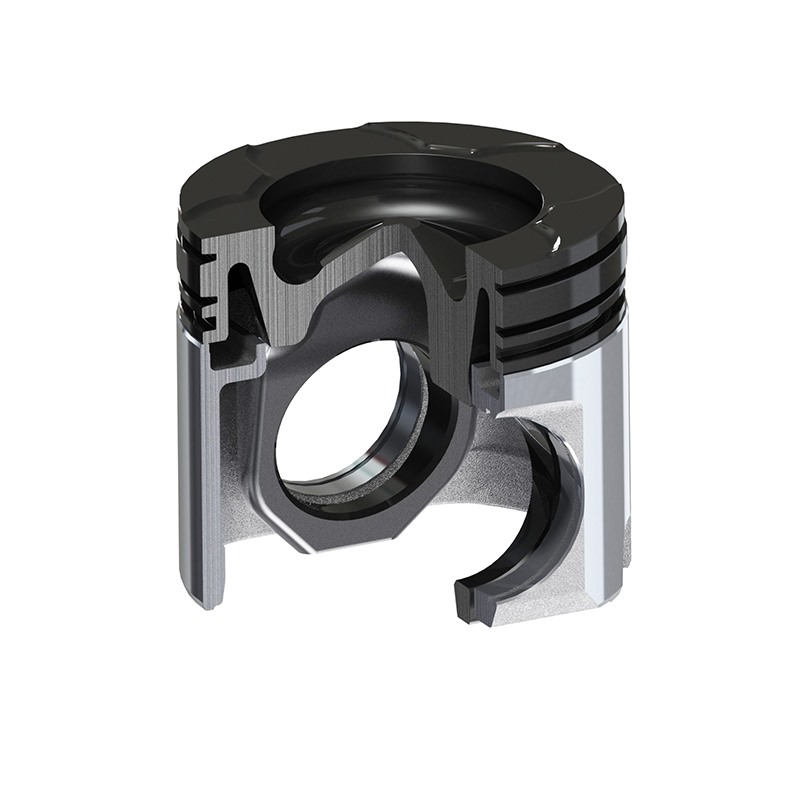

Key Materials Used in Pistons
The choice of materials significantly affects piston performance. Pistons must endure high temperatures and intense pressures.
Aluminum Alloy Pistons
Aluminum alloy pistons are commonly used due to their lightweight structure. They reduce engine weight and improve efficiency. Their thermal conductivity allows rapid heat dissipation. Aluminum pistons also support faster engine operation. However, they may wear quicker under extreme stress compared to other materials.
Steel Pistons
Steel pistons offer superior strength and durability. They handle higher stress levels effectively. These pistons perform well in heavy-duty engines, especially under prolonged high-pressure conditions. Steel’s lower thermal expansion gives stable performance during temperature changes. However, steel pistons are heavier, which can impact engine speed and efficiency.
Comparison of Material Properties
Aluminum alloy pistons are lightweight and enhance fuel efficiency. Steel pistons focus on strength and heat resistance. Aluminum is suitable for high-speed applications, while steel suits heavy-duty and high-pressure use. Choosing the right material depends on the engine type and its operational demands.
Main Components of a Piston
Pistons have several critical components that ensure efficient engine operation. Each part plays a unique role in the combustion cycle, enhancing performance and durability. Understanding these components is essential for optimizing maintenance and repair processes.
