Introduction to Rotary and Piston Engines
Engines power vehicles and machines through fuel combustion. Rotary vs piston engines are two popular types. While each operates differently, they serve similar purposes. Understanding their designs and functions helps in choosing the right one.
What is a Rotary Engine?
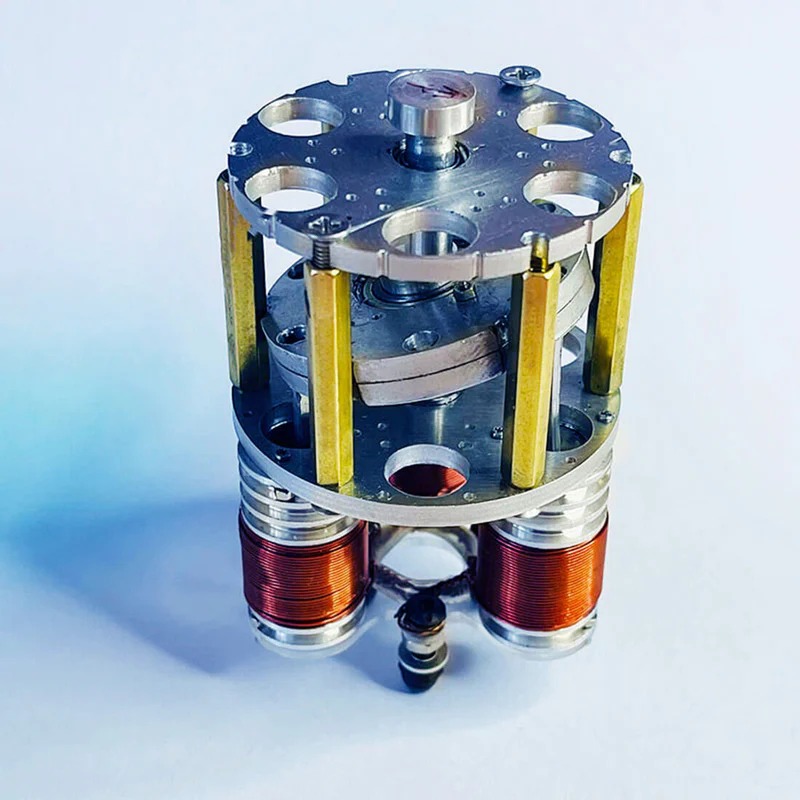
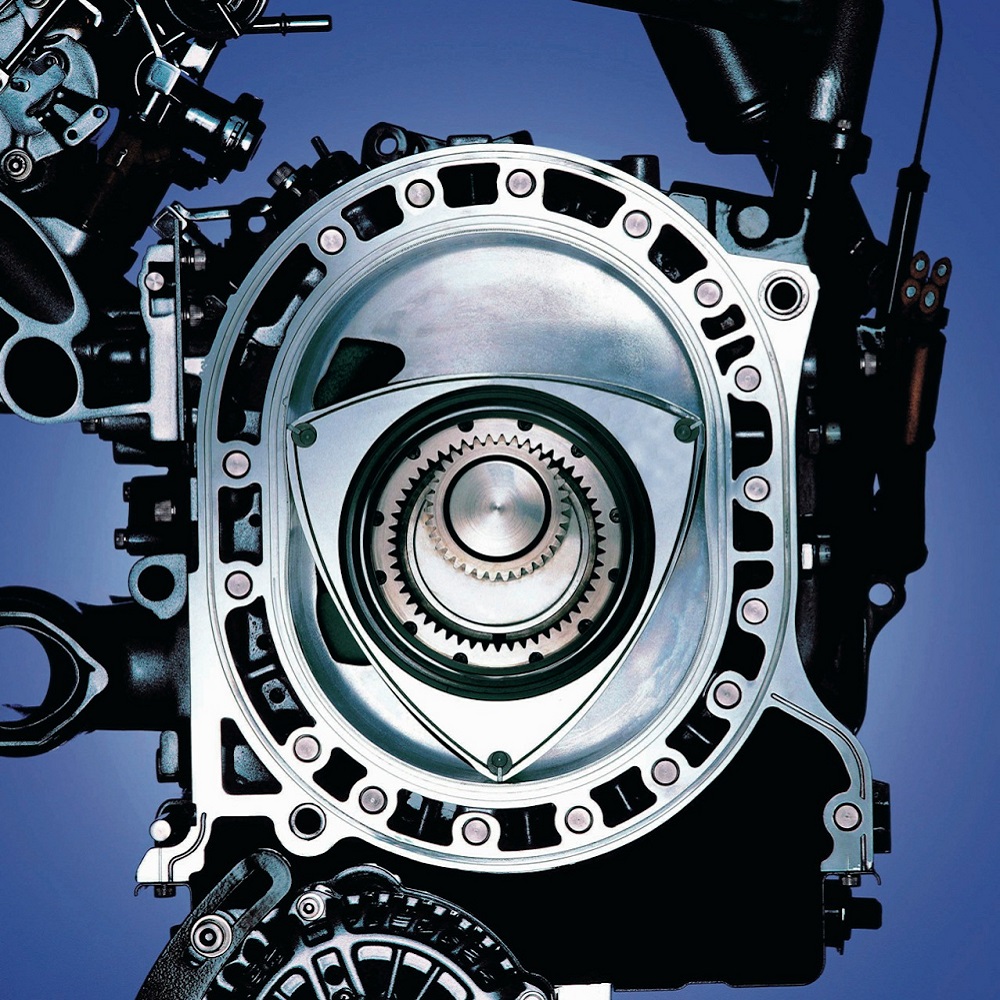
A rotary engine uses a rotating triangular rotor to generate power. The rotor moves within an oval-shaped chamber called a stator. Combustion occurs in the chamber, producing energy for motion. Rotary engines are compact and have fewer moving parts than piston engines.
