Introduction to One Cylinder Diesel Engines
One cylinder diesel engine is compact and efficient power units. They operate using the diesel cycle, which involves compression ignition. Unlike multi-cylinder engines, these engines have only one cylinder for combustion. This design makes them simpler, lighter, and easier to maintain.
Diesel engines rely on fuel injection and air compression for ignition. The cylinder acts as the main combustion chamber. In one cylinder engines, only one piston moves inside the cylinder. This piston compresses air and injects diesel fuel to start combustion.
These engines are widely used in various industries, especially for low-power needs. They are known for their durability and fuel efficiency. Their simple design ensures reliable performance in tough conditions. Understanding how one cylinder diesel engines work is key to maximizing their benefits.
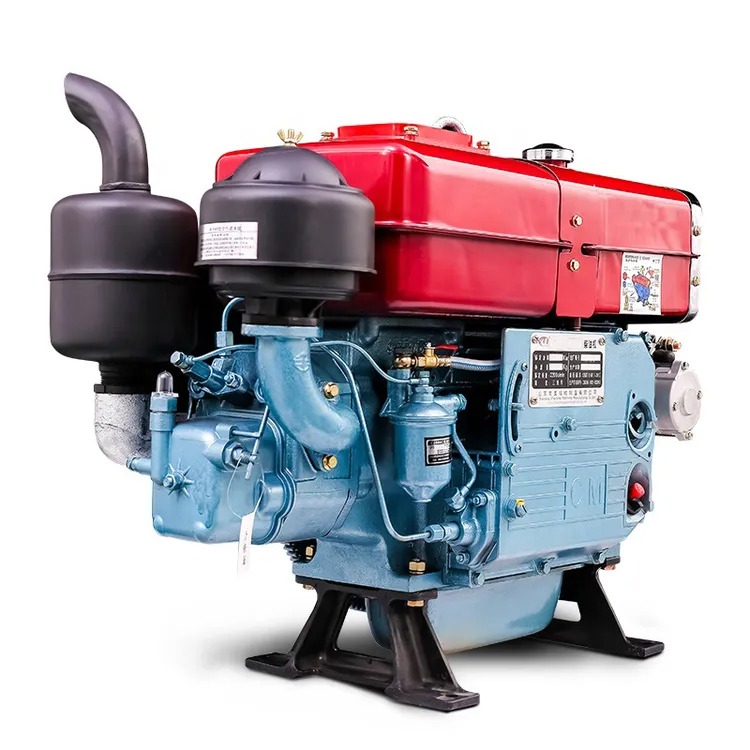

Key Components of a One Cylinder Diesel Engine
Understanding the key components of a one cylinder diesel engine is essential. These components ensure smooth operation and efficient performance. Here are the primary parts:
- Cylinder: The cylinder forms the engine’s core. Combustion takes place inside the cylinder when air and fuel mix.
- Piston: The piston moves up and down in the cylinder. It compresses air and transfers energy to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: The crankshaft converts the piston’s linear motion into rotational motion, driving the engine’s output.
- Fuel Injector: The fuel injector sprays diesel fuel into the cylinder. It ensures proper air-fuel mixing and effective combustion.
- Air Intake and Exhaust Valves: These valves regulate air entering and exhaust gases exiting the cylinder.
- Flywheel: The flywheel stores rotational energy. It provides smoother operation by balancing the engine’s power cycle.
- Cooling System: The cooling system prevents engine overheating by maintaining the cylinder’s optimal temperature.
- Compression Ring and Oil Ring: These rings around the piston minimize air and oil leakage during operation.
Each of these components has a vital role. Together, they make the one cylinder diesel engine efficient and reliable.
How Combustion Works in a One Cylinder Engine
Combustion is the core process that powers a one cylinder diesel engine. It converts fuel into mechanical energy. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how combustion works in such an engine:
- Air Intake Phase: The engine draws air into the single cylinder through the intake valve. This phase prepares the air for compression.
- Compression Phase: The piston moves upward, compressing the air inside the cylinder. This increases air pressure and temperature significantly.
- Fuel Injection Phase: The fuel injector sprays a fine mist of diesel into the highly compressed air. Diesel is injected at the right moment to ensure efficient combustion.
- Ignition and Power Phase: The high temperature causes the diesel to ignite spontaneously. This creates an explosion that forces the piston downward. This movement generates the engine’s mechanical power.
