What is an Engine Cylinder Head?
An engine cylinder head is a crucial component of an internal combustion engine. It is mounted on top of the engine block, forming a seal to contain the combustion process. The cylinder head houses essential parts like valves, spark plugs, and, in some engines, the camshaft.
The cylinder head creates the combustion chamber when combined with the engine block. This is where fuel and air mix, ignite, and produce energy to power the engine. It also contains passages that allow coolant to flow, keeping the engine from overheating.
Additionally, it supports airflow by helping intake air enter and exhaust gases exit the engine. Its design impacts engine performance, fuel efficiency, and power output. Cylinder heads must withstand high pressure and temperature during engine operation.
Overall, the engine cylinder head is vital for engine functionality and performance.

Functions of an Engine Cylinder Head
The engine cylinder head performs several key functions essential for engine operation. Here’s a detailed look at its main roles:
- Sealing the Combustion Chamber: The cylinder head forms an airtight seal with the engine block, containing the combustion process. This ensures that the fuel-air mixture ignites efficiently and generates optimal power.
- Housing Critical Components: The cylinder head holds important parts like valves, spark plugs, and sometimes the camshaft. These components work together to manage air intake, fuel combustion, and exhaust release.
- Facilitating Airflow: It manages the intake of fresh air into the cylinders and the expulsion of exhaust gases. Proper airflow is critical for efficient engine performance and reduced emissions.
- Cooling and Heat Dissipation: Internal coolant passages in the cylinder head prevent the engine from overheating. These passages circulate coolant, keeping the combustion chamber temperature under control.
- Affecting Engine Performance: The design of the cylinder head influences fuel efficiency, engine power, and overall performance. Advanced designs focus on improving airflow and combustion efficiency.
- Supporting Lubrication: The cylinder head helps distribute engine oil to the components it houses, ensuring smooth operation.
These functions make the engine cylinder head a critical factor in keeping an engine running efficiently and reliably. Proper maintenance ensures it performs all these roles effectively.
Anatomy of an Engine Cylinder Head
Understanding the anatomy of an engine cylinder head is essential for assessing its functionality and maintenance. The cylinder head is intricately designed to perform multiple vital roles in the engine’s performance. Its structure and components are carefully engineered to facilitate power generation, airflow, cooling, and combustion.
Components of a Cylinder Head
The cylinder head contains several critical components that contribute to efficient engine operations:
- Valves: These control the intake of air and fuel, and the release of exhaust gases. The number and arrangement of valves vary among engines.
- Spark Plugs: Spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber, generating power to run the engine.
- Camshaft (if applicable): In some engines, the camshaft is housed in the cylinder head. It regulates valve movement.
- Combustion Chamber: This is where the fuel and air mix, ignite, and produce energy.
- Coolant Passages: These passages allow coolant to flow, preventing the engine from overheating during operation.