What is a Piston Engine?
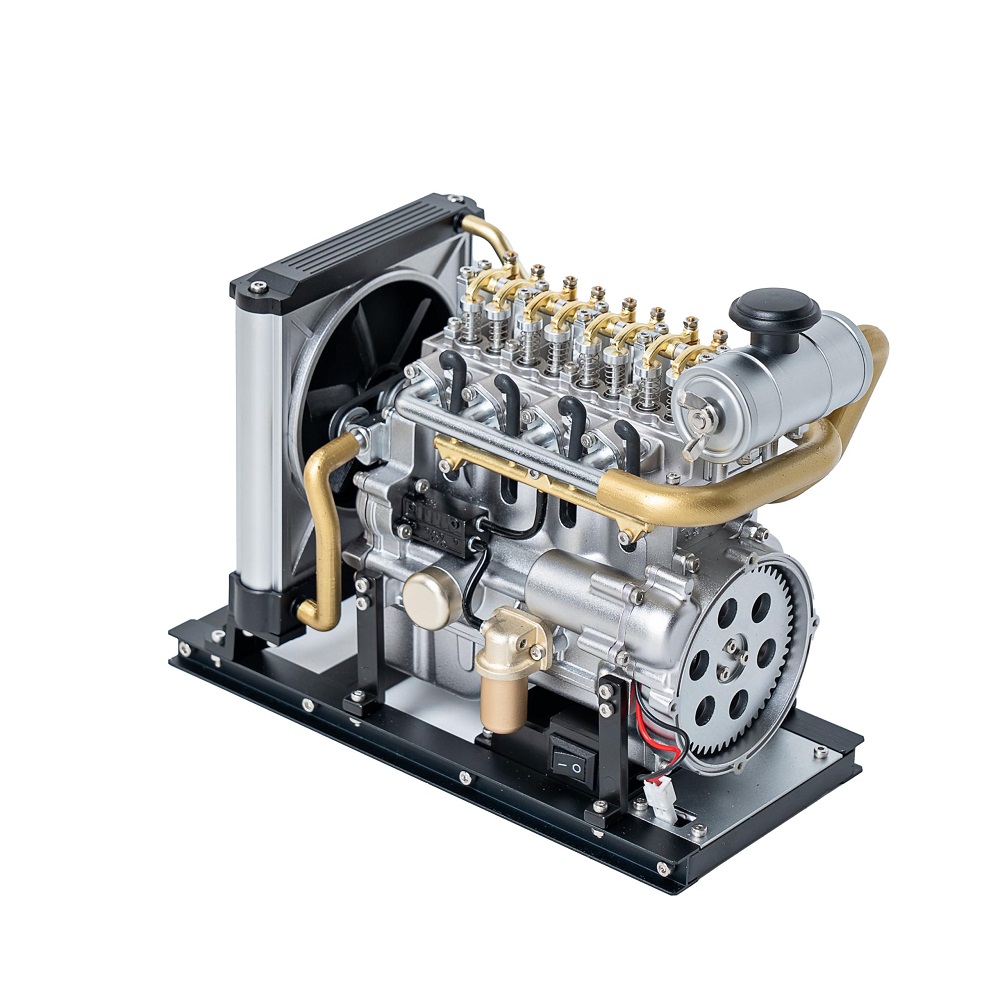
A piston engine relies on cylinders and pistons to generate power. Pistons move up and down within cylinders during combustion. This movement turns a crankshaft, creating motion. Piston engines are widely used in cars, trucks, and airplanes due to their versatility and durability.

