The world of engine design is vast and diverse, with various configurations offering distinct benefits and limitations. Two of the most prominent engine designs are the rotary engine vs piston. While both types serve the purpose of converting fuel into mechanical energy, their methods of operation, efficiency, and applications differ significantly. In this article, we will delve into the mechanics of both rotary engine vs piston, compare their advantages and disadvantages, and evaluate which engine design may be considered superior under different circumstances.
Understanding Engine Types
The Basics of Piston Engines
Piston engines, also known as reciprocating engines, are perhaps the most common types of engines found in automotive applications. They work using a series of cylinders arranged in a linear or V configuration. Each cylinder houses a piston that moves up and down within the cylinder. The engine operates in a four-stroke cycle: intake, compression, power, and exhaust.
During the intake stroke, the piston descends, creating a vacuum that draws in the air-fuel mixture. Next, the piston ascends during the compression stroke, compressing the mixture. The ignition occurs during the power stroke, pushing the piston back down and generating the force needed to turn the crankshaft. Finally, the exhaust stroke expels the spent gases from the cylinder. This continuous cycle produces the power needed to propel vehicles and machinery.
The Basics of Rotary Engines
Rotary engines, also known as Wankel engines, employ a completely different mechanism for generating power. Instead of pistons moving up and down, a rotary engine uses a triangular rotor that orbits within an epitrochoidal housing. This unique design enables the rotor to perform similar functions to a piston in a conventional engine, delivering power through efficient combustion cycles.
Each revolution of the rotor completes the four functions of the engine: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust. Rotary engines benefit from fewer moving parts, typically making them lighter and more compact than piston engines. As a result, they can be found in specific applications, such as sports cars and some aircraft.
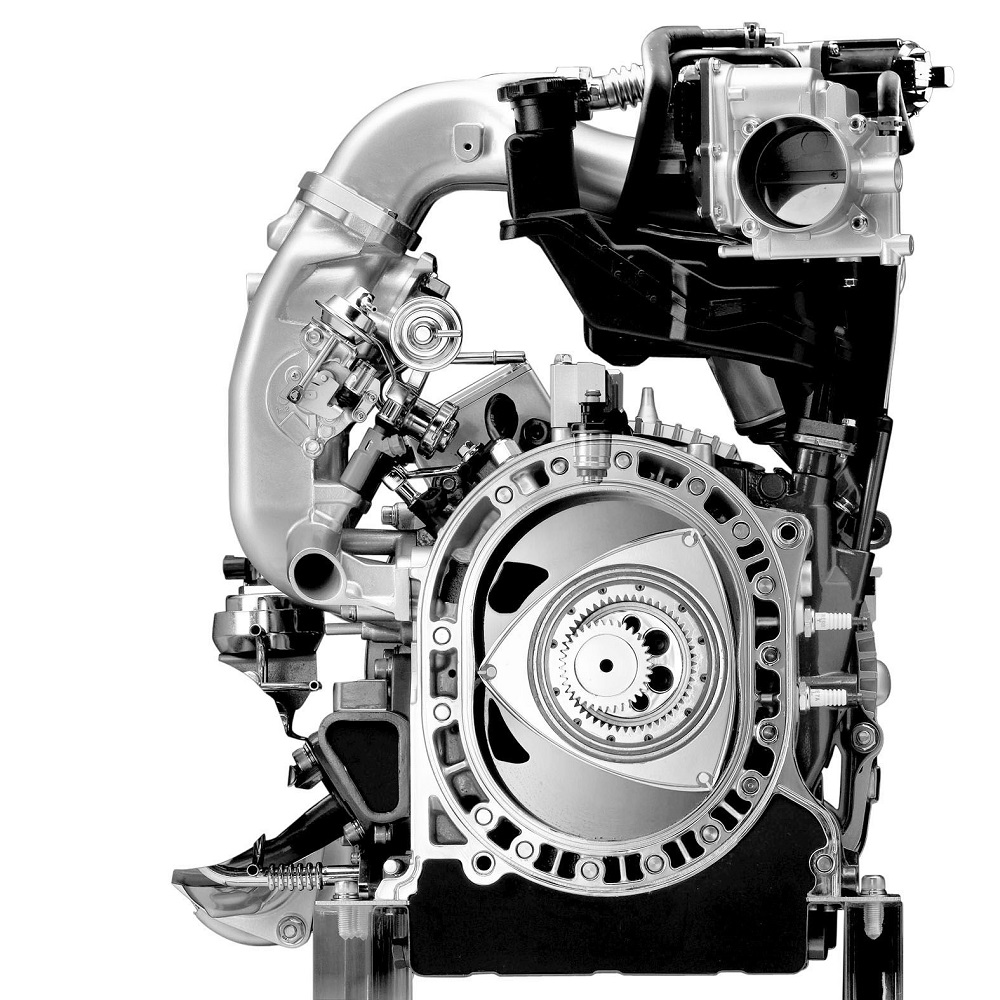
Key Differences in Design
Structural Complexity
One major difference between rotary engine vs piston is their structural complexity. Piston engines consist of several components, including pistons, crankshafts, connecting rods, and valves. These parts work together to create a synchronized operation that can be relatively intricate. Maintenance can also involve significant labor due to the number of parts involved.
