Introduction to 16 Cylinder Engines
A 16 cylinder engine is a marvel of engineering. It features 16 pistons working together to generate immense power. These engines are designed for performance, efficiency, and reliability in demanding applications. Let’s explore their history, purpose, and benefits.
A Brief History of Multicylinder Engines
Multicylinder engines have evolved since the late 19th century. Early automobiles mainly used single-cylinder engines. By the 1920s, manufacturers began experimenting with engines featuring more cylinders to improve power output. This led to the development of V8, V12, and eventually 16 cylinder configurations. Early designs of 16 cylinder engines appeared in luxury cars and aircraft. Over time, advancements in technology made them more efficient and capable. Today, these engines are rare but remain significant in specialized industries.
Why 16 Cylinders? Benefits and Applications
The 16 cylinder engine offers several advantages:
- Superior Power: It delivers unmatched horsepower and torque levels, making it ideal for high-performance vehicles.
- Smooth Operation: More cylinders mean smoother running engines with reduced vibrations.
- Heavy-Duty Applications: These engines excel in industrial, marine, and aviation settings where reliability is crucial.
However, their large size and complexity limit their use to particular niches. Luxury cars, supercars, and heavy machinery often rely on these engines. Despite advancements in smaller engines, the 16 cylinder engine remains relevant in specific applications due to its incredible power and efficiency.
Anatomy of a 16 Cylinder Engine
Understanding the anatomy of a 16 cylinder engine helps in appreciating its engineering brilliance. These engines are complex structures built for unmatched power and precision. Let’s delve into their key components, configurations, and material choices.
Internal Components and Structure
A 16 cylinder engine consists of several critical components:
- Cylinders and Pistons: These are at the heart of the engine. Sixteen pistons move inside the cylinders to generate power through combustion.
- Crankshaft: It converts the up-and-down motion of the pistons into rotational energy for the drivetrain.
- Camshaft and Valvetrain: These parts control the intake and exhaust valves, ensuring proper airflow and fuel mixture.
- Connecting Rods: They link the pistons to the crankshaft, transferring their motion effectively.
- Cooling System: This complex system includes radiators and pumps, designed to manage the immense heat generated.
- Lubrication System: Vital for reducing friction, the system ensures smooth operation of all moving parts.
The structure of a 16 cylinder engine is highly optimized for durability, power, and efficiency.
Differences Between Inline and V Configurations
16 cylinder engines mainly come in two configurations, each offering distinct benefits:
- Inline Configuration:
- All cylinders are aligned in a single row.
- It simplifies the design but increases the engine’s length.
- Less common due to space limitations in most applications.
- V Configuration:
- The cylinders are arranged in two rows (banks) forming a “V” shape.
- It reduces engine size while maintaining power.
- This design improves balance and ease of installation in vehicles.
The V configuration is more popular in automotive and industrial applications due to its compactness and stability.
Materials Used in Manufacturing
Durability is crucial for 16 cylinder engines. Manufacturers prefer high-strength, lightweight materials:
- Aluminum Alloys: Widely used for engine blocks and cylinder heads to reduce weight while maintaining strength.
- Cast Iron: Often used for its durability in components like engine blocks in heavy-duty settings.
- Titanium: Employed for parts like connecting rods to reduce weight and enhance performance.
- Steel: Commonly used in crankshafts for strength and resistance to high-stress conditions.
- Ceramic Coatings: Applied to certain parts to withstand extreme heat in high-performance engines.
The choice of materials ensures a balance between durability, heat resistance, and weight optimization.
In summary, the anatomy of a 16 cylinder engine highlights its advanced design. Each element serves a specific role in delivering tremendous power, reliability, and efficiency.
