What is a Coolant Sensor?
A coolant sensor, also known as an engine coolant temperature sensor (ECT sensor), plays a key role in monitoring the engine’s temperature. It measures the temperature of the engine’s coolant and sends the data to the car’s engine control unit (ECU). The ECU uses this information to regulate fuel injection, ignition timing, and other essential functions.
The coolant sensor is typically located near the thermostat or in the cylinder head. Made of durable materials, it can withstand high temperatures. It uses a thermistor to detect temperature, usually exhibiting lower resistance at high temperatures and higher resistance at low temperatures.
By accurately sensing coolant temperature, the sensor protects the engine from overheating. It also improves fuel efficiency and reduces emissions. In modern cars, the coolant ensures optimal engine performance. It communicates critical information, allowing the car to function smoothly in various conditions.
A faulty coolant sensor can lead to incorrect temperature readings, affecting the engine’s performance. In some cases, it may even trigger the check engine light. Therefore, understanding the basics of the coolant sensor is crucial for maintaining your car’s efficiency and longevity.
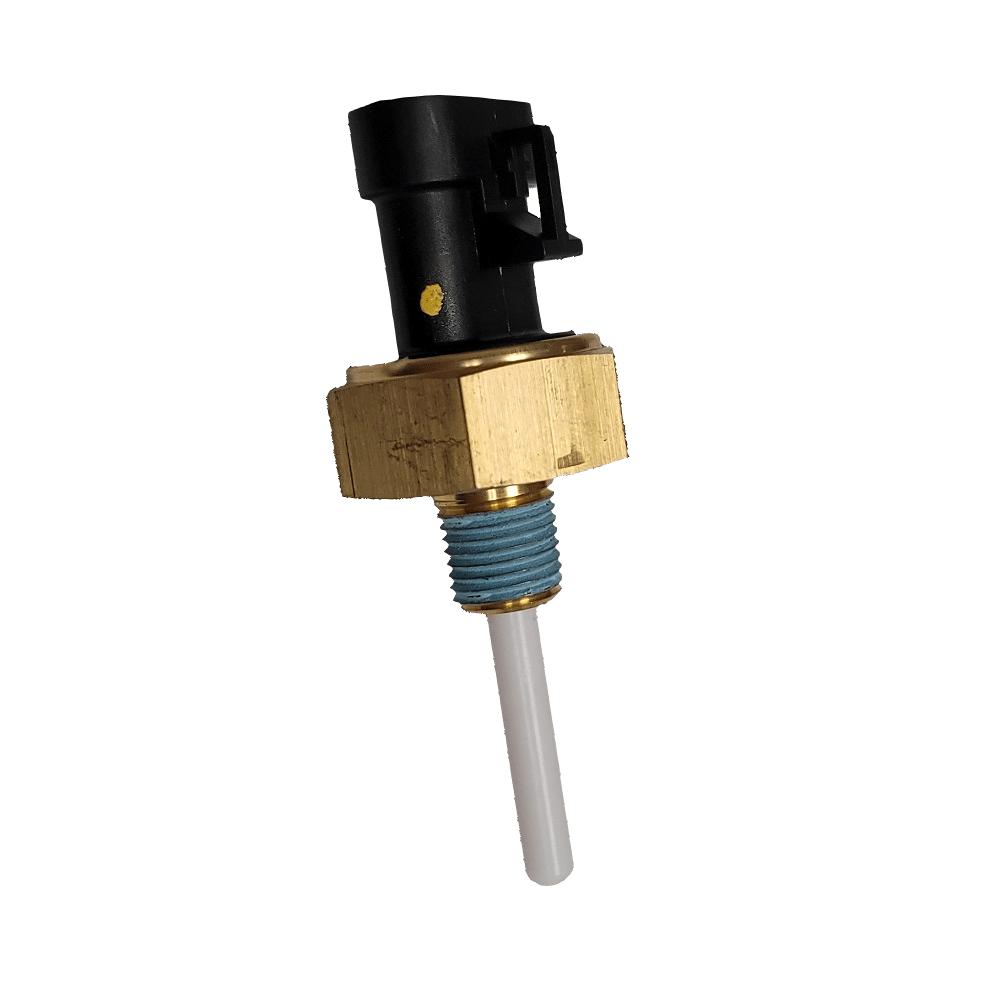
How Coolant Sensors Work
Coolant sensors operate by closely monitoring the temperature of the engine’s coolant. The sensor contains a thermistor, which changes its electrical resistance based on the temperature. At higher temperatures, the thermistor’s resistance drops, and at lower temperatures, its resistance increases.