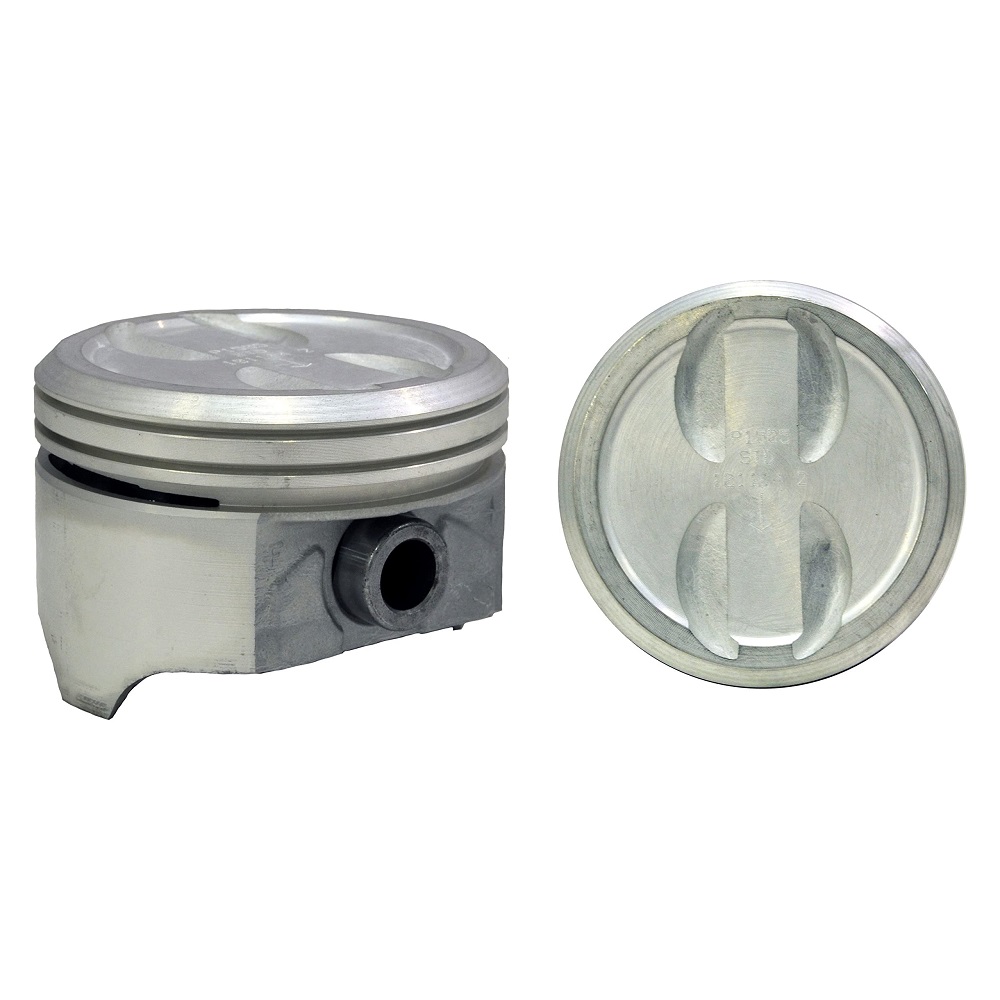
Piston Head
The piston head, or crown, is the top surface of the piston. It faces the combustion chamber and directly receives the force from the burning air-fuel mixture. Its shape influences combustion efficiency and thermal management. Flat-top piston heads improve compression, while dome-shaped ones increase the air-fuel mixture’s turbulence for better combustion.
Piston Skirt
The piston skirt is the lower section of the piston, guiding its movement within the cylinder. It prevents the piston from tilting or wobbling during operation. The skirt ensures smooth motion and minimizes contact friction with the cylinder walls. This part is often coated with materials to reduce wear and heat buildup.
Piston Rings
Piston rings sit in grooves on the piston’s outer surface. They serve three primary purposes:
- Sealing the combustion chamber to maintain gas pressure.
- Controlling oil movement to avoid excessive oil consumption.
- Dissipating heat from the piston to the cylinder walls.
High-quality rings prevent blow-by and reduce wear, enhancing engine reliability and performance.
Piston Pin
The piston pin, also known as the wrist pin, connects the piston to the connecting rod. It transfers the piston’s linear motion to the crankshaft. The pin must withstand high loads and temperatures during engine operation while ensuring smooth movement. Strong and durable materials are essential for this component to prevent failures under stress.
Functionality of Piston Components in Engines
Piston components are essential for an engine’s operation and performance. Each part contributes to power generation and efficiency.
How Pistons Work
Pistons convert combustion energy into mechanical motion. During the combustion cycle:
- Intake Stroke: The piston moves downward, drawing the air-fuel mixture into the cylinder.
- Compression Stroke: It moves upward, compressing the air-fuel mixture for efficient ignition.
- Power Stroke: The ignited mixture expands, pushing the piston downward, generating motion.
- Exhaust Stroke: The piston pushes exhaust gases out of the cylinder, completing the cycle.
This continuous up-and-down motion powers the crankshaft, driving engine operations.
Role of Piston Rings in Compression and Oil Control
Piston rings are critical for sealing and protection. They have three key roles:
- Compression: They maintain gas pressure, preventing leaks from the combustion chamber.
