Introduction to Pneumatic Piston Actuators
Pneumatic piston actuator is essential in industrial automation and mechanical systems. They convert compressed air into mechanical force. This force is used to perform various functions, like opening and closing valves or enabling precise movements in machinery.
What Are Pneumatic Piston Actuators?
A pneumatic piston actuator is a device that uses air pressure to generate motion. It relies on compressed air to move a piston inside a cylinder. The motion can either be linear or rotary, depending on the system’s design. Each actuator is designed to generate substantial force, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Their compact and efficient nature makes them a popular choice across industries.
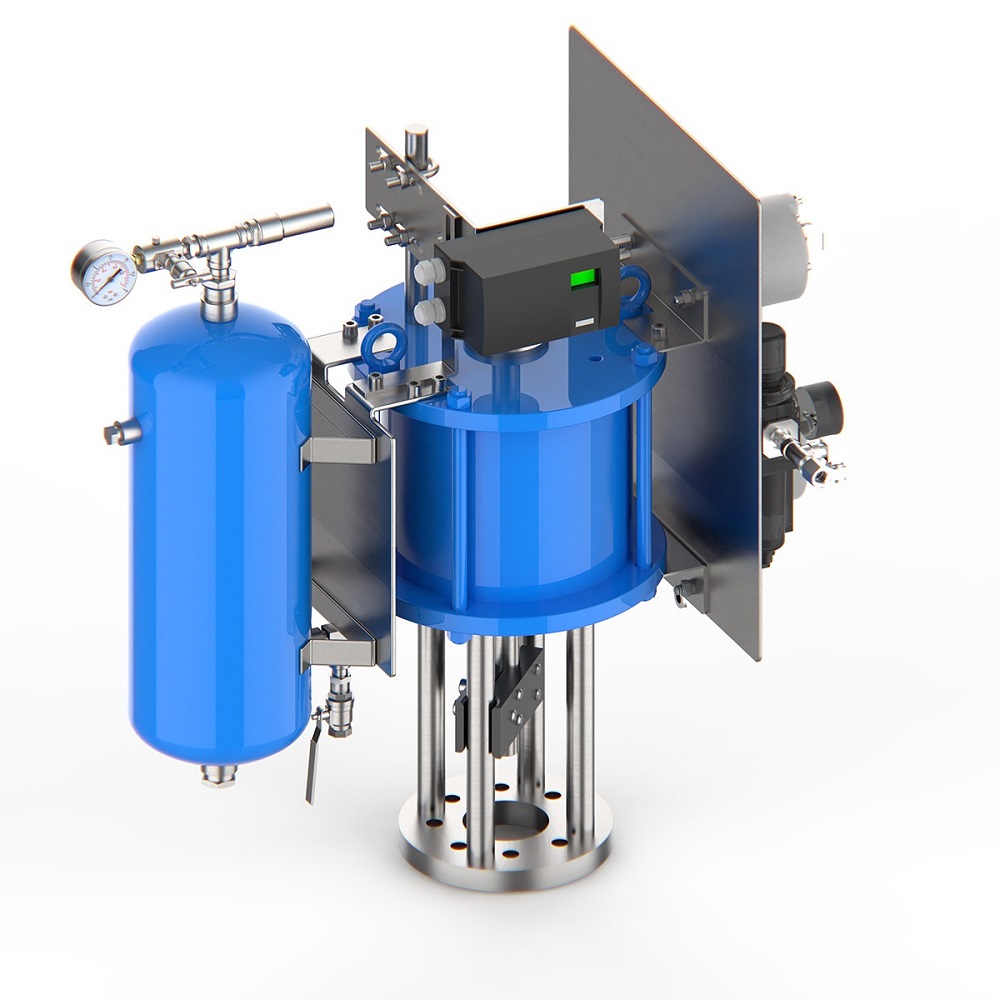
Key Components of a Pneumatic Piston Actuator
- Cylinder: Houses the piston and guides its movement.
- Piston: Converts air pressure into mechanical force.
- Seals: Prevent air leakage, ensuring efficient operation.
- Ports: Allow air to enter or exit the cylinder.
- Rod: Transfers motion from the piston to the external mechanism.
- Spring (in some models): Aids in returning the actuator to its original position.
These components work together to ensure smooth and reliable actuator performance. Choosing high-quality materials for these components improves durability and efficiency. Proper maintenance also ensures a long service life for pneumatic piston actuators.