The coolant sensor records these temperature changes and converts them into an electrical signal. This signal is sent directly to the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU then interprets this data to adjust critical engine functions. These include fuel injection, ignition timing, and idle speed.
The coolant sensor ensures fuel efficiency by regulating the air-fuel mixture. For a cold engine, it increases fuel flow to help it warm up quickly. When the engine reaches its optimal temperature, it stabilizes the fuel mixture. This process reduces fuel consumption and emissions significantly.
Furthermore, the coolant sensor prevents engine overheating by alerting the ECU to any abnormal temperature spikes. It triggers the cooling fans or adjusts engine performance to maintain safe operating temperatures. Without a working coolant sensor, the engine could overheat and sustain damage.
Modern cars often have more sophisticated systems with multiple sensors working together. These sensors provide accurate temperature data in real-time. This solidifies the coolant sensor’s role as a critical component for optimal engine performance and longevity.
Importance of Coolant Sensors in Modern Cars
Coolant sensors are crucial for the efficient performance of modern cars. They play a key role in monitoring and managing engine temperature. This information helps the engine control unit (ECU) adjust important functions like fuel injection and ignition timing.
Ensuring Optimal Temperature
A coolant sensor ensures the engine operates within the optimal temperature range. Overheating can cause severe damage, like a blown gasket or warped cylinder head. On the other hand, a cold engine reduces efficiency and increases emissions. The coolant sensor helps maintain the balance, ensuring better performance and durability for the engine.
Improving Fuel Efficiency
Modern cars rely on precise air-fuel mixture ratios for maximum efficiency. The coolant sensor provides real-time temperature data that allows the ECU to adjust the fuel mixture. For example, it increases fuel during cold starts and reduces it once the engine warms up. This process minimizes fuel wastage and reduces harmful emissions.

Protecting Engine Components
Frequent temperature changes can harm engine components. A functioning coolant sensor prevents these issues by keeping the temperature within safe limits. It also activates cooling mechanisms like radiator fans during unexpected temperature spikes. Over time, this protection extends the lifespan of vital engine parts.
Enhancing Overall Performance
With modern advancements, coolant sensors have become more accurate and responsive. They help enhance the driving experience by enabling smoother acceleration and reliable engine performance. Additionally, they work with other sensors to maintain stability under varying conditions.
Integral Role in Modern Vehicles
Today’s vehicles are equipped with advanced computers and sensors. Coolant sensors serve as an essential link in this network. They ensure the engine operates efficiently in diverse environments and contribute to reducing the car’s environmental impact. Investing in a reliable coolant sensor keeps your vehicle running smoothly and helps maintain overall engine health.
Signs of a Faulty Coolant
A faulty coolant sensor can cause various issues in your vehicle. Here are some common signs:
Check Engine Light Turns On
One of the first signs is the illuminated check engine light. A malfunctioning coolant sensor may send incorrect temperature readings to the ECU, triggering the warning light.
Poor Fuel Efficiency
A faulty sensor can lead to inaccurate air-fuel mixture adjustments. This can cause your engine to consume more fuel, lowering its efficiency and increasing costs.
Engine Overheating or Running Cold
If the coolant sensor fails, the engine may overheat or stay too cold. Overheating can cause serious damage, while a cold engine reduces performance.
Hard Starts and Stalling
Incorrect temperature readings can disrupt fuel injection, causing hard starts or stalling. This issue usually happens during cold starts when the engine needs more fuel.
Increased Exhaust Emissions
Faulty sensors can affect fuel combustion and lead to higher emissions. This may result in regulatory issues or impact the environment negatively.
Poor Engine Performance
You may notice reduced acceleration or sluggish response. An inaccurate coolant sensor can limit optimal engine operation, affecting overall performance.
Erratic Temperature Gauge Readings
The temperature gauge in your vehicle may show inconsistent or incorrect readings. This happens when the sensor fails to provide accurate data to the ECU.
Recognizing these signs early can prevent serious engine damage. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of a faulty coolant sensor can improve your car’s efficiency and reliability.