- Oil Control: Rings regulate oil movement, stopping excessive oil usage and contamination.
- Heat Dissipation: They transfer heat from the piston to cylinder walls, reducing temperature buildup.
Effective piston rings help maintain engine efficiency and reliability.
Impact of Piston Pins on Movement and Stability
The piston pin connects the piston to the connecting rod. It enables:
- Movement Transmission: It transfers the piston’s linear motion to the crankshaft seamlessly.
- Stability: It prevents tilting or misalignment during operation.
Piston pins must handle high loads and temperatures. Strong materials ensure their durability and function under stress. Proper installation prevents performance issues and damage.
Common Problems and Maintenance Tips
Piston components are vital for engine efficiency. However, they can encounter various problems over time. Regular maintenance helps prevent damage and ensures optimal engine performance.
Wear and Tear on Pistons
Pistons face significant stress during engine operation. Common causes of wear include:
- Friction: Persistent contact with the cylinder walls causes surface wear.
- High Temperatures: Excessive heat leads to material degradation over time.
- Contamination: Dirt or debris can scratch and damage the piston surface.
- Improper Lubrication: Insufficient oil increases friction, accelerating wear.
Frequent maintenance and quality oil reduce wear and prolong piston life.
Signs of Piston Damage
Spotting early signs of piston damage prevents engine failure. Common indicators include:
- Excessive Smoke: Blue smoke signals oil leakage into the combustion chamber.
- Knocking Sounds: Abnormal noises may indicate damaged or loose piston rings.
- Loss of Power: Reduced engine performance could arise from worn piston components.
- Oil Consumption: Frequent oil refills suggest poor sealing by worn piston rings.
Address these signs promptly to avoid further damage to the engine.
Tips for Prolonging Piston Lifespan
Extending piston life saves costs and ensures engine longevity. Key tips include:
- Use High-Quality Oil: Choose premium oils to reduce friction and wear.
- Regular Maintenance: Inspect pistons and components during routine engine checks.
- Proper Filtration: Replace air and oil filters to avoid contaminants.
- Avoid Overheating: Monitor engine temperatures and address cooling system issues promptly.
- Replace Worn Parts: Act quickly to replace faulty piston rings or pins.
By following these steps, you can maintain healthy piston components and a reliable engine.
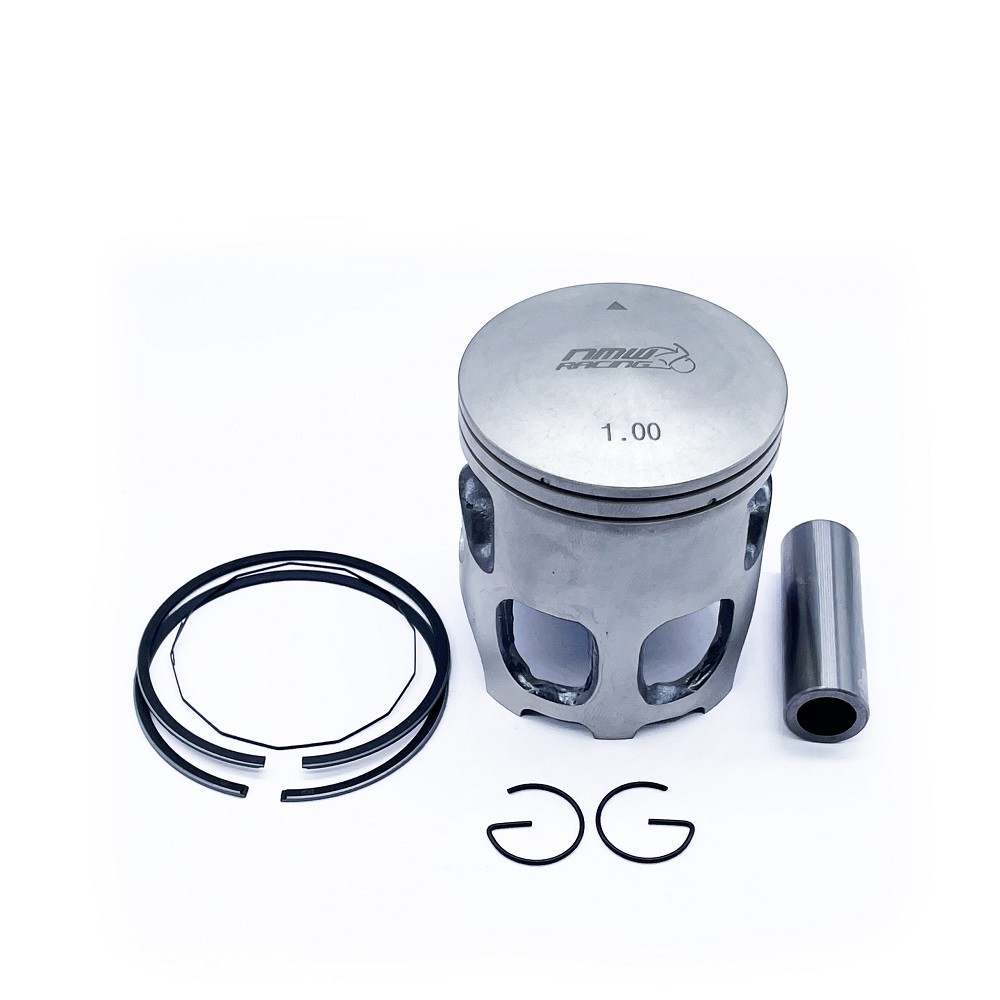

Innovations in Piston Technology
Engine technology is constantly evolving, and pistons are no exception. New advancements are designed to improve mechanical efficiency, enhance durability, and reduce environmental impact. Understanding these innovations can help choose the best piston components for modern engines.
Lightweight Pistons
Lightweight pistons reduce engine weight and improve fuel efficiency. Common materials include advanced aluminum alloys and composite materials. These pistons allow for faster acceleration by reducing inertia. They also support high-speed engine performance. However, they must be durable enough to handle extreme temperatures and pressures. Manufacturers continue to optimize light materials for better strength-to-weight ratios.