- Valve Springs and Retainers: These secure the valves in place and ensure they operate smoothly.
- Oil Passages: Oil passages deliver lubrication to moving parts, reducing friction and wear.
Each component is essential for the overall performance and durability of the engine cylinder head.
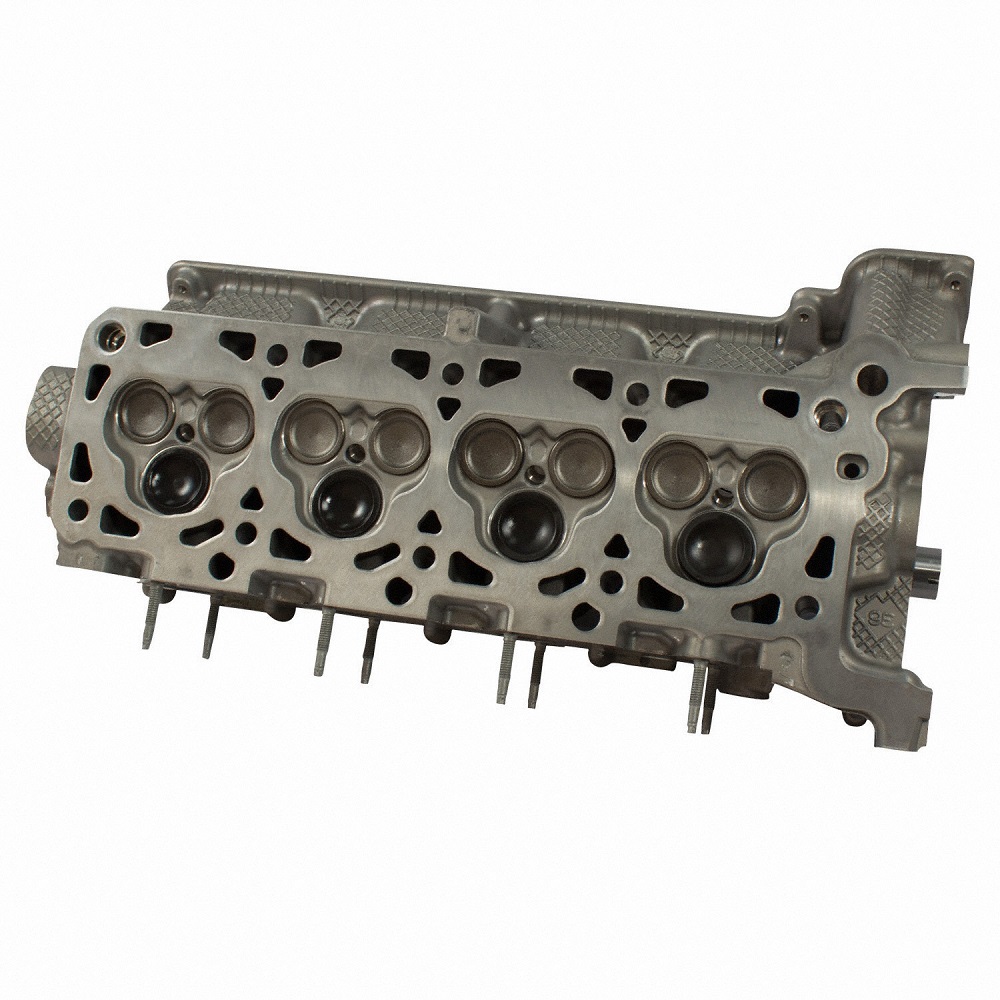
Material Used in Cylinder Heads
Materials used to manufacture cylinder heads significantly impact their durability, efficiency, and heat resistance. Common materials include:
- Aluminum: Aluminum is lightweight and offers excellent heat dissipation. It is widely used in modern engines.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron is durable and can withstand extreme pressure and temperature. It is often used in heavy-duty engines.
- Alloys: High-performance engines may use alloy mixtures for added strength and thermal conductivity.
Selecting the right material depends on the engine type, intended performance, and operating conditions. Both design and material choice contribute to the cylinder head’s efficiency and reliability.
Types of Engine Cylinder Heads
Engine cylinder heads come in different types. The choice depends on engine design, performance needs, and application. Each type serves specific functions and offers unique advantages. Below are common types of engine cylinder heads:
Flathead Cylinder Heads
Flathead cylinder heads are simple in design. They position valves inside the engine block. This design makes them compact and easier to manufacture. However, airflow is less efficient compared to other designs. Flathead heads are now rarely used but were popular in early car engines.
Overhead Valve (OHV) Cylinder Heads
OHV cylinder heads, also called “pushrod” heads, house valves above the engine block. A camshaft located inside the block controls the valves using pushrods. These heads create better airflow than flatheads and are widely used in modern internal combustion engines.
Overhead Cam (OHC) Cylinder Heads
OHC cylinder heads contain the camshaft on top of the cylinder head. There are two subtypes:
- Single Overhead Cam (SOHC): One camshaft operates both intake and exhaust valves. This offers simple control but limits performance.
- Double Overhead Cam (DOHC): Two camshafts separately control intake and exhaust valves. DOHC provides better performance, higher RPM, and superior airflow.
Crossflow Cylinder Heads
Crossflow cylinder heads enhance airflow efficiency. Air enters on one side and exits exhaust gases on the other side. This layout reduces heat buildup and improves engine power. Crossflow heads are common in high-performance engines.
Hemispherical (Hemi) Cylinder Heads
Hemi cylinder heads feature a dome-shaped combustion chamber. This design improves air-fuel mixing and combustion efficiency. Hemi heads create high power and torque, making them ideal for muscle cars and performance engines.
Multi-Valve Cylinder Heads
Multi-valve cylinder heads include three or more valves per cylinder. Common configurations are 4 valves per cylinder. This allows better airflow and higher engine efficiency. Multi-valve heads are popular in both racing and modern passenger vehicles.

Turbo Cylinder Heads
Turbo cylinder heads are designed with forced induction systems, such as turbochargers. These heads handle high pressure and temperatures, boosting engine power significantly. Turbo heads are common in high-performance cars.
