Introduction to 12 Cylinder Engines
12 cylinder engine is renowned for their power, smooth operation, and unique design. These engines are often associated with luxury and high-performance vehicles due to their ability to deliver impressive performance and refinement. Understanding these engines introduces their design, history, and diverse applications, enhancing appreciation for their engineering marvels.
What is a 12 Cylinder Engine?
A 12 cylinder engine consists of 12 cylinders arranged in a specific configuration. Each cylinder holds a piston, which works to create power by compressing and igniting fuel. The engine typically operates using gasoline combustion, which generates energy to propel vehicles. Common layouts for these engines include inline and V-type arrangements.

A Brief History of 12 Cylinder Engines
The 12 cylinder engine emerged around the early 20th century. The first major usage was in luxury cars and aircraft engines. Manufacturers favored its smoothness and power for premium brand automobiles. Over the decades, carmakers like Ferrari, Aston Martin, and Rolls-Royce popularized these engines in iconic sports and luxury vehicles.
Common Applications of 12 Cylinder Engines
These engines are primarily used in high-end cars due to their superior power and performance. Sports cars benefit from their ability to deliver speed and smooth acceleration. Luxury cars adopt them for their quiet and refined operation. Additionally, some heavy-duty machinery and vintage aircraft utilize 12 cylinder engines for their reliability and power.
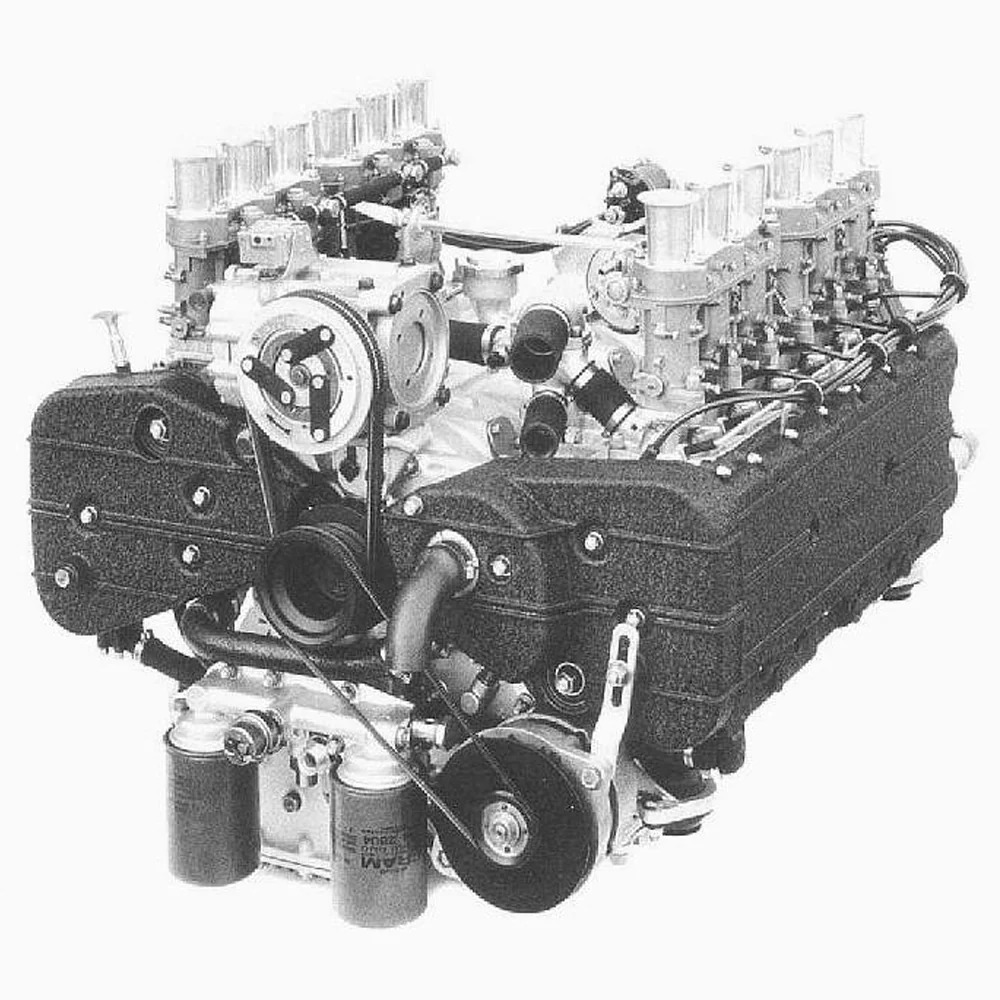
Anatomy of a 12 Cylinder
Understanding the anatomy of a 12 cylinder engine reveals why it delivers superior performance. Each part of the engine contributes to its overall efficiency, power, and smoothness. This section examines how the engine layout, design, and components work together.
Engine Layout and Design
12 cylinder engines usually come in two common configurations: inline and V-type.