Principles of Operation
Understanding how a pneumatic piston actuator operates is essential for proper application and maintenance. These devices rely on compressed air to generate movement and perform mechanical tasks. Their operational principles ensure the consistent and efficient delivery of force in various industrial applications.
How Does a Piston Actuator Function?
Pneumatic piston actuators work by converting air pressure into mechanical motion. Compressed air is introduced into the cylinder through ports. This air pushes the piston, creating movement either forward or backward along the cylinder. The movement direction depends on the setup of air flow and internal components.
In single-acting actuators, compressed air moves the piston in one direction, while a spring returns it. In double-acting actuators, air pressure controls both forward and backward motion, eliminating the need for a spring. The controlled air flow ensures precise and repeatable motions for various tasks.
Valves often manage the airflow to the actuator, ensuring proper timing and control. This mechanism is highly reliable due to the robustness and simplicity of its design.
Types of Movements: Linear and Rotary
Pneumatic piston actuators produce two main types of movements: linear and rotary.
- Linear Movement: The piston moves in a straight line within the cylinder. This type of movement is common in actuators used to open or close valves and other equipment where straight motion is needed.
- Rotary Movement: In these systems, linear motion converts into rotary motion. Gears or other mechanical components enable the piston’s linear stroke to create rotational force. Rotary actuators are often found in applications requiring angular positioning, such as in dampers or control systems.
Both types of movement ensure adaptable and efficient operations in diverse industries. Carefully choosing the right movement type ensures optimal performance for specific applications.

Types of Piston Actuators
Pneumatic piston actuators come in different types, designed to suit various industrial needs. Understanding these types helps in selecting the right actuator for specific applications.
Single-Acting vs. Double-Acting Actuators
Single-acting actuators use compressed air for motion in one direction. A spring returns the piston after air is released. These actuators are simple and suitable for basic tasks. They consume less air and are often used for smaller loads.
Double-acting actuators use air pressure for motion in both directions. They do not require springs for returning the piston. These actuators provide precise and powerful movements. They are ideal for larger loads and continuous operations due to their reliable performance.
Single-acting actuators are compact and cost-effective, but double-acting actuators deliver greater force and flexibility.
Spring-Return Pneumatic Actuators
Spring-return actuators are a subtype of single-acting actuators. They use a spring to reset the piston after operation. This design ensures safety by returning to its initial position during air loss.
They are widely used in applications where fail-safe operation is critical, such as in valves and emergency systems. Spring-return actuators enhance operational reliability and ensure system safety during unexpected failures.
Choosing between these actuator types depends on power needs, operational reliability, and specific application requirements.
Applications of Piston Actuators
Pneumatic piston actuators are versatile devices used across multiple industries and applications. Their ability to provide consistent force and precise motion makes them essential in various mechanical systems. Below are some key applications where these actuators play an important role.
Industrial Uses in Automation
Pneumatic piston actuators are widely utilized in industrial automation processes. They control the movement of machinery and equipment, enabling efficient operations. Common applications include:
- Assembly Lines: Actuators perform repetitive motions required for assembling products.
- Material Handling: They move and position materials during manufacturing.
- Packaging Systems: Actuators assist in opening, closing, or sealing containers.
Their reliability and speed help streamline automation systems, reducing human intervention and increasing productivity.

Applications in the Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas sector greatly benefits from pneumatic piston actuators. These actuators are used in systems requiring high precision, such as:
- Valve Operations: They operate pipeline valves for controlling flow and pressure.
- Drilling Equipment: Actuators are used in hydraulic and pneumatic drilling tools.
- Safety Systems: Spring-return actuators ensure fail-safe positions during emergencies.
Their sturdy design ensures reliable performance even under tough environmental conditions like extreme temperatures and high pressures.
Use in Valves and Control Systems
Pneumatic piston actuators are integral to valves and control systems in various industries. They precisely regulate fluid or gas flow, making them ideal for:
- Flow Control Valves: Actuators open or close valves to manage flow rates.
- Pressure Regulators: They help maintain specific pressure levels in pipelines.
- Dampers: Actuators adjust dampers for airflow control in HVAC systems.
These applications highlight their importance in ensuring smooth and efficient operation in critical systems.
By understanding these applications, industries can better leverage the capabilities of pneumatic piston actuators for improved efficiency and performance.
Advantages of Pneumatic Piston Actuators
Pneumatic piston actuators offer broad advantages, making them indispensable for many industries and applications. Their unique properties enhance efficiency and usability across diverse systems.