How They Work: A Breakdown of Functionality
Understanding how rotary vs piston engines function reveals their unique strengths and limitations. Both engine types transform fuel into motion, but their mechanics differ significantly.
Rotary Engine Mechanics
Rotary engines use a triangular rotor to convert combustion into energy. The rotor moves in an oval-shaped chamber called a stator. As the rotor spins, it creates cycles for intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust. This motion generates power efficiently. Rotary engines have fewer moving parts compared to piston engines. Their compact design helps reduce vibrations and simplifies functionality.
Piston Engine Mechanics
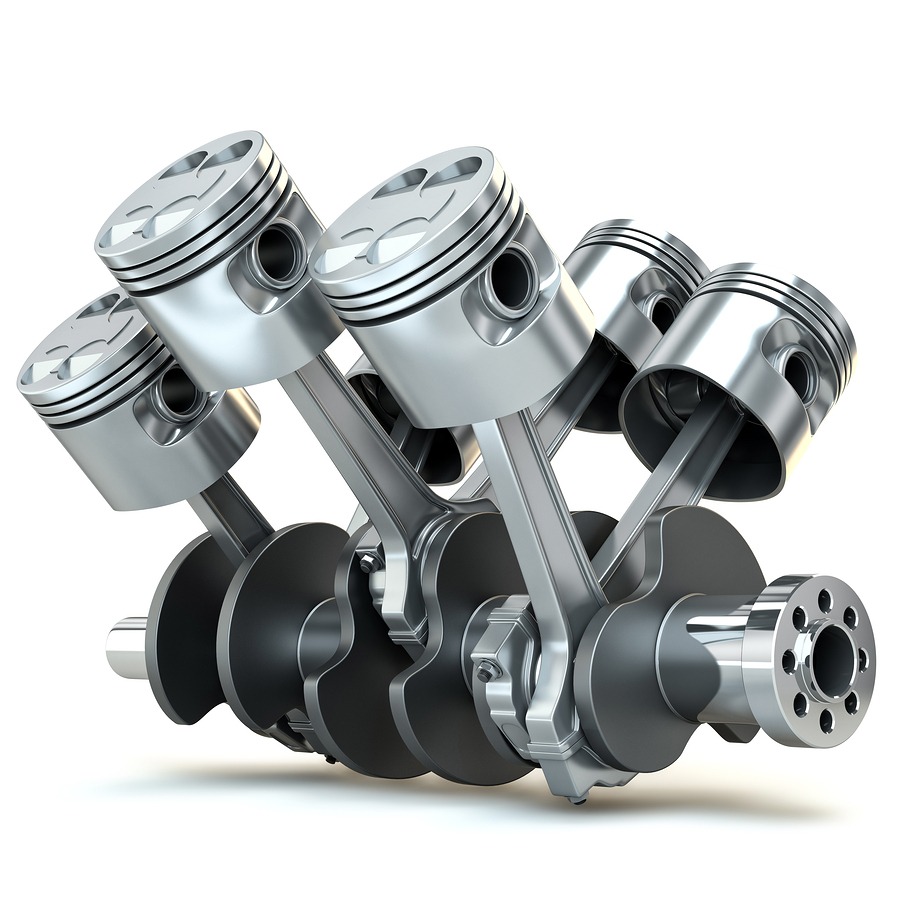
Piston engines rely on up-and-down movements of pistons inside cylinders. Combustion pushes the pistons downward, generating force. This motion spins a crankshaft, producing rotational energy for movement. Each cylinder goes through intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust strokes. Piston engines feature multiple cylinders to balance power output. Their design supports a wide range of fuel types and applications, making them versatile.
Advantages of Rotary Engines
Rotary engines offer several key advantages that make them appealing for specific applications. These benefits include compact design, lightweight construction, higher RPM potential, and simplicity in their mechanics.
Compact Design and Lightweight
Rotary engines are much smaller than piston engines. They have fewer parts, which minimizes bulk. Their compact design makes them lightweight. This characteristic aids in reducing vehicle weight. Lightweight engines improve fuel efficiency and handling in vehicles. These features are especially useful for sports cars and aircraft.
Higher RPM Potential
Rotary engines can achieve high RPM levels efficiently. The smooth rotation of the triangular rotor supports rapid motion. This characteristic enhances performance for speed-focused applications. Unlike piston engines, vibrations are minimal at high speeds. Engines designed for racing or aviation benefit greatly from this capability.