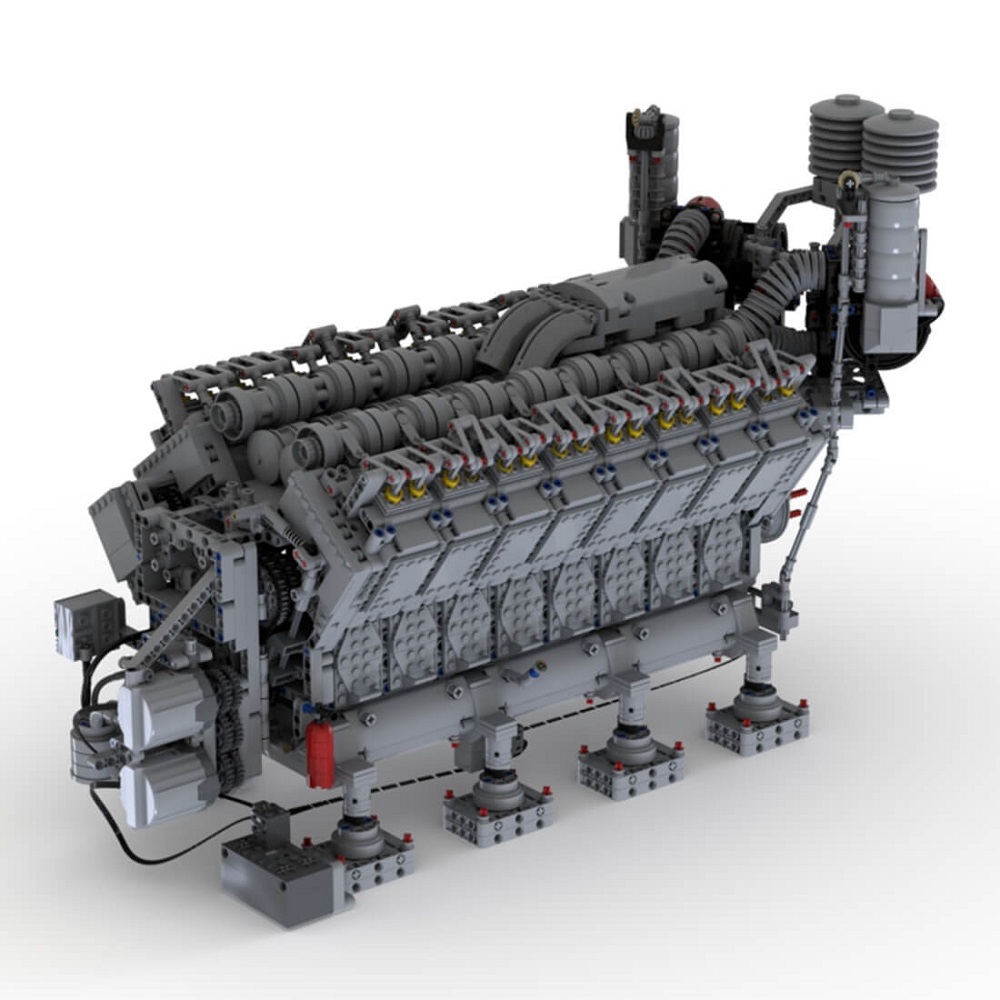
Performance Characteristics
Understanding the performance characteristics of a 16 cylinder engine showcases its unique capabilities. These engines are renowned for their power, efficiency, and smooth operation. Let’s explore their power output, efficiency compared to smaller engines, and noise management.
Power and Torque Output
The 16 cylinder engine delivers exceptional horsepower and torque. This makes it ideal for demanding applications.
- High Horsepower: These engines can produce 1,000+ horsepower, enabling top performance in supercars.
- Massive Torque: They exhibit immense pulling power, suitable for heavy-duty machinery and marine uses.
- Consistent Output: The balanced cylinder configuration ensures uniform power delivery across all RPM ranges.
This power output makes the 16 cylinder engine stand apart from smaller configurations.
Efficiency Comparison to Smaller Engines
Despite their size, 16 cylinder engines maintain surprising efficiency in certain applications.
- Optimized Fuel Usage: They can operate efficiently at high loads, unlike smaller engines working at peak capacity.
- Durability at Scale: Their robust build allows longer operational life with consistent performance.
- Specific Applications: Efficiency is showcased more in large-scale industrial or marine roles compared to cars.
Although smaller engines have their place, 16 cylinder engines excel in specialized settings requiring high output.
Noise and Vibration Handling
16 cylinder engines ensure minimized noise and vibration, thanks to their engineering.
- Smooth Running: The high number of cylinders reduces uneven firing, leading to smooth engine operation.
- Vibration Dampening: Advanced balancing of components prevents excessive vibrations.
- Controlled Noise Levels: Their design often includes noise-dampening materials for quieter functioning.
This combination of smoothness and noise control adds to the usability of these engines in various applications.
In conclusion, the performance characteristics of 16 cylinder engines highlight their unmatched power, efficiency, and smooth operation. They remain a cornerstone of high-performance engineering.

Applications of 16 Cylinder
16 cylinder engines are designed for specialized applications that demand immense power and reliability. They serve important roles in automotive, industrial, and large-scale marine and aeronautics fields.
Automotive Industry: Supercars and Luxury Vehicles
- Unmatched Performance: Supercars use 16 cylinder engines for incredible speed and agility.
- Luxury Appeal: High-end vehicles showcase these engines as symbols of premium engineering.
- Smooth Power Delivery: Their balanced operation ensures a seamless driving experience.
Notable examples include Bugatti’s Veyron and Chiron models, which feature quad-turbocharged W16 engines.