Effects of a Malfunctioning Coolant on Engine Performance
A malfunctioning coolant sensor can significantly affect your engine’s performance and longevity. It can disrupt critical functions controlled by the ECU, leading to a variety of issues.
Incorrect Air-Fuel Mixture
When the coolant sensor provides incorrect temperature data, the ECU may mismanage the air-fuel mixture. This mismanagement can lead to excessive fuel consumption and reduced efficiency. Over time, it damages engine components.
Unstable Engine Temperature
A faulty coolant sensor may fail to detect abnormal temperature changes. This can cause the engine to overheat or remain too cold. Overheating may harm components like the cylinder head or gasket. A cold engine wastes fuel and increases emissions.
Reduced Engine Performance
Malfunctioning sensors can limit engine functions such as ignition timing and fuel delivery. You may experience poor acceleration, sluggish operation, or stalling during use. These issues are especially noticeable during cold starts.
Increased Exhaust Emissions
Incorrect temperature readings may cause incomplete combustion. As a result, exhaust emissions increase, affecting the environment. Cars with frequent emissions issues may fail regulatory inspections.
Hard Engine Starts and Stalling
With inaccurate temperature data, the engine may struggle during startup. It can stall frequently, especially in cold weather. These difficulties add stress to the ignition system and fuel injectors.
Risk of Engine Damage
Without accurate temperature monitoring, overheating becomes a serious risk. This can result in long-term engine damage, leading to costly repairs or replacement.
Temperature Gauge Malfunction
A defective coolant sensor may send incorrect data to the temperature gauge. Drivers rely on this gauge for monitoring engine health. Erratic readings can lead to confusion and delayed responses in critical situations.
In summary, a faulty coolant sensor compromises engine efficiency, increases wear on components, and can result in costly repairs. Timely diagnosis and replacement are key to preventing performance issues and ensuring a smooth driving experience.
Steps to Diagnose Coolant Issues
Diagnosing a coolant sensor issue is essential to avoid engine performance problems. Here are the steps:
Step 1: Check Warning Signs
Monitor for common symptoms of a faulty coolant sensor. These include the check engine light, engine overheating, poor fuel efficiency, erratic temperature gauge readings, or increased emissions. Any of these signs might indicate a malfunction.