- Exhaust Phase: The exhaust gases generated in the cylinder are expelled through the exhaust valve as the piston moves upward again, completing the cycle.
This process repeats continuously in a one cylinder diesel engine. The engine’s design ensures efficiency and durability during each step.
The engine’s simplicity allows smooth combustion control. This contributes to its effectiveness in transforming diesel into usable energy. The crankshaft and flywheel then work together to convert this energy into rotational force, which powers the intended machinery or application.
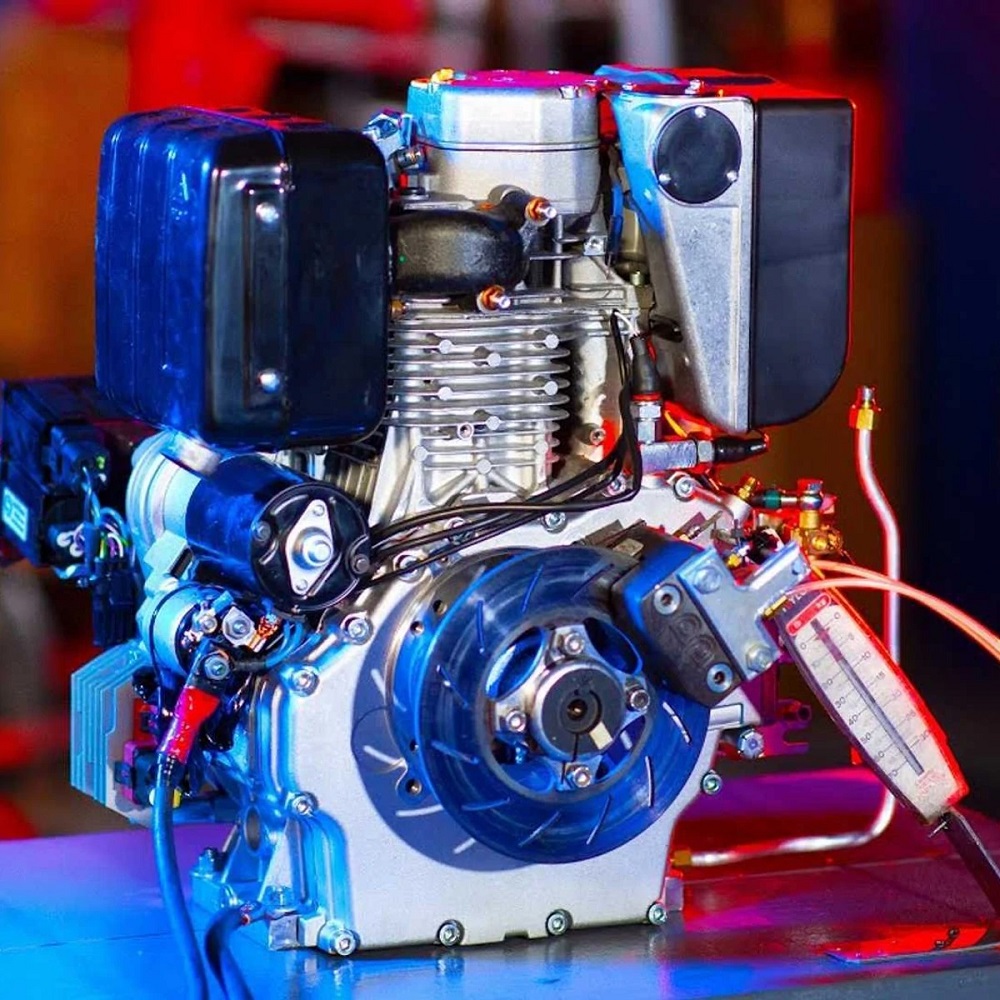
Advantages of One Cylinder Engines
One cylinder diesel engines offer several distinct advantages. Their design focuses on simplicity and reliability, making them a preferred choice for many applications.
1. Compact and Lightweight
These engines are small and lightweight, ideal for areas with space constraints. Their reduced size allows easy transportation and installation in various equipment.
2. High Fuel Efficiency
One cylinder diesel engines consume less fuel due to their efficient combustion process. This results in lower operating costs and better energy utilization.
3. Cost-Effective
With fewer parts, these engines are economical to manufacture and maintain. This makes them budget-friendly for industries and individual users.