Cost-Effectiveness
Pneumatic piston actuators are cost-effective due to their simple design and affordable components. They require less upfront investment compared to other actuator types. Their long service life helps reduce replacement costs. Maintenance is straightforward, often requiring only basic repairs. Their operating cost is low because they use air as the driving force, eliminating expensive power sources.
Reliability and Durability
These actuators are known for their strong reliability in demanding environments. Their robust construction ensures performance under extreme conditions like high temperatures or corrosive settings. With fewer moving parts, they have lower risks of mechanical failure. High-quality seals prevent air leaks and ensure consistent motion. Regular maintenance keeps them durable for long-term use in critical applications.
Energy Efficiency
Pneumatic piston actuators excel in energy efficiency, relying on compressed air, a renewable resource. Unlike hydraulic systems, they avoid oil-based operation, reducing environmental concerns. Precise control of air flow minimizes energy waste. Their efficiency helps lower energy consumption in factories and industrial setups. By optimizing airflow and reducing losses, they ensure smooth and energy-conscious operation.
These attributes make pneumatic piston actuators an excellent choice for industries looking for affordable, reliable, and eco-friendly solutions.

Challenges and Limitations
Pneumatic piston actuators are efficient devices, but they come with specific challenges. Understanding these limitations helps in maintaining their performance and addressing issues proactively.
Common Issues Faced
- Air Leakage: Worn-out seals or damaged components can cause air leakage, reducing efficiency.
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture and harsh environmental conditions may lead to rust and wear.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Extreme temperatures can impact seals, resulting in operational inefficiencies.
- Load Limitation: Pneumatic actuators may struggle with extremely heavy loads compared to hydraulic systems.
- Inconsistent Force: Compressed air systems can sometimes deliver uneven force if not regulated properly.
These common issues highlight the importance of regular inspections and maintenance to prevent failures.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Regular Inspection: Check seals, ports, and the piston for wear or damage.
- Lubrication: Keep moving parts properly lubricated to reduce friction and prevent wear.
- Clean Air Supply: Ensure the air used is clean and dry to avoid contamination issues.
- Tight Sealing: Replace defective seals promptly to prevent air leaks and maintain efficiency.
- Pressure Settings: Regularly verify and adjust air pressure to ensure consistent actuator performance.
- Corrosion Protection: Apply protective coatings or use corrosion-resistant materials for harsh environments.
Proper maintenance mitigates operational risks and keeps pneumatic piston actuators functioning efficiently for extended periods.