Step 2: Scan for Error Codes
Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve error codes from your vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU). Codes related to the coolant sensor will help pinpoint the issue.
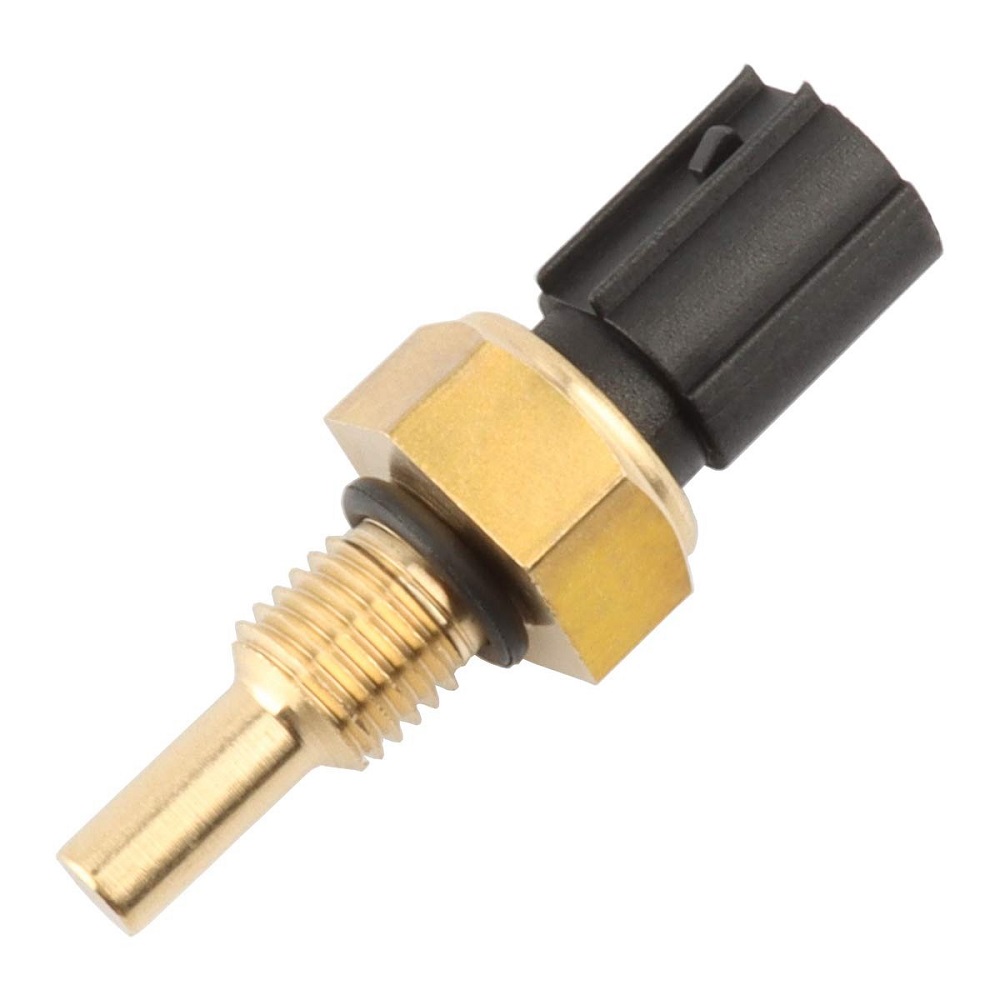

Step 3: Test the Sensor’s Resistance
Disconnect the coolant sensor from its electrical connection. Use a multimeter to check the sensor’s resistance values at different temperatures. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. A faulty sensor often gives constant or abnormal resistance values.
Step 4: Examine the Wiring and Connections
Check the wiring connected to the coolant sensor for signs of damage. Look for frayed wires or corroded connectors. Damaged wiring can cause inaccurate readings or sensor failure.
Step 5: Inspect for Physical Damage
Visually inspect the sensor for damage, such as cracks or corrosion. If it looks damaged, replacement may be necessary.
Step 6: Monitor Coolant Levels
Low coolant levels can also affect sensor readings. Check if the coolant reservoir is full and replenish if necessary. Ensure there are no leaks in the cooling system.
Step 7: Seek Professional Diagnosis
If steps fail to resolve the issue, consult a professional mechanic. They use specialized tools for accurate diagnostics and can confirm if the issue lies with the coolant sensor or other components.
Diagnosing coolant sensor problems early prevents further damage and ensures smoother engine performance. Regular checks help maintain the sensor’s efficiency and prolong engine health.
How to Replace a Coolant
Replacing a coolant sensor is a straightforward task if done correctly. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Gather Tools and Supplies
Prepare the necessary tools, including a wrench, safety gloves, and possibly a multimeter. Check your vehicle manual for specific requirements.
Step 2: Ensure Safety First
Turn off the engine and allow it to cool completely. Disconnect the battery to avoid electrical mishaps.
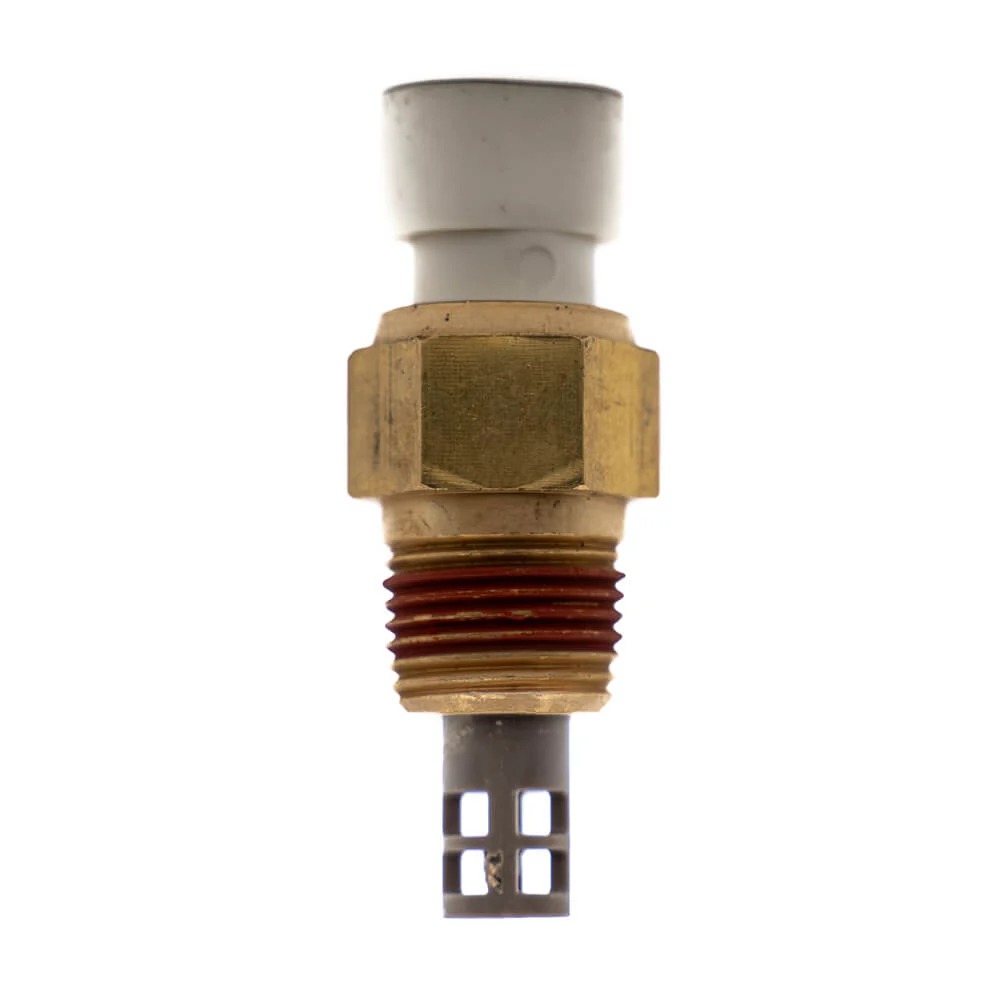
Step 3: Locate the Coolant Sensor
Find the coolant sensor. It is usually located close to the thermostat or on the cylinder head. Your vehicle’s manual can help.
Step 4: Drain Coolant
To access the sensor, drain the coolant partially. Use a clean container to collect it for reuse.
Step 5: Disconnect the Old Sensor