4. Durable and Reliable
Their simple design enhances durability. They perform reliably under tough conditions, making them suitable for heavy-duty usage.
5. Easy Maintenance
The single cylinder design simplifies maintenance tasks. Repairs and inspections are quicker and require fewer resources.
6. Lower Emissions
Compared to larger engines, one cylinder diesel engines produce fewer emissions. This improves environmental sustainability.
7. Versatility
These engines can be adapted to various applications, from agriculture to construction. Their versatility serves diverse needs effectively.
The numerous advantages of one cylinder diesel engines highlight their practicality and efficiency for multiple uses. Such benefits make them a popular choice across industries.
Common Applications of One Cylinder Engines
One cylinder diesel engines are used in a variety of industries. Their compact size and efficiency make them versatile. Let’s explore some of their common applications:
1. Agricultural Machinery
One cylinder diesel engines power small agricultural tools. They are used in water pumps, tillers, and sprayers. Their reliability is vital for farming in remote areas.
2. Construction Equipment
These engines are found in small construction machines. They power concrete mixers, compactors, and mini-excavators. Their durability and low maintenance are perfect for tough construction tasks.
3. Generators
One cylinder diesel engines are widely used in small generators. They serve as backup power sources for homes and businesses. Their fuel efficiency ensures long operation during power outages.

4. Marine Engines
In the marine industry, these engines are used in small boats and fishing vessels. They provide reliable propulsion in challenging water conditions.
5. Industrial Equipment
These engines are used in smaller industrial machines. Applications include air compressors, conveyor belts, and small-scale processing units.
6. Portable Equipment
One cylinder diesel engines are ideal for portable devices. Examples include pressure washers, pumps, and handheld drilling equipment. Their lightweight design allows easy portability.
7. Two-Wheelers and Small Vehicles
Some small vehicles, like motorcycles and scooters, also use one cylinder diesel engines. Their fuel efficiency ensures low operating costs.
8. Remote and Off-Grid Applications
In remote areas, these engines power basic household devices. They operate water pumps and even mill grain in some regions.
These diverse applications highlight the engine’s adaptability to different needs. One cylinder diesel engines remain a favored option for their simplicity and effectiveness.
Maintenance Tips for One Cylinder Engines
Proper maintenance keeps one cylinder diesel engines running efficiently and prolongs their lifespan. Regular care ensures optimal performance and reduces the risk of major faults. Below are essential maintenance tips:
1. Follow a Routine Maintenance Schedule
Stick to a regular maintenance timetable. Check and service the engine at recommended intervals for best results.
2. Inspect and Replace Oil Regularly
Regularly check the engine oil level. Replace old oil to maintain lubrication and prevent wear.
3. Clean the Air Filter
Inspect the air filter for clogging. Clean or replace it to ensure proper air intake.
4. Check the Fuel System
Examine fuel lines and the injector regularly. Ensure the fuel system is clean and free of leaks.
5. Inspect the Cooling System
Monitor the cooling system’s condition. Clean and service it to prevent overheating.
6. Tighten Loose Bolts and Fasteners
Check for loose bolts and fasteners. Tighten them to keep the engine securely assembled.
7. Watch for Wear and Tear
Inspect parts for wear and replace damaged components promptly. Address small issues before they worsen.

8. Avoid Overloading the Engine
Use the engine within its specified capacity. Overloading can cause overheating and damage.
9. Store Properly
Store the engine in a dry, clean place. Protect it from dirt, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
10. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
Always refer to the user manual for specific maintenance instructions and recommended practices.
By following these simple tips, your one cylinder diesel engine will deliver consistent and reliable performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in One Cylinder Engines
Troubleshooting one cylinder diesel engine problems is essential for maintaining performance and reliability. Common issues can impact operation, but they are often simple to diagnose and fix. Below are practical steps to identify and address typical problems.
1. Engine Won’t Start
- Cause: Empty fuel tank, clogged fuel line, or air in the fuel system.
- Solution: Check fuel level, clean fuel lines, and bleed the fuel system to remove air.
2. Loss of Power
- Cause: Dirty air filter, faulty injector, or poor compression.
- Solution: Clean or replace the air filter, inspect and repair the injector, and check cylinder compression.
3. Excessive Smoke
- Cause: Incorrect fuel mix, blocked exhaust, or worn piston rings.