Simplicity of Moving Parts
Rotary engines feature fewer moving parts compared to piston engines. A triangular rotor replaces the pistons and crankshaft of conventional designs. This simplicity reduces mechanical wear and tear. Fewer parts mean easier assembly and lower production costs. The straightforward design also simplifies maintenance and repairs, saving time and effort.

Advantages of Piston Engines
Piston engines offer numerous benefits, making them a preferred choice for many applications. Their design excels in terms of fuel efficiency, versatility, and durability. Let’s explore these advantages in detail.
Fuel Efficiency
Piston engines are known for their effective fuel combustion. They use precise control over the intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust strokes. This ensures optimal fuel use in every cycle. Advanced technologies, like direct fuel injection, improve efficiency further. These engines also work well with various fuel types like gasoline, diesel, and biofuels. This adaptability enhances fuel economy and reduces operational costs.
Broad Application in Vehicles
Piston engines power a wide range of vehicles. They are commonly found in cars, trucks, buses, and motorcycles. Their design supports diverse applications, from everyday commuting to heavy-duty transport. Airplanes and ships also frequently use piston engines for reliability. This versatility makes them useful across many industries. Replacement parts are widely available, ensuring easy repairs anywhere.
Robustness and Longevity
Piston engines are designed for durability. They can handle high pressure and temperature during operation. Regular maintenance ensures they last for decades. Their sturdy construction withstands wear and tear better than rotary engines. Due to their reliability, piston engines are ideal for long-term use. Applications in trucks, airplanes, and industrial machines depend heavily on their robustness.
Key Differences Between Rotary and Piston Engines
Understanding the key differences between rotary vs piston engines helps in selecting the right one. Let’s examine how they vary in design, performance, and maintenance.
Design and Construction
Rotary engines have a triangular rotor spinning in an oval chamber. They have fewer moving parts. This makes them compact and lightweight. Piston engines have cylinders with pistons moving up and down. These are connected to a crankshaft. Piston engines are larger and more complex. Their construction includes multiple components, such as valves and timing belts. Designers prioritize durability and precise operation.
Performance Characteristics
Rotary engines deliver smooth high-RPM performance. They produce less vibration, ideal for speed-focused uses. However, they often consume more fuel and oil. Piston engines offer better torque and fuel efficiency. Their precise combustion process supports strong power generation. Piston engines excel in low-speed performance. These characteristics make them versatile for various vehicles.
Maintenance and Durability
Rotary engines require frequent maintenance. They face issues like oil leakage and rotor wear. Their simpler design makes repairs straightforward but more frequent. Piston engines are more durable and handle high pressures better. They have a longer lifespan with proper care. Replacement parts for piston engines are easier to find. Maintenance is less frequent but involves more complex repairs.
Each engine type has strengths and weaknesses. Choosing between rotary vs piston depends on your specific needs.

Applications of Rotary and Piston Engines
Both rotary and piston engines serve specific purposes across various industries. Understanding their applications can help identify the ideal engine type for particular needs.
Common Uses of Rotary Engines
Rotary engines are popular in applications requiring high performance and lightweight designs. Sports cars, like Mazda RX-series, often use rotary engines due to their compact construction and smooth RPM handling. Aircraft, especially small planes and experimental models, benefit from the reduced vibrational impact. Motorcycles and marine applications also favor rotary engines for similar reasons. However, these engines are less common in heavy-duty vehicles due to lower torque levels and higher fuel consumption.
Common Uses of Piston Engines
Piston engines dominate the automotive and industrial sectors. They power cars, trucks, and buses, proving their versatility. Airplanes, especially larger commercial models, rely on piston engines for durability and robust performance. Ships, agricultural machines, and industrial generators frequently use piston engines for reliability under extensive use. Their ability to operate on various fuel types also makes them practical for different environments and purposes. Wide availability of replacement parts further boosts their usage across diverse applications.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Engine Type
Understanding the challenges and limitations of rotary and piston engines helps in making informed decisions. Both engine types have specific issues that affect their performance or usability.
Rotary Engine Issues
Rotary engines are compact, but they come with notable challenges. One major issue is oil consumption. These engines burn oil along with fuel, leading to higher usage and emissions. The internal seals, like apex seals, wear out quickly. This results in reduced engine efficiency and performance. Rotary engines are less fuel-efficient compared to piston engines. Their higher operating temperatures also contribute to wear and tear. Reliability becomes a concern for long-term use in demanding applications.
Another limitation is their lack of torque at low speeds. This makes them unsuitable for heavy-duty vehicles. Maintenance needs are more frequent, even though repair processes are relatively simple. Additionally, rotary engines are less common, so replacement parts are harder to find. This restricts their practical use for many industries.
Piston Engine Drawbacks
Piston engines offer durability, but they have their own drawbacks. They feature more complex designs and parts. This increases the cost and time required for repairs. Piston engines are bulkier, adding weight to vehicles, which can limit performance.
Vibrations during operation can be an issue, especially at high speeds. This affects the smoothness of performance compared to rotary engines. Piston engines are also sensitive to fuel quality. Poor-quality fuel can reduce efficiency and increase the risk of mechanical problems.
Environmental concerns arise due to piston engines’ emissions. While advancements improve efficiency, these engines still release more pollutants. Maintenance involves intricate processes, such as valve timing adjustments. In comparison to rotary engines, piston engines tend to be less suitable for high-speed applications like racing.
Recognizing these challenges highlights the strengths and weaknesses unique to each engine type. Choices should align with application needs and long-term goals.
Which Engine is Right for Factors to Consider
Choosing between rotary vs piston engines depends on your needs. Various factors influence the decision.
Purpose and Application
The intended use heavily impacts the choice of engine type. Rotary engines suit lightweight applications requiring high RPMs. They are ideal for sports cars, motorcycles, and small aircraft. These engines perform well in speed-focused environments but struggle with heavy-duty tasks.
Piston engines work better for versatile and high-torque applications. They power cars, trucks, buses, and airplanes. These engines also handle industrial tasks and agricultural machinery. Their adaptability makes them useful across various industries.
Maintenance and Costs
Maintenance and associated costs differ significantly between the two engines. Rotary engines require frequent but straightforward maintenance due to rotor and seal wear. Oil consumption adds to the operational cost over time. Replacement parts can be harder to find, raising repair costs.
Piston engines need less frequent maintenance but involve complex repairs. Multiple components, like timing belts and valves, add to repair time and expense. However, these engines have widely available parts, reducing replacement costs.
Long-Term Reliability
Long-term reliability depends on engine durability. Rotary engines face issues with seals and wear under prolonged use. They are less reliable for heavy tasks and extended periods of operation. Conversely, piston engines can endure high pressures and temperatures. Proper care ensures their longevity.
Rotary engines may suit short-term, performance-driven applications. Meanwhile, piston engines are more dependable for long-term, heavy-duty usage.
Considering purpose, maintenance, and reliability factors helps determine the better engine type for your needs.
Maintenance Considerations and Lifespan
Routine Maintenance Practices
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity of any engine. Piston engines typically involve regular oil changes, valve adjustments, and fuel system checks. Most motorcycle and automotive shops are familiar with these practices, which makes maintenance relatively straightforward. The general availability of parts and mechanics specializing in piston engines contributes to making upkeep easier and cost-effective.
Unique Maintenance Needs of Rotary Engines
In contrast, rotary engines require specific maintenance considerations. One key focus is on monitoring the apex seals, which are vital for the engine’s operation. These seals can wear over time and lead to performance issues if not properly maintained. Additionally, rotary engines need consistent oil levels and quality checks to function correctly. Due to these specialized needs, finding mechanics familiar with rotary engines may be more challenging. Riders must remain proactive regarding these unique maintenance requirements to ensure reliable performance.
Lifespan Expectations
The lifespan of an engine can vary greatly between rotary and piston types. Piston engines can often surpass 200,000 miles with proper care, making them a reliable choice for long-term use. Regular maintenance and timely repairs play a significant role in achieving this longevity. In contrast, rotary engines generally have a shorter lifespan, often falling below 100,000 miles without significant upkeep. This difference in durability should be considered when choosing between engine types, as it impacts long-term ownership costs and reliability.

Conclusion: Making An Informed Decision
Selecting between rotary vs piston engine is crucial for any vehicle enthusiast. By understanding the differences, benefits, and potential drawbacks of each engine type, you can make a more informed decision. Whether you prioritize performance and compactness or fuel efficiency and longevity, each engine has something to offer.
As you consider the pros and cons of rotary vs piston engines, factor in your specific needs and preferences. Assess how often you travel, the type of riding experience you desire, and your long-term plans. This holistic approach ensures that you select an engine that aligns with your lifestyle.
Ultimately, both rotary and piston engines present unique opportunities for exhilaration and adventure. Embracing your choice while being aware of its implications can lead to a richer and more fulfilling riding experience. Enjoy the journey ahead, knowing you’ve made a well-informed decision about your engine type!

Leave a Reply