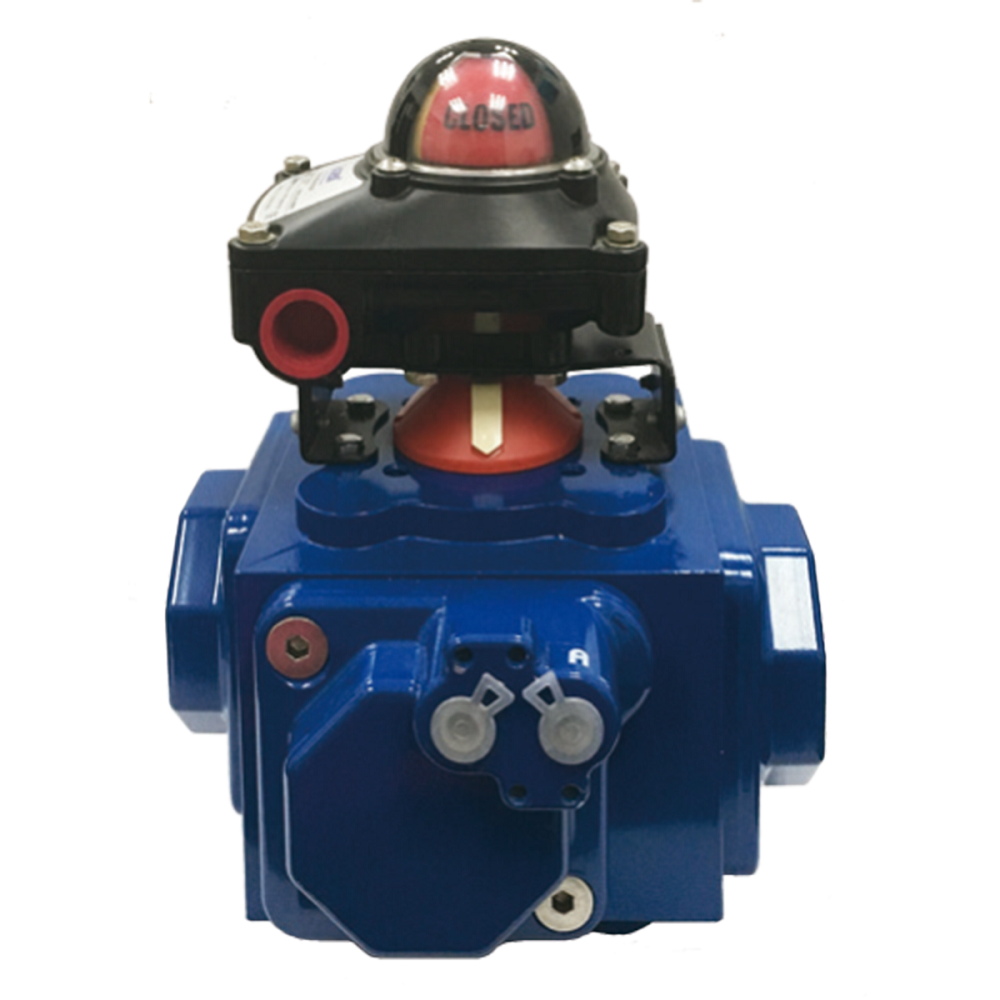

Selection Criteria for Pneumatic Piston Actuators
When choosing a pneumatic piston actuator, selecting the right one ensures efficiency and reliability. Consider the system’s requirements, environment, and operational demands to make the best choice.
Considering Load Requirements
Load requirements play a major role in selecting the appropriate actuator. Follow these points to analyze:
- Determine Load Weight: Understand the maximum and minimum load the actuator will handle.
- Force Requirement: Calculate the force needed for smooth operations. Double-acting actuators provide more force compared to single-acting types.
- Precision Needs: Assess if the application needs fine or coarse control of movement.
- Frequency of Operation: Frequent operations require actuators built for durability and consistent performance.
Matching the actuator’s force and load capacity ensures reliable and efficient operation.
Environmental and Operational Conditions
The operating environment impacts actuator performance. Choose an actuator that withstands its surroundings. Consider the following:
- Temperature Range: Select materials and seals suitable for extreme hot or cold conditions.
- Exposure to Corrosive Substances: Use corrosion-resistant materials for harsh environments with chemicals or moisture.
- Dust and Particles: Ensure proper filters to prevent dust from affecting performance.
- Humidity Levels: Opt for actuators with moisture-resistant properties in high-humidity areas.
- Vibration and Shock: For high-vibration environments, choose actuators with robust mounting and designs.
By assessing load and environmental needs, you can choose a pneumatic piston actuator that guarantees long-term reliability and optimal performance.
Future Trends in Pneumatic Actuators
The field of pneumatic actuators is constantly evolving to meet modern industrial demands. Innovations focus on improving efficiency, reliability, and integration with advanced technologies. By understanding future trends, industries can stay ahead and leverage improved pneumatic solutions effectively.
Advances in Materials and Design
Innovative materials and designs are enhancing the performance of pneumatic piston actuators. These advances address durability, efficiency, and adaptability.
- Lightweight Materials: New alloys and composites reduce weight without losing strength. This improvement enhances portability.
- Improved Seals: Advanced sealing materials prevent air leaks and extend actuator lifespan.
- Corrosion Resistance: Specialized coatings protect components against moisture and chemicals, boosting durability in harsh environments.
- Compact Designs: Manufacturers are developing smaller actuators to integrate into tight spaces more easily.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Optimized internal components reduce energy loss and improve operational performance.
These developments enhance precision and reliability, making pneumatic actuators suitable for modern applications.