Industrial Uses: Generators and Machinery
- Heavy-Duty Reliability: Industries use 16 cylinder engines for large-scale generators and machinery.
- Constant Power Supply: These engines deliver consistent output for demanding applications.
- Durability: Their robust design ensures long operational life under extreme loads.
Power plants rely on these engines for uninterrupted energy generation in critical operations.
Marine and Aeronautics: Large-Scale Applications
- Marine Propulsion: Large ships utilize 16 cylinder engines for smooth and powerful navigation.
- Aviation Advancements: Some aircraft use these engines for exceptional thrust and reliability.
- Extreme Performance: Their high torque makes them ideal for challenging environments in these fields.
Marine vessels and aircraft benefit from their ability to handle massive loads efficiently.
In summary, the applications of 16 cylinder engines span high-performance vehicles, industrial machinery, and large-scale transportation systems. These engines are indispensable in fields where power and reliability matter most.
Challenges and Limitations
While 16 cylinder engines deliver incredible performance, they come with significant challenges and limitations. These factors impact their practicality and broader adoption across various industries.
Maintenance and Repair Complexities
Maintaining and repairing a 16 cylinder engine is a demanding task.
- Complex Design: These engines feature intricate parts that require specialized equipment for maintenance.
- High Skill Requirements: Only trained professionals can handle the precision needed to service the engine.
- Long Downtimes: Repairs often take longer, leading to operational delays in critical applications.
- Expensive Parts: Replacement components are difficult to source and are usually costlier due to their uniqueness.
The engine’s size and intricacy make regular servicing a time-intensive and costly affair.
Fuel Consumption and Environmental Impact
A 16 cylinder engine consumes vast amounts of fuel, which affects both cost and sustainability.
- High Fuel Usage: These engines are fuel-hungry, especially at maximum load conditions.
- CO2 Emissions: Their large-scale combustion generates significant greenhouse gases, contributing to environmental concerns.
- Inefficiency in Some Roles: For less demanding tasks, their fuel economy is poor compared to smaller engines.
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter laws regarding emissions limit their adoption and increase compliance costs.
This makes 16 cylinder engines less favorable in a world moving toward greener and more efficient solutions.

Cost of Production and Ownership
Building and owning a 16 cylinder engine is an expensive venture.
- High Initial Costs: The manufacturing process involves premium materials and advanced engineering.
- Operation Expenses: Fuel consumption and maintenance add significantly to the overall cost of ownership.
- Limited Market: Fewer buyers and specific uses drive up production expenses.
- Resale Challenges: Their niche applications make reselling these engines difficult.
These costs make the engine affordable only for specialized industries or luxury markets.
In conclusion, the challenges of 16 cylinder engines lie mainly in their maintenance demands, environmental impact, and high costs. Addressing these limitations is key to ensuring their sustained relevance in niche applications.
Engineering Innovations in 16 Cylinder
As technology advances, engineering innovations continue to enhance the performance of 16 cylinder engines. These developments aim to address challenges related to cooling, power delivery, and sustainability. Here’s a look at three key innovations that are reshaping these remarkable engines.
Advanced Cooling Systems
Managing heat is critical for the efficiency and longevity of 16 cylinder engines. Advanced cooling systems are crucial for maintaining optimal temperatures under high loads.
- Efficient Radiators: Larger radiators with improved airflow reduce overheating in extreme conditions.
- Powerful Pumps: High-capacity water pumps circulate coolant effectively, even under heavy workloads.
- Thermal Sensors: These sensors monitor temperature in real-time, ensuring quick adjustments to prevent damage.
- Liquid-Cooled Designs: Many 16 cylinder engines now use liquid cooling, which is superior to air cooling.
Advanced cooling systems ensure reliability and prevent thermal degradation in these high-performance engines.
Turbocharging and Supercharging Technologies
To maximize power, 16 cylinder engines utilize turbocharging and supercharging technologies. These methods significantly enhance engine output and efficiency.
- Turbocharging: Compresses air entering the engine, increasing power without increasing engine displacement.
- Supercharging: Uses a belt-driven compressor for instant power boosts, improving acceleration and torque.
- Dual-Charged Systems: Some engines combine turbochargers and superchargers for optimized performance across all speed ranges.
- Fuel Efficiency Benefits: These technologies deliver more power per unit of fuel consumed.
Turbocharging and supercharging provide the power and responsiveness needed for high-demand applications.
Hybrid and Sustainable Fuel Options
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in engine development. Engineers are exploring hybrid systems and alternative fuels to make 16 cylinder engines more eco-friendly.
- Hybrid Integration: Electric motors supplement the engine’s power, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
- Biofuels: These renewable fuels are tested to lower environmental impact without sacrificing power.
- Hydrogen Fuel: Hydrogen combustion offers nearly zero-emission solutions for future propulsion systems.