- Solution: Use proper fuel, check the exhaust for blockages, and replace worn piston rings.
4. Overheating
- Cause: Malfunctioning cooling system, low coolant, or excessive engine load.
- Solution: Inspect the cooling system, refill coolant, and ensure proper engine loading.
5. Unusual Noise
- Cause: Loose bolts, worn bearings, or damaged crankshaft.
- Solution: Tighten bolts, replace damaged bearings, and inspect the crankshaft.
6. Fuel Leaks
- Cause: Damaged fuel line or loose connections.
- Solution: Replace damaged fuel lines and tighten all connections securely.
7. Vibration During Operation
- Cause: Imbalanced flywheel or loose components.
- Solution: Balance the flywheel and secure all components properly.
8. Difficulty in Fuel Injection
- Cause: Clogged fuel injector or poor fuel quality.
- Solution: Clean the fuel injector and use high-quality diesel fuel.
9. Weak Compression
- Cause: Worn piston rings or damaged cylinder walls.
- Solution: Replace piston rings and repair cylinder walls as needed.
10. Electrical Problems
- Cause: Faulty wiring or dead battery.
- Solution: Inspect wiring, replace damaged wires, and recharge or replace the battery.
By understanding and fixing these common issues, you can optimize the performance and lifespan of your one cylinder diesel engine. Regular inspections and proactive care are key to preventing major problems. Ensure that troubleshooting aligns with manufacturer guidelines for best results.

Future Trends in One Cylinder Engine Technology
The development of one cylinder diesel engines continues to evolve, offering innovative features and cutting-edge technologies. These advancements aim to improve performance, efficiency, and sustainability. Here are some notable future trends:
1. Enhanced Fuel Efficiency
Engine designs are focusing on maximizing fuel efficiency. Improved injection systems and optimized airflow enhance combustion.
2. Reduced Emissions
Stricter environmental regulations drive the need for cleaner engines. Advanced filtration and after-treatment systems reduce harmful emissions.
3. Electronic Engine Control Units (ECU)
Modern one cylinder diesel engines increasingly rely on ECUs. These systems ensure precise fuel injection timing and enhanced engine control.
4. Hybrid Integration
Future engines may combine diesel power with electric systems. Hybrid designs reduce fuel consumption and improve efficiency.
5. Lightweight Materials
Innovative materials, like aluminum alloys and composites, reduce engine weight. This boosts portability and overall efficiency.
6. Enhanced Durability
New coatings and materials improve the engine’s lifespan. These advancements mitigate wear and resist harsh conditions.
7. Smart Monitoring Systems
Advanced sensors and monitoring systems are becoming standard. They track engine performance and provide real-time data.
8. Automation and Connectivity
IoT-enabled diesel engines integrate into smart systems. This allows remote monitoring and automated operations.
9. Waste Heat Recovery
New designs recycle waste heat into energy, increasing overall efficiency. This trend focuses on better energy utilization.
10. Adaptation for Renewable Fuels
Engines are being adapted to use renewable fuels, such as biodiesel. This reduces reliance on traditional diesel.
The future of one cylinder diesel engine technology looks promising. These innovations aim to offer better performance while addressing environmental concerns effectively.
Embracing the Power of One Cylinder Diesel Engines
The Value of Choosing Diesel
Choosing a one cylinder diesel engine is a decision grounded in performance, reliability, and efficiency. Whether used in agricultural machinery, portable generators, or light commercial vehicles, these engines deliver the power needed to get the job done. Understanding the advantages and applications helps individuals make informed choices when selecting the right engine for their needs.
The Versatility of Diesel Engines
The versatility of one cylinder diesel engines allows them to adapt to various situations, making them indispensable in many sectors. As technology advances, these engines continue to evolve, providing even greater performance and sustainability. Their compact design and fuel efficiency make them an attractive option for a wide range of users.
Ready for the Road Ahead
As we look to the future, one cylinder diesel engines are set to remain a crucial component of many industries. With ongoing innovations and a focus on sustainability, they are positioned to meet the demands of modern society. Whether you’re a farmer, contractor, or casual user, embracing the power of one cylinder diesel engines will ensure you are ready for the challenges ahead. Enjoy the benefits and reliability that these engines bring, knowing that they are built for the long haul.

Leave a Reply