Coating Technologies for Reduced Friction
Modern pistons use advanced coatings to minimize friction and wear. Popular coatings include molybdenum-based and ceramic options. These coatings lower heat buildup and reduce the risk of scuffing. They also improve lubrication properties, ensuring smooth piston movement. Reduced friction means longer piston life and improved engine reliability. Coating technology is a key area of focus for enhancing piston performance.
Future Trends in Piston Manufacturing
Future pistons will incorporate smart materials and manufacturing techniques. Additive manufacturing, such as 3D printing, is growing in popularity for precision designs. Nanotechnology may enable stronger and lighter pistons. Environmentally friendly materials could replace traditional metals and alloys. Piston designs will likely focus on noise reduction and greener performance. These trends aim to meet the increasing demands of fuel efficiency and sustainability in modern engines.
Choosing the Right Piston Components
Selecting the correct piston components is crucial for efficient and durable engine performance. Several factors should be kept in mind when evaluating pistons to match your engine’s needs. Additionally, different engines require tailored piston solutions based on their specific applications.
Factors to Consider
- Material Selection: Choose pistons based on strength, wear resistance, and heat dissipation needs. Aluminum alloy pistons suit lightweight engines, while steel pistons work well in heavy-duty conditions.
- Engine Type: Match piston components to the engine—high-speed engines need lightweight options, whereas heavy-duty engines require durability.
- Thermal Conductivity: Select materials with good heat dissipation properties to prevent overheating and maintain efficiency.
- Fit and Dimensions: Ensure pistons fit seamlessly with cylinder walls and other components to avoid issues like blow-by.
- Cost and Longevity: Invest in quality components that last longer to save money and reduce frequent replacements.
- Coatings: Opt for pistons with advanced coatings such as ceramic or molybdenum to reduce friction and wear.
Applications in Different Types of Engines
- Automotive Engines: Modern cars benefit from aluminum pistons for improved fuel efficiency and speed. Performance engines may use coated pistons for reduced friction.
- Heavy-Duty Engines: Trucks and industrial machines require steel pistons to withstand intense pressure and heat.
- Racing Engines: High-performance engines use lightweight pistons for fast acceleration and high RPM handling.
- Marine Engines: Corrosion-resistant pistons are necessary for engines in humid environments.
- Specialized Engines: High-temperature or unique setups may demand tailored pistons, such as composite materials.
Considering these points ensures that the piston components you choose align with operational requirements, enhancing overall engine reliability and performance.