In contrast, rotary engines feature fewer moving parts. The main components are the rotor, the housing, and the output shaft. This simplified design contributes to lighter weight and easier assembly. Many find that routine maintenance is more straightforward, as fewer components require attention.
Size and Weight
The difference in design leads to distinct variations in size and weight between the two types of engines. Piston engines can vary in size, ranging from small four-cylinder engines to large V8 engines. As the number of cylinders increases, so does the overall size and weight of the engine.
Rotary engines, however, tend to be more compact for the power they deliver. With a rotary engine’s unique shape and few moving parts, manufacturers can create engines that occupy less space and weigh less than their piston counterparts. This size advantage often appeals to car enthusiasts and designers who value performance and efficiency.

Performance Comparisons
Power Output and Efficiency
One of the key considerations when comparing rotary engine vs piston is their power output and efficiency. Piston engines generate power through a series of controlled explosions that push the pistons downward. Their design allows for high torque and horsepower outputs, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from everyday vehicles to high-performance sports cars.
On the other hand, rotary engines are known for their smooth power delivery and consistent performance at higher RPMs. They can produce a significant amount of power relative to their size, making them highly efficient for sports applications. However, rotary engines often have a reputation for being less fuel-efficient than piston engines, particularly in standard driving conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Durability is another critical factor when comparing these engine types. Piston engines have been around for many years, and advancements in materials and design have led to improved longevity and performance. However, they are more prone to wear due to the number of moving parts and constant friction within the engine.
Conversely, rotary engines benefit from their fewer moving parts, leading to reduced wear over time. However, they can be more susceptible to specific mechanical issues, such as apex seal wear. Proper maintenance and care are essential to extend the lifespan of both engine types; nevertheless, some enthusiasts argue that rotary engines can last as long as, if not longer than, traditional piston engines with appropriate handling.