Diesel Cylinder Heads
Diesel cylinder heads are built specifically for compression ignition engines. They endure high pressures and temperatures typical of diesel combustion. They often incorporate robust materials like cast iron for durability.
Knowing these types helps in selecting the right cylinder head for your engine. Each type has pros and cons based on your engine’s needs.
Common Problems with Cylinder Heads and Their Causes
Engine cylinder heads are robust components, but they can face issues over time. Understanding these problems and their causes can help in timely maintenance and repair. Here are some common issues:
1. Cracks in the Cylinder Head
Cracks often occur due to overheating or sudden temperature changes. This can happen if the cooling system fails or if the engine overheats repeatedly. Cracked cylinder heads can lead to leakage of coolant or oil.
2. Warping of the Cylinder Head
Warping occurs when the cylinder head overheats and loses its shape. Overheating can come from a failing cooling system or prolonged heavy engine use. Warped cylinder heads lead to improper sealing, reducing engine efficiency.
3. Gasket Failure
The cylinder head gasket forms an essential seal between the head and the engine block. A blown gasket can result from high pressure, overheating, or improper installation. It causes coolant and oil to mix, leading to engine damage.
4. Valve Damage
Valves in the cylinder head can wear out or get damaged over time. Excessive heat, poor lubrication, or dirt build-up can result in bent or broken valves. This affects combustion and engine performance.
5. Oil or Coolant Leaks
Leaks occur if the seals or gaskets inside the cylinder head wear out. Damaged seals allow oil or coolant to escape, leading to low fluid levels and potential engine overheating.
6. Worn Guides and Seats
The cylinder head contains valve guides and seats that can wear down over time. This can result in poor valve seating, leading to reduced compression and engine performance.
Causes of Cylinder Head Problems
- Overheating is a leading cause of most cylinder head issues.
- Poor maintenance can result in fluid leaks and component wear.
- Using low-quality coolant or oil can accelerate wear and corrosion.
- Normal wear and tear due to engine age and extensive usage.
Regular maintenance and prompt repair of cylinder head issues ensure the engine remains reliable and high-performing.

Repair and Maintenance Tips for Cylinder Heads
Proper care of engine cylinder heads ensures reliability and extends engine life. Neglect can lead to costly repairs. Maintaining cylinder heads requires attention to several aspects.
Inspect for Early Signs of Damage
Regularly check for cracks, leaks, or warping. Early detection can prevent severe issues. Look for coolant or oil leaks, as these often signal gasket or seal problems. Address damaged components immediately.
Maintain Coolant System Efficiency
Overheating causes major cylinder head damage. Keep coolant levels optimal to avoid heat issues. Flush and replace the coolant regularly. Inspect the radiator and water pump for wear or defects.
Lubricate Moving Parts
Keep all moving parts properly lubricated. Check oil levels frequently. Replace oil based on manufacturer recommendations. Use high-quality engine oil to reduce friction and wear.
Replace Worn Gaskets Timely
The cylinder head gasket is vital for sealing. Replace it as soon as wear signs appear. Regular gasket checks can prevent leaks and ensure a firm seal between the head and engine block.
Clean Cylinder Head Components
Clean the cylinder head and its parts, such as valves, to prevent dirt build-up. Use professional engine cleaning solutions for effective results. Remove carbon deposits regularly to enhance airflow and combustion.
Follow Manufacturer Maintenance Intervals
Follow maintenance schedules provided in the vehicle’s manual. Conduct routine inspections on the cylinder head. Replace parts and fluids per the guidelines for prolonged durability.
Avoid Excessive Engine Stress
Overloading the engine stresses the cylinder head. Use the engine within safe limits. Avoid sudden temperature changes which can crack or warp the head.
Use Quality Replacement Parts
If repairing, choose high-quality cylinder head parts. Inferior parts reduce performance and durability. Original parts from trusted manufacturers are ideal for reliability.
Consult Experts for Major Repairs
Professional help is recommended for complex repairs or replacements. Specialized tools are often needed for cylinder head maintenance. Skilled technicians ensure precise work and prevent further damage.
Caring for cylinder heads is essential to engine performance. Routine inspection, lubrication, and proper repairs ensure a long-lasting engine.
Advancements in Cylinder Head Technology
The evolution of engine cylinder head technology has significantly enhanced engine performance and efficiency. Manufacturers continuously innovate to address challenges such as emissions control, fuel economy, and power output. Here are some notable advancements:

Enhanced Materials
- Lightweight Alloys: Modern cylinder heads often use aluminum alloys. These are lighter and dissipate heat faster than traditional cast iron, improving engine efficiency.