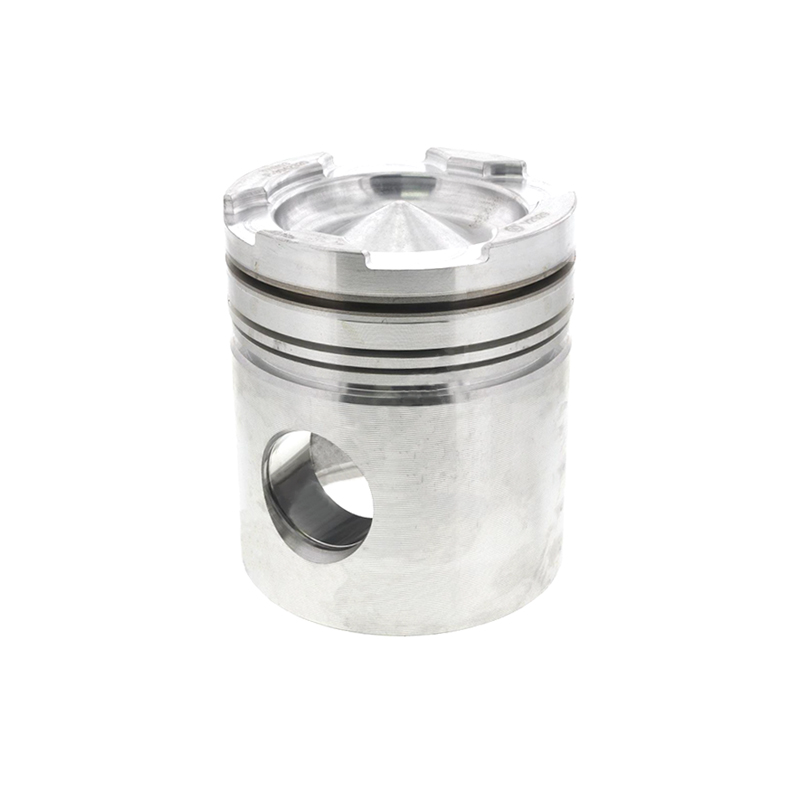

Piston Maintenance Tips
Regular Inspection
Regular inspection of piston components is vital for maintaining engine health. During routine maintenance, mechanics should check for signs of wear, degradation, or improper installation. Each component should be assessed for proper alignment, function, and any damage that could affect performance.
Pay close attention to piston rings, as they are critical for ensuring proper sealing and overall engine efficiency. Look for signs of wear, such as scoring on the ring grooves or abnormal oil consumption. Early detection of issues can save time and expense in the long run.
Keep Up with Oil Changes
Proper lubrication is essential for piston longevity. Engine oil provides the necessary lubrication to prevent friction between moving components. Regularly scheduled oil changes are vital for ensuring that the oil remains clean and effective at providing lubrication.
Using high-quality oil designed for specific engine types can help protect vital components, including pistons. It is also essential to monitor the oil level and quality regularly. Deteriorated or insufficient oil can lead to excessive wear and premature failure of piston components.
Consider Upgrades Wisely
As an engine enthusiast, upgrading piston components can be tempting. However, it is crucial to do so wisely. Choosing components that are compatible with the engine setup and intended use is critical. Upgrading without understanding how each component will interact can lead to performance issues or reduced reliability.
Consulting with experts or performing thorough research before making upgrades ensures that choices align with your goals. Compatibility and quality are paramount to achieving desired results. The importance of informed decisions cannot be overstated when working on piston enhancements.

Conclusion
Understanding piston components is vital for engine enthusiasts looking to enhance their vehicles. The piston plays a pivotal role in converting combustion energy into mechanical power, making it an essential part of the engine. Recognizing the functions of various piston components, including the piston crown, skirt, piston pin boss, and piston rings, affords deeper insights into engine performance.
Upgrading these components can bring many benefits, from improved performance to increased reliability and better fuel efficiency. Regular maintenance, including inspections and oil changes, is crucial to ensuring the longevity of piston components and overall engine health. By approaching piston maintenance and upgrades intelligently, enthusiasts can optimize their engines for both performance and longevity.
In summary, investing time and effort into understanding piston components provides a solid foundation for aspiring mechanics and seasoned enthusiasts alike. This knowledge not only enhances one’s skillset but also fosters respect for the intricate workings of automotive engines. With the right information and commitment, any enthusiast can gain the confidence needed to work on their engines and enjoy the thrill of the open road.

Leave a Reply