Carefully unplug the electrical connector attached to the sensor. Avoid pulling the wires too hard to prevent damage.
Step 6: Remove the Sensor
Use a wrench to unscrew the old coolant sensor. Check surrounding areas for dirt or corrosion and clean if necessary.
Step 7: Install the New Sensor
Place the new coolant sensor in position and tighten it securely. Connect the electrical wiring securely.
Step 8: Refill the Coolant
Top up the coolant using the drained liquid or fresh coolant. Ensure it reaches the required levels.
Step 9: Test the Installation
Reconnect the battery and start the engine. Check the temperature gauge and ensure it functions properly.

Additional Tips
- Double-check all connections. Loose wiring can affect the sensor’s performance.
- Dispose of drained coolant responsibly. It is toxic and harmful to the environment.
- If unsure, consult a professional mechanic to avoid errors during replacement.
By following these steps, you can replace the coolant sensor efficiently. Maintaining your sensor ensures balanced engine temperature and enhanced performance.
Tips for Maintaining Your Coolant Sensor
Proper maintenance of your coolant sensor ensures efficient engine performance and longevity. Follow these tips:
Check Regularly for Damage
- Inspect the sensor for visible cracks, corrosion, or any signs of physical wear.
- Check the wiring and connectors for frays or loose connections.
Keep Coolant at Optimal Levels
- Regularly check your vehicle’s coolant levels.
- Refill or replace coolant if it’s low or contaminated.
- Use the correct type of coolant for your vehicle’s requirements.
Clean Surrounding Areas
- Keep the area around the coolant sensor clean.
- Remove dirt and debris to prevent obstruction and contamination.
Inspect the Cooling System
- Check the radiator, thermostat, and other cooling components.
- Look for leaks or worn-out parts that could affect the sensor.
Perform Routine Engine Checks
- Conduct regular tune-ups to address underlying engine issues.
- Monitor the temperature gauge for unusual readings.
Use Quality Parts
- Replace old or worn sensors with high-quality, vehicle-specific parts.
- Avoid using cheap or non-compatible components.
Seek Professional Service
- Schedule periodic checks with a qualified mechanic.
- Use an OBD-II scanner to detect potential sensor issues early.
By following these simple steps, you can extend your coolant sensor’s lifespan. This ensures better fuel efficiency, optimal engine temperature, and overall vehicle performance.

Leave a Reply