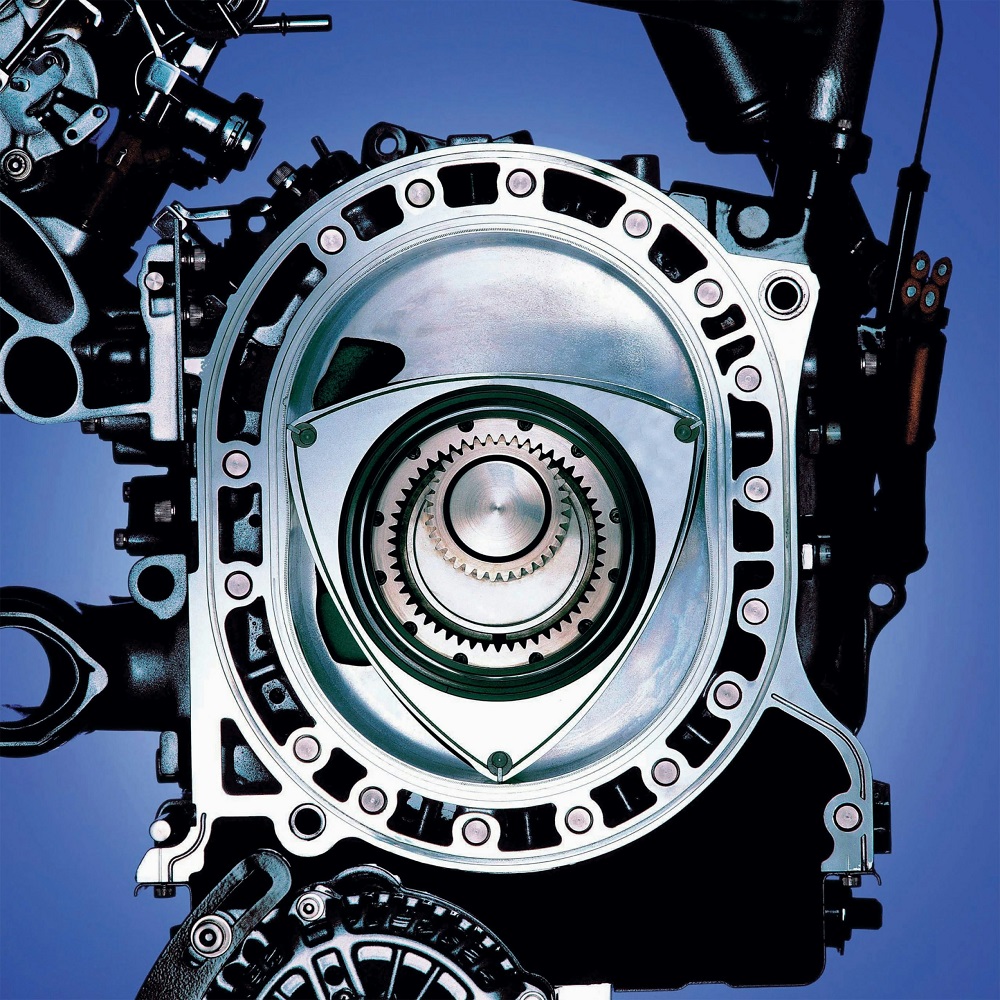
Applications of Each Engine Type
Piston Engine Applications
Piston engines are incredibly versatile and can be found in a wide variety of applications. They power most automobiles, trucks, and motorcycles on the market today. Their adaptability allows them to cater to numerous sectors, from everyday commuting to high-end performance vehicles.
In addition to vehicles, piston engines are commonly used in machinery and industrial applications. They serve as power sources in generators, pumps, and lawn equipment. Their robust performance and ability to produce high torque make them ideal for these uses, demonstrating the effectiveness of piston engine technology.
Rotary Engine Applications
Rotary engines, while less common, find their place in specific niche applications. The Mazda RX series of cars famously features rotary engines, showcasing their performance potential and unique design. Enthusiasts celebrate these vehicles for their exceptional power-to-weight ratio and distinctive engineering.
Outside of automobiles, rotary engines can also be found in some aircraft, go-karts, and small boats. Their lightweight and compact design benefits applications that require high power in a limited space. Although rotary engines have a smaller market share, they maintain a passionate following among dedicated fans who appreciate their unique appeal.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Initial Investment
When considering the purchase of a vehicle or machine featuring either piston or rotary engines, cost is a significant factor. Generally, piston engine vehicles dominate the market and cover a wide price range based on features and specifications. While cheaper models are readily available, premium performance vehicles with piston engines can come with significant price tags.
Rotary engine vehicles, while less prevalent, may fall into specific pricing brackets. Sports cars featuring rotary engines can often be more expensive due to their niche appeal and performance capabilities. Prospective buyers should assess the features and benefits versus cost for both engine types when making a decision.