- Inline Configuration: All cylinders are arranged in a straight line. This layout is rare for modern cars due to its length.
- V-Type Configuration: Cylinders are split into two banks at a specific angle. It is more compact and widely used today.
The angle in V-type engines typically ranges between 45° to 60°. This design reduces vibrations, ensuring smooth engine operation. Due to its compact shape, it fits well into various vehicle designs, particularly sports cars and luxury vehicles.
Key Components and Their Functions
A 12 cylinder engine consists of several essential components working together efficiently:
- Pistons: The pistons compress air and fuel for combustion. They move in coordinated strokes.
- Cylinders: Cylinders contain the pistons and enable combustion.
- Crankshaft: This part converts piston motion into rotational power to propel the vehicle.
- Camshafts: Camshafts control the opening and closing of valves for air and fuel movement.
- Valves: Valves regulate the airflow, ensuring efficient combustion.
- Fuel Injectors: Injectors deliver fuel to each cylinder for consistent power.
- Cooling System: The cooling system prevents overheating during engine operation.
Each component has a vital role in ensuring precision and performance in a 12 cylinder engine.
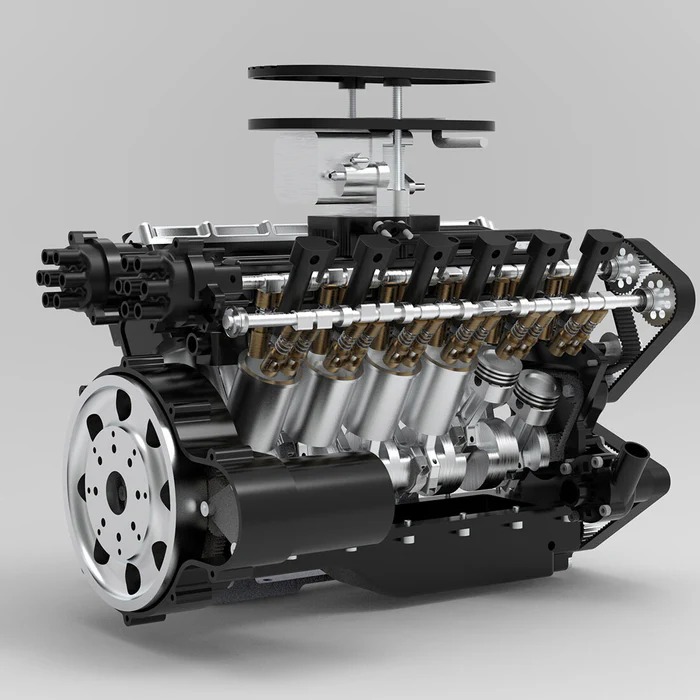

Differences Between Inline and V-type Configurations
There are several notable differences between inline and V-type configurations:
- Size: Inline engines are longer, whereas V-type engines are more compact and shorter.
- Vibration: V-type engines have less vibration due to their balanced design.
- Usage: V-type designs are favored in modern sports and luxury cars, while inline engines are uncommon.
The V-type configuration is more popular for its practicality, smooth operation, and adaptability.
How Does a 12 Cylinder Operate?
Understanding the operation of a 12 cylinder engine sheds light on its power and efficiency. The process involves fuel combustion, precise mechanical coordination, and advanced engineering components working together seamlessly.
Fuel Combustion Process in a 12 Cylinder Engine
The fuel combustion process is the core of a 12 cylinder engine’s operation. Here’s how it works:
- Air-Fuel Mixture: Air mixes with fuel and enters each cylinder.
- Compression: Pistons compress the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders.
- Ignition: Spark plugs ignite the compressed mixture, causing combustion.
- Power Generation: The explosion pushes pistons downward, generating energy to rotate the crankshaft.
- Exhaust: Burnt gases exit the engine through exhaust valves.
This cycle—intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust—occurs repeatedly and rapidly, producing the power 12 cylinder engines are famous for.
Crankshaft and Piston Arrangement
The crankshaft and piston arrangement ensure smooth and efficient power generation. Here’s how they function:
- Pistons in Each Cylinder: Each cylinder contains a piston that moves up and down.
- Crankshaft Function: The pistons’ movement rotates the crankshaft, converting linear motion into rotational force.
- Precision Timing: The pistons fire sequentially, ensuring continuous power delivery and reducing vibrations.
- Balance: The V-type arrangement, common in 12 cylinder engines, ensures even force distribution.
This configuration contributes to the engine’s smoothness and allows it to deliver superior power.
Advantages of a 12 Cylinder Engine’s Operation
12 cylinder engines offer numerous operational benefits:
- Exceptional Power Output: These engines deliver immense horsepower and torque.
- Smoothness: Their balanced design minimizes vibrations for a seamless driving experience.
- Quick Acceleration: The constant power output supports rapid speed increases, ideal for sports cars.