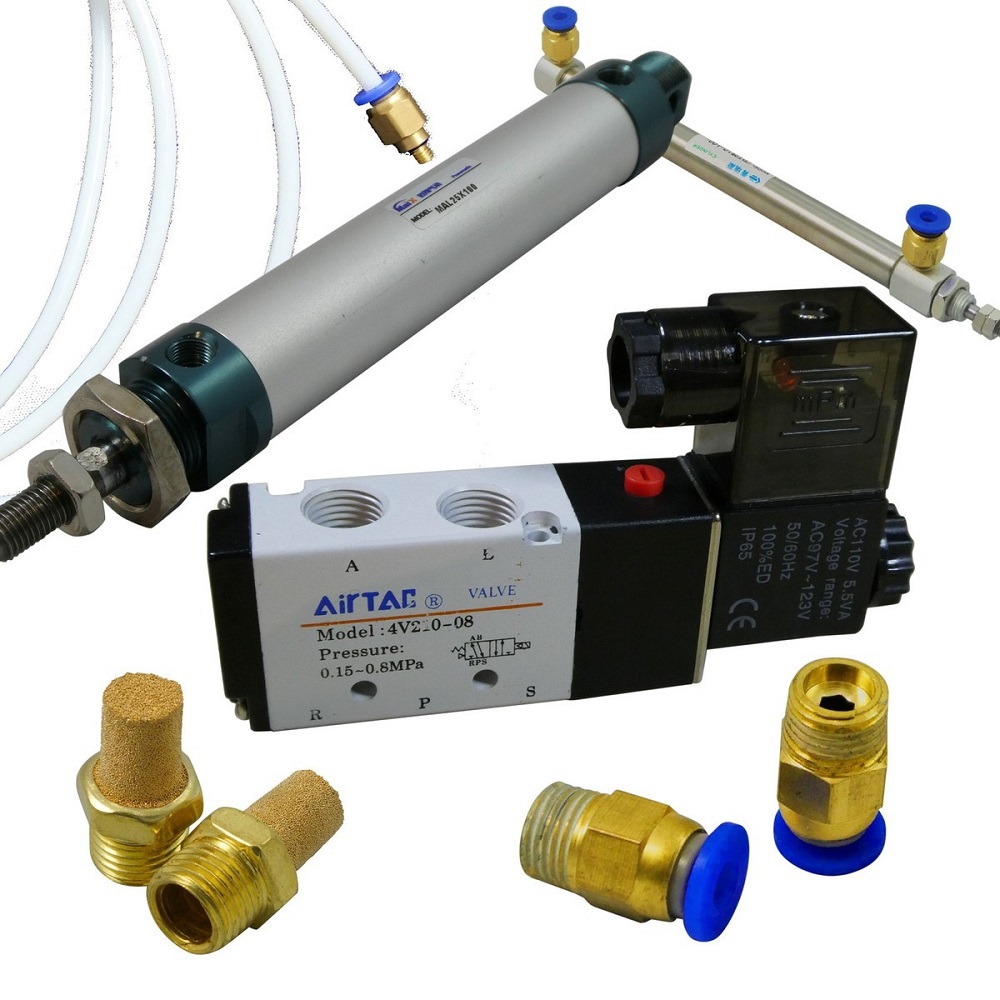

Integration with Smart Technologies
Smart technologies are transforming pneumatic systems for better monitoring, control, and automation. Integration with intelligent features is a key trend.
- IoT Connectivity: Actuators can now connect to IoT networks for real-time data sharing.
- Sensors: Built-in sensors monitor airflow, pressure, and actuator performance.
- Predictive Maintenance: Smart systems identify issues before they cause failures, reducing downtime.
- Programmable Controls: Users can program precise motion controls for complex operations.
- Energy Optimization: Automated systems adjust air usage to save energy and reduce costs.
By integrating smart technologies, pneumatic piston actuators can achieve greater flexibility for advanced industrial needs.
Future advancements in materials and tech integration will continue to redefine pneumatic actuators. Industries must adopt these trends to remain efficient and competitive.
Embracing the Benefits of Piston Actuators
A Worthy Investment for Industries
In summary, pneumatic piston actuator represent a vital component in the landscape of industrial machinery. Their capacity for efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and versatility makes them an attractive choice for various applications. By understanding the key features, maintenance requirements, and best practices for operation, industries can maximize their investment in pneumatic solutions. As technology continues to advance, these actuators will likely play an even more significant role in optimizing production processes.
Encouraging a Proactive Approach
Riders, manufacturers, and operators alike should embrace a proactive approach to integrating pneumatic piston actuators into their operations. Regular maintenance practices and proper usage techniques will ensure that these machines function effectively. The benefits gained from a quality pneumatic piston actuator can greatly impact productivity and reliability in industrial settings. Committing to efficiency and safety will lead to a more productive operating environment.
A Sustainable Future with Pneumatic Solutions
Finally, as industries move toward more sustainable practices, pneumatic technologies will continue to adapt and innovate. The evolution of pneumatic piston actuator signifies the potential for eco-friendly solutions with minimal environmental impact. Embracing this shift will contribute to a greener future while maintaining efficiency in manufacturing. By choosing pneumatic systems, industries not only equip themselves with advanced technology but also become participants in creating sustainable solutions. The future of pneumatic piston actuators looks bright, promising exciting developments for years to come.

Leave a Reply