- Durable Composites: Advanced composite materials are now used to increase strength and thermal resistance.
Improved Combustion Chambers
- Enhanced Designs: Engineers create more efficient combustion chamber shapes to enhance airflow and fuel mixture.
- Direct Injection Technology: This allows precise fuel delivery, improving combustion and reducing emissions.
Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
- Optimized Valve Operation: VVT adjusts valve timing based on driving conditions. This improves both power and fuel efficiency.
- Reduced Emissions: Timely valve adjustments help engines meet stringent emissions standards.
Turbocharging and Forced Induction
- Turbo-Compatible Heads: Cylinder heads are now designed for turbochargers, increasing engine power without increasing size.
- Higher Efficiency: These enhancements improve power output while maintaining fuel economy.
Multi-Valve Technology
- More Valves per Cylinder: Multi-valve heads, such as four valves per cylinder, improve airflow and engine efficiency.
- Better Performance: They allow higher engine speeds and better combustion.
Advanced Cooling Systems
- Optimized Coolant Passages: Improved designs enhance heat dissipation, reducing the risk of overheating.
- Thermal Coatings: Heat-resistant coatings are applied to extend the life and performance of cylinder heads.
Additive Manufacturing
- 3D Printing: This allows for more complex and efficient cylinder head designs with reduced manufacturing costs.
- Prototyping: Faster development of customized designs ensures quicker time-to-market for new engines.
Integration with Electronics
- Sensors in Cylinder Heads: Advanced sensors monitor temperature, pressure, and overall performance in real-time.
- Smart Control Systems: These systems optimize engine operations using real-time data from cylinder head sensors.
Benefits of New Technologies
- Improved Engine Performance: Innovations boost power output and torque.
- Enhanced Fuel Efficiency: Newer designs reduce fuel consumption.
- Lower Emissions: Advanced technology meets environmental regulations and reduces harmful gases.
- Increased Durability: Stronger materials and better cooling systems extend the lifespan of cylinder heads.
These advancements in cylinder head technology continue to shape the future of internal combustion engines. They improve overall engine performance, support regulatory compliance, and meet the growing demand for efficient power sources.
How to Choose a High-Quality Cylinder Head
Choosing a high-quality engine cylinder head is essential for optimal engine performance and durability. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a cylinder head:
1. Material Selection
- Aluminum or Cast Iron: Aluminum heads are lightweight and have excellent heat dissipation. Cast iron heads are more durable and suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Application-Specific Materials: For high-performance engines, consider alloy mixtures that offer greater strength and thermal resistance.
2. Compatibility with Engine Type
- Match with Engine Design: Ensure the cylinder head fits your specific engine model and type.
- Valve Configuration: Choose a head with the correct number of valves for your engine.
- Turbo Compatibility: If your engine uses a turbocharger, select a head designed to handle forced induction.
3. Quality of Manufacturing
- Reputable Manufacturers: Buy from trusted manufacturers with a record of producing high-quality cylinder heads.
- Precision Engineering: Look for heads built with advanced techniques like CNC machining for precise performance.
4. Performance Needs
- Airflow Design: Choose a cylinder head that enhances airflow for better performance and fuel efficiency.
- Multi-Valve Heads: Opt for multi-valve designs for higher engine speeds and improved combustion.
5. Durability and Heat Resistance
- Thermal Management Features: Select a cylinder head with optimized coolant passages and heat-resistant materials.
- Reinforced Components: Ensure the head has a robust structure to withstand high pressure and temperature.
6. Maintenance and Longevity
- Ease of Maintenance: Pick heads designed for easy cleaning and servicing.
- Corrosion Resistance: Check for materials that resist corrosion for a longer lifespan.
7. Budget and Cost Efficiency
- Balance Cost and Quality: Avoid very cheap options as they may compromise on durability and performance.
- Long-Term Value: Invest in a head that saves repair costs in the long run.
8. Warranty and Support
- Warranty Options: Select a cylinder head covered by a reasonable warranty.
- After-Sales Support: Reliable customer support can assist in installation and troubleshooting.
Tips for Finding the Best Cylinder Head
- Consult your vehicle’s manual for specifications.
- Seek expert advice for performance or custom applications.
- Read reviews or get recommendations from trusted sources.
- Avoid used or refurbished cylinder heads for better reliability.
By considering the above factors, you can choose a cylinder head that matches your engine’s needs and enhances its performance.

Leave a Reply