- Durability: The efficient design reduces stress on individual engine components.
- Prestige and Performance: 12 cylinder engines are synonymous with luxury and high-end vehicles.
The operation of a 12 cylinder engine reflects intricate engineering, combining power and sophistication. These engines set the bar for high-performance and luxury vehicles alike.
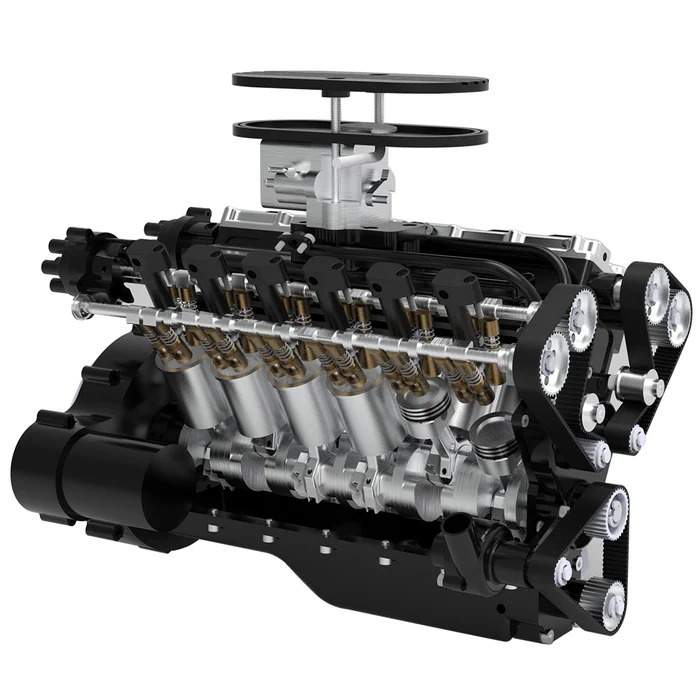

Performance and Efficiency of 12 Cylinder
Understanding the performance and efficiency of a 12 cylinder engine highlights its capabilities and limitations. These engines are designed to deliver outstanding power and smoothness. Yet, efficiency remains a key factor to evaluate.
Power Output and Torque
12 cylinder engines are known for their remarkable power and torque output.
- Exceptional Horsepower: These engines can produce upwards of 600 horsepower, perfect for high-performance needs.
- Consistent Torque: With 12 cylinders, the torque delivery remains smooth and consistent.
- High Speed Potential: They enable fast acceleration, making them ideal for racing and sports cars.
- Improved Performance: Multiple cylinders ensure a steady flow of power, enhancing overall driving performance.
Cars with these engines experience high responsiveness and precision, ensuring top-tier driving dynamics.
Fuel Economy Considerations
Despite their performance, 12 cylinder engines are not known for fuel efficiency.
- Higher Fuel Consumption: These engines need significant fuel due to their size and power.
- Luxury vs Efficiency: They are usually used in high-end cars where performance outweighs economy.
- Modern Enhancements: Advances in engine design aim to improve fuel efficiency, but progress is limited.
- Cost of Fuel: High fuel usage adds to the operational costs of vehicles with these engines.
Fuel economy is often the primary drawback for customers considering these powertrain options.
How It Compares to Other Engine Types
Compared to other engines, 12 cylinder engines stand out for specific reasons:
- Versus 8 Cylinder Engines: 12 cylinder engines offer smoother operation and more power but consume more fuel.
- Versus 4 and 6 Cylinder Engines: They deliver significantly higher performance but are heavier and costlier.
- Torque Consistency: The superior balance and consistent power set them apart from smaller engines.
- Market Segment: 12 cylinder engines are designed for high-end or specialized vehicles.
While these engines excel in power and luxury, their practicality may not suit all vehicle users.
Advantages of 12 Cylinder
12 cylinder engines stand out for their superior features and appeal. They offer distinct benefits that make them a preferred choice for high-performance and luxury vehicles.
Smooth Performance and Balance
- Seamless Operation: These engines minimize vibrations due to their balanced design and innovative architecture.
- Refined Performance: Power delivery is consistent and flawless, ensuring smooth acceleration and deceleration.
- Precision: With 12 cylinders firing sequentially, they maintain consistent power flow at all times.
High Power and Luxury Appeal
- Exceptional Power: 12 cylinder engines generate immense horsepower, ideal for performance enthusiasts.
- Luxury Symbol: These engines are synonymous with opulence and are often found in premium vehicles.
- Prestige: Cars with these engines are associated with elite engineering and high social status.
- Performance Excellence: Rapid acceleration and agility provide a thrilling driving experience.
Compatibility with Sports and Luxury Vehicles
- Versatility: These engines fit well in both sports cars and luxury sedans.
- Tailored Design: The compact V-type layout makes them suitable for modern vehicle designs.
- Enhanced Driving Dynamics: Their smooth power and torque delivