Overview of the Cylinder Head
Definition and Purpose
A cylinder head is a crucial part of an engine. It sits above the cylinders and seals the combustion chamber. Its main purpose is to help the engine function effectively. The cylinder head engine supports engine components such as valves, spark plugs, and fuel injectors. It ensures optimized airflow and fuel delivery for combustion. It also plays a role in cooling the engine by distributing heat.
Key Components of a Cylinder Head
Cylinder heads consist of several essential parts:
- Valves: These control air intake and exhaust gases in the combustion process.
- Spark Plug: It ignites the fuel-air mixture inside the combustion chamber.
- Fuel Injector: This delivers fuel into the combustion chamber in precise amounts.
- Head Gasket: It seals the cylinder head to the engine block and prevents leaks.
- Cooling Channels: These circulate coolant to manage engine temperature.
Effective design and quality materials ensure the durability of cylinder heads. Proper performance is vital for engine efficiency and reliability. Cylinder heads must withstand pressure, heat, and other challenging conditions.

How the Cylinder Head Works
The cylinder head plays a vital role in the overall engine performance. It ensures efficient combustion and supports essential components for smooth operation. Understanding how it functions provides insight into engine mechanics.
Role in Combustion Process
The cylinder head engine is key to the combustion process. It seals the top of the cylinder, forming a tight combustion chamber. Inside the chamber, the air-fuel mixture is ignited by the spark plug. The cylinder head helps control airflow and fuel delivery during combustion.
It hosts the intake and exhaust valves. These valves regulate the entry of air and fuel and the exit of exhaust gases. Correct valve operation ensures optimal engine power and efficiency. The cylinder head must also manage heat generated during combustion. Cooling channels within the cylinder head circulate coolant to prevent overheating.
Interaction with Other Engine Parts
The cylinder head interacts directly with many engine components. It connects to the engine block via the head gasket. This gasket seals the cylinder head tightly to prevent leaks. The gasket endures high pressure and heat during engine operation.
Fuel injectors situated in the cylinder head control fuel supply for burning. The spark plug, embedded in the cylinder head, ignites this mixture with precise timing. Intake and exhaust valves control the flow of air and gases, ensuring that the combustion process cycles efficiently.
These interactions between the cylinder head and other parts are essential for engine reliability. Proper functioning results in better fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and overall engine durability.

Different Types of Cylinder Heads
Cylinder heads come in various designs to suit different engine configurations. The design impacts engine performance, efficiency, and compatibility. Below are the three main types of cylinder heads commonly used.
Inline Cylinder Heads
Inline cylinder heads are used in engines with cylinders arranged in a straight line. These are simple and commonly found in smaller cars and motorcycles.
Key Features:
- Compact and lightweight design.
- Easy to manufacture and maintain.
- Fewer moving parts, leading to reduced wear.
Inline cylinder heads are less complex, making them cost-effective. However, they may not deliver the high power needed for larger vehicles.
V-Type Cylinder Heads
V-type cylinder heads are designed for engines with cylinders arranged in a “V” formation. These are often used in high-performance cars, SUVs, and trucks.
Key Features:
- Compact design despite having more cylinders.
- High performance and power output.
- Ideal for engines requiring more torque and horsepower.
This configuration allows for a lower engine profile and better fuel distribution. However, it is more complex and expensive to produce.
Flat Cylinder Heads
Flat cylinder heads work with “boxer” or horizontally opposed engines. These are commonly seen in sports cars and some motorcycles.
Key Features:
- Low center of gravity for better stability.
- Even weight distribution across the vehicle.
- Enhanced cooling efficiency.
While flat cylinder heads offer excellent balance and performance, they are costlier to manufacture. Their unique design also requires specialized maintenance.
Each type of cylinder head has specific applications based on engine design and vehicle requirements. Choosing the right type ensures optimal performance.

Common Materials Used in Cylinder Heads
Cylinder heads are made from materials that must withstand high temperatures and pressures. The choice of material impacts engine performance, weight, and durability.
Aluminum vs. Cast Iron
Aluminum and cast iron are the two primary materials used for cylinder heads. Each has unique properties that suit different engines.
Aluminum Cylinder Heads:
- Lightweight and reduces engine weight overall.
- Excellent heat conduction for efficient cooling.
- Easily cast into complex shapes for modern engine designs.
- Less durable under extreme pressure compared to cast iron.
Cast Iron Cylinder Heads:
- Heavier but extremely durable and resistant to wear.
- Retains strength under high compression and pressure.
- Less efficient in heat dissipation compared to aluminum.
- Cheaper to produce, making them cost-effective.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Material
Aluminum Cylinder Heads provide good performance features, especially for lightweight and fuel-efficient engines. They improve cooling efficiency, which is vital for preventing overheating. Their light weight contributes to better fuel economy and faster engine response. However, aluminum can deform or crack under extreme heat and compression.
Cast Iron Cylinder Heads are preferred for heavy-duty and high-performance engines. They offer unmatched durability, making them ideal for engines exposed to extreme stress. Yet, their heavier weight can negatively impact fuel efficiency and vehicle handling. The slower heat dissipation may also lead to higher engine temperatures during prolonged use.
The material selection depends on engine requirements and vehicle design. Aluminum suits modern cars where efficiency and weight savings are priorities. Cast iron is ideal for robust, high-torque engines used in trucks and SUVs.
Signs of Cylinder Head Issues
Cylinder head problems can impact engine performance and reliability. Identifying these issues early is crucial.
Cracks and Leaks
Cracks and leaks are common signs of cylinder head damage. These issues can harm engine functionality.
- Cracks: Cylinder heads can crack due to overheating or extreme pressure. Cracks may lead to loss of compression, reducing engine power.
- Leaks: Leaks can occur in the head gasket or cooling channels of the cylinder head. Coolant or oil leaks are noticeable under the vehicle or in the engine bay.
- Causes of Damage: Frequent causes include poor maintenance, overheating, or manufacturing defects. Regular checks help avoid these problems.
Addressing cracks and leaks promptly prevents further damage. Delayed repairs can lead to costly engine repairs.
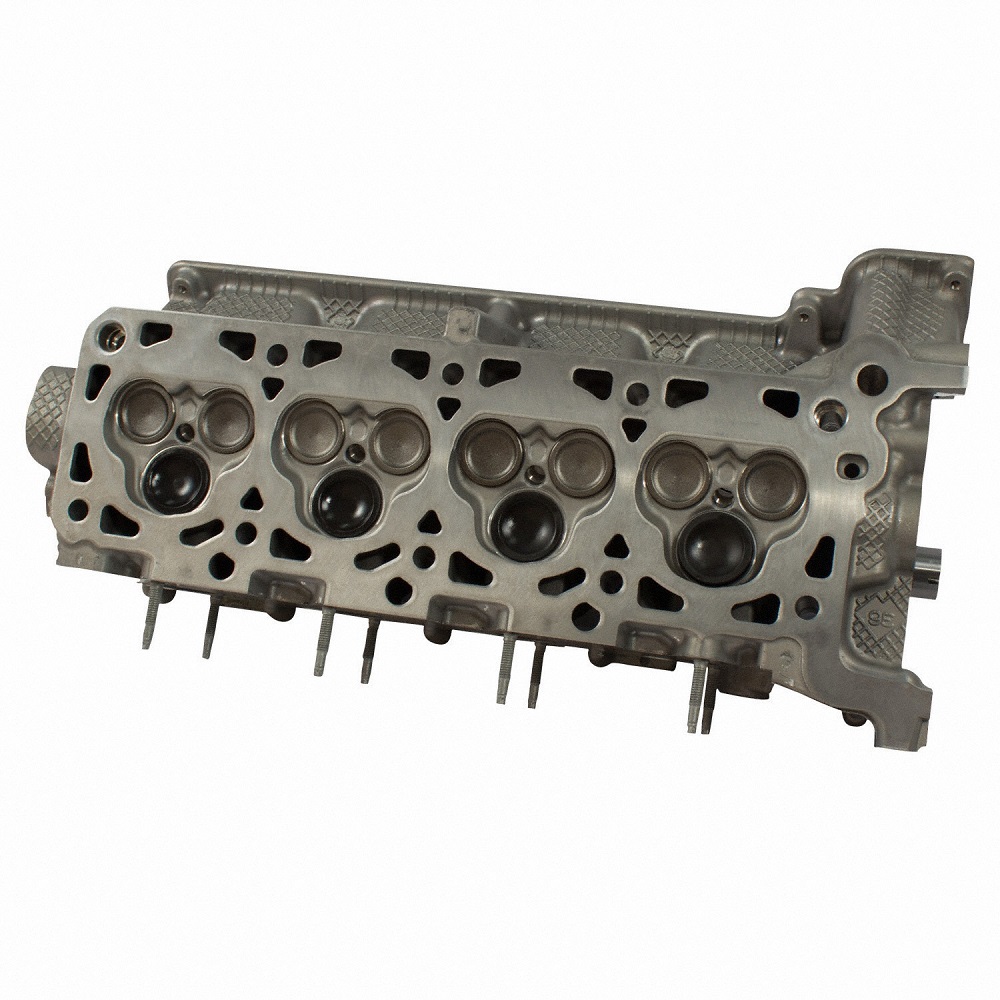
Symptoms of Malfunction
Faulty cylinder heads exhibit noticeable symptoms. Paying attention to these signs can save the engine.
- Loss of Power: Reduced engine power may indicate compression issues due to head damage.
- Overheating: Overheating occurs when coolant leaks or cooling channels malfunction in the cylinder head. Engine temperature rises quickly.
- Smoke from Exhaust: White or blue smoke from the exhaust is a sign of cylinder head trouble. White smoke suggests coolant leak, while blue smoke indicates oil burn.
- Unusual Noises: Knocking or ticking sounds may arise from damaged valves within the cylinder head.
Monitoring these symptoms ensures timely diagnosis. Immediate action can prevent worsening conditions affecting the cylinder head engine performance.
Maintenance and Care for Cylinder Heads
Proper maintenance of the cylinder head engine is essential for efficient performance and durability. Regular care helps prevent costly repairs and ensures the engine runs smoothly. Below, we cover key aspects of maintaining and caring for cylinder heads.
Cleaning and Inspection
Routine cleaning and inspection are necessary to maintain the cylinder head’s condition. Here’s how to properly clean and inspect your cylinder heads:
- Removing Deposits: Use a degreaser to clean oil and grease deposits. Scrub carefully with a soft brush.
- Inspect Cracks: Look for visible cracks or damage on the surface.
- Check Gaskets: Examine the head gasket for signs of wear and tear, such as cracks or leaks.
- Valve Inspection: Inspect intake and exhaust valves for carbon buildup or misalignment.
- Cooling Channels: Ensure the cylinder head’s cooling channels are free of blockages or corrosion.
- Fuel System Check: Verify that fuel injectors are clean and functioning.
Maintain cleanliness to prevent contamination and ensure efficient combustion. Regular inspections can detect problems early and help avoid major engine issues.
Repair vs. Replacement Considerations
When cylinder head problems occur, you must decide between repair and replacement. Consider these factors when making the decision:
- Extent of Damage: Minor issues like surface cracks or leaks can often be repaired. Severe damage may require replacement.
- Repair Costs: Compare the cost of repairs to the price of a new cylinder head. Repairs are cheaper for minor issues, but replacements save money in the long run for major damage.
- Age and Condition of the Engine: Older engines with worn-out cylinder heads often benefit from replacement.
- Material Type: Aluminum cylinder heads, being more prone to warping or cracking under intense heat, may need replacement if extensively damaged. Cast iron heads, due to their durability, are easier to repair.
- Professional Assessment: Consult an experienced mechanic for a thorough assessment.
Proper maintenance practices, timely cleaning, and inspections enhance the lifespan of the cylinder head. When issues occur, evaluate repair or replacement options based on the damage and engine condition. This ensures the longevity and reliability of the cylinder head engine.
Innovations in Cylinder Head Design
The cylinder head engine has seen significant advancements in design and technology over the years. These innovations aim to improve performance, sustainability, and fuel efficiency. Modern designs focus on delivering power while reducing environmental impacts and operational costs.

Advanced Technologies
New technologies have revolutionized the functionality of cylinder heads. These innovations enhance engine efficiency and reliability.
- Variable Valve Timing (VVT): This technology adjusts valve timings for optimal performance. It ensures better power and fuel efficiency.
- Turbocharging and Supercharging: These systems increase air intake, boosting engine power. They improve response without increasing engine size.
- Direct Fuel Injection: Advanced fuel injectors deliver fuel precisely. This ensures better combustion and improved efficiency.
- Integrated Exhaust Manifolds: Combining the manifold with the cylinder head improves exhaust flow. It also reduces emissions and engine weight.
- Lightweight Materials: Modern cylinder heads use advanced materials like reinforced aluminum alloys. These reduce engine weight and enhance heat dissipation.
These technologies make engines more powerful while conserving fuel and reducing weight. They also contribute to a smoother and quieter ride.
Environmental Impacts and Efficiency
Cylinder head designs now prioritize environmental sustainability. Reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency are top goals.
- Low Emissions: Modern designs reduce harmful emissions through better valve control and combustion.
- Reduced Friction: Advanced designs reduce internal friction. This leads to less energy loss and better efficiency.
- Thermal Management: Improved cooling systems prevent overheating. They enable engines to operate at optimal temperatures.
- Hybrid Engine Compatibility: Many cylinder heads now support hybrid engines. These cater to vehicles using both electric and traditional fuel sources.
Engine manufacturers aim to create designs that align with global environmental standards. These innovations support a cleaner and greener future in transportation.
Advanced technologies and eco-friendly designs ensure that cylinder head engines meet modern demands. These developments provide drivers with better performance and reduced environmental impact.
Conclusion
The Impact of Cylinder Head Design on Performance
Cylinder heads play a critical role in the performance and efficiency of internal combustion engines. As a key component, their design elements directly affect how effectively an engine operates. Innovations in materials, airflow dynamics, and thermal management will continue to shape the advancements in cylinder head engineering.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Engine Design
The future of cylinder head design is evolving alongside trends in automotive technology. As manufacturers shift toward hybrid and electric vehicles, traditional designs will be reimagined. The demand for reduced emissions and improved fuel efficiency will drive research and development efforts in the area of cylinder head design.
Embracing the Journey of Automotive Innovation
As we reflect on the evolution of the cylinder head engine, it is clear that this component has come a long way in terms of functionality and performance. The journey of engine design exhibits humanity’s ability to innovate and adapt. Whether you’re an enthusiast or a casual driver, understanding cylinder head functionality enhances your appreciation for the intricate world of automotive engineering and design. Embrace the innovations that lie ahead as the industry continues to evolve in exciting ways.

Leave a Reply