- Engine Modifications: Adjustments allow compatibility with newer, greener fuel types.
These innovations help 16 cylinder engines remain relevant in a world focused on sustainability.
In conclusion, advanced cooling, charging technologies, and sustainable fuel options are transforming 16 cylinder engines. These innovations not only enhance performance but also ensure adaptability to modern environmental standards.
Notable 16 Cylinder in History
16 cylinder engines have left a lasting mark in automotive and mechanical engineering history. Their impressive power and unique designs have driven technological advancements. Let’s explore iconic models, influential manufacturers, and record-breaking achievements.
Iconic Models in Automotive Designs
Several automotive masterpieces feature 16 cylinder engines, showcasing engineering brilliance:
- Bugatti Veyron and Chiron: Both feature quad-turbocharged W16 engines, combining immense power and luxury.
- Cadillac Sixteen: This concept car boasted a naturally aspirated V16 engine, emphasizing performance and elegance.
- Cizeta-Moroder V16T: Known for its transversely mounted V16 engine, this supercar represents bold design choices.
- Auto Union Type C/D: A 1930s racing car equipped with a V16 engine, dominating Grand Prix circuits.
These models symbolize innovation and audacious engineering in the automotive world.
Famous Manufacturers Behind These Engines
Pioneering manufacturers have played a crucial role in developing 16 cylinder engines:
- Bugatti: Known for its W16 engine designs, they have elevated supercar performance standards.
- Cadillac: Cadillac’s V16 models set new benchmarks in automotive luxury during the 1930s.
- Rolls-Royce: Produced V16 engines that powered both cars and aircraft, ensuring top-tier quality.
- BRM (British Racing Motors): Designed V16 engines specifically for high-speed race cars.
These companies have continuously pushed technical boundaries, enhancing the engine’s legacy.
Record-Breaking Achievements
16 cylinder engines have powered groundbreaking achievements in speed and performance:
- World Speed Records: The Bugatti Veyron Super Sport reached 267 mph, claiming the title of the fastest car.
- Racing Success: Auto Union’s V16-powered cars dominated European racing during the 1930s.
- Engineering Feats: Engines like the W16 established new benchmarks for compact yet immensely powerful designs.
- Industry Recognition: Cadillac’s V16 cars are celebrated as engineering icons of their era.
These accomplishments highlight the unmatched capabilities of 16 cylinder engines.
In summary, the history of 16 cylinder engines is rich with iconic designs, influential manufacturers, and extraordinary achievements. They remain a symbol of engineering excellence and innovation.
Future of 16 Cylinder Engines
16 cylinder engines, despite their niche, remain at the forefront of engineering innovation. Their future depends on advancements that address efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. Let’s explore trends in development, their role in sustainability, and their relevance today.
Trends in Engine Development
Engine technology evolves rapidly to meet modern demands. For 16 cylinder engines, several trends stand out:
- Downsizing with Efficiency: Engineers focus on maintaining power while reducing engine size and weight.
- Electrification: Hybrid systems integrate electric power with traditional combustion for optimized performance.
- Smart Technology: Sensors and AI enhance control, efficiency, and real-time monitoring.
- Alternative Fuels: Focus shifts to biofuels, synthetic fuels, and hydrogen to reduce environmental impact.
- Modular Designs: Modular components improve flexibility and reduce development costs.
These trends help keep 16 cylinder engines viable in a competitive and changing industry.
Role in Sustainable Automotive Innovations
Sustainability is a critical focus in the automotive industry. 16 cylinder engines adapt to embrace this shift:
- Hybrid Solutions: Combining electric and combustion power reduces emissions and fuel consumption.
- Emission Reductions: Advanced exhaust systems and cleaner fuels lower environmental impact.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Engines designed for compatibility with renewable energy sources push sustainability further.
- Improved Efficiency: Cutting-edge materials and designs enhance fuel economy without sacrificing power.
Through innovation, these engines contribute to greener automotive solutions while meeting performance demands.
Relevance in Modern Mechanical Engineering
16 cylinder engines hold a crucial place in modern mechanical engineering for specialized applications:
- Power-Demanding Industries: They remain indispensable in marine, industrial, and aeronautical applications.
- Symbol of Prestige: In luxury and supercars, they represent innovation and exclusivity.
- R&D Platforms: Engineers use them to test and apply cutting-edge materials and techniques.
- Educational Value: They serve as models for studying advanced engineering principles.
Their relevance persists where high power, durability, or prestige matter most.
In conclusion, the future of 16 cylinder engines lies in advancements in sustainable development, hybridization, and specialized engineering. These powerful engines continue to evolve and thrive in their unique domains.
Leave a Reply