Maintenance Costs
Maintenance costs vary significantly between rotary engine vs piston as well. Piston engines typically require regular oil changes, valve adjustments, and more comprehensive maintenance due to the number of moving parts. While this maintenance is relatively straightforward for most mechanics, the cumulative cost can add up over time.
Rotary engines require different types of care, focusing primarily on the apex seals, which are known to wear down over time. Scheduled inspections and oil changes are crucial for ensuring reliable performance. Many owners find rotary engines relatively easy to maintain, but repairs may require specialty knowledge, potentially increasing costs if specialized services are needed.

The Future of Engine Types
Innovations in Piston Engines
As automotive technology continues to advance, piston engines are evolving as well. Innovations in materials, such as lightweight alloys and advanced manufacturing techniques, are helping piston engines become more efficient and powerful. Manufacturers are also increasingly exploring hybrid and electric technologies alongside traditional piston engines to meet growing environmental regulations and consumer demand.
Smart technologies and computer systems are also being integrated into piston engines. These advancements can enhance performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. As the industry moves toward sustainability, developments like these will play a significant role in shaping the future of piston engines.
Advances in Rotary Engine Technology
Rotary engines have seen less development compared to their piston counterparts but remain relevant through continuous innovation. Recent advancements focus on improving reliability, efficiency, and reducing emissions. Manufacturers are investigating new engine designs, fuel types, and materials that could enhance the rotary engine’s performance.
Moreover, the resurgence of interest in vintage and classic cars with rotary engines has motivated some enthusiasts to work on performance upgrades and retrofit solutions. Innovations aimed at solving previous concerns, such as apex seal wear and fuel consumption, could help reinvigorate the appeal of rotary engines in the marketplace.
FAQ:
- What is the main difference between rotary engines and piston engines?
The main difference lies in their design and operation. Piston engines use reciprocating motion with multiple cylinders and pistons working in a linear fashion, while rotary engines (like the Wankel engine) use a triangular rotor that rotates in an elliptical chamber, allowing for compact size and fewer moving parts. - What are the advantages of rotary engines?
Rotary engines typically offer a higher power-to-weight ratio, smoother operation, and more compact design compared to piston engines. They also tend to have fewer moving parts, which can lead to reduced mechanical complexity and potential maintenance requirements. - What are the advantages of piston engines?
Many people widely favor piston engines for their efficiency, reliability, and abundance of parts. They generally provide better fuel efficiency, especially at lower RPMs, and manufacturers commonly use them in a wide range of vehicles—from cars to aircraft—giving them a long-standing track record in various applications. - Are rotary engines more efficient than piston engines?
Generally, piston engines are more fuel-efficient, especially under load and during highway cruising. Rotary engines, while powerful and compact, tend to consume more fuel and have higher emissions, making them less favorable for some applications in terms of efficiency. -
What applications commonly use rotary engines?
Rotary engines, while less common than piston engines, are primarily found in sports cars (notably Mazda RX series), some small aircraft, and specialized applications like motorcycles and drones. Their unique characteristics make them suitable for high-performance and lightweight needs.

Conclusion: Which Engine Design Reigns Supreme?
In conclusion, both rotary engine vs piston feature unique advantages and characteristics. Piston engines dominate in terms of versatility and widespread use, powering the majority of vehicles on the road today. They excel in various applications, ranging from everyday commuting to high-performance automotive performance.
Conversely, rotary engines offer a distinctive appeal characterized by their compact design, smooth acceleration, and performance advantages. While they are less common, loyal enthusiasts admire the unique engineering and driving experience they provide.
Ultimately, the decision between a rotary and piston engine hinges on individual preferences, intended applications, and maintenance considerations. As advancements in technology, materials, and design continue to shape both engine types, the dialogue around which design reigns supreme may evolve.
Understanding the efficiency differences between rotary and piston engines, along with the strengths and weaknesses of each design, empowers consumers and enthusiasts to make well-rounded decisions as they explore the exciting world of automotive engineering. Whether opting for a classic rotary engine vehicle or investing in a modern piston-powered marvel, understanding these differences ensures a more rewarding and satisfying experience both on and off the road.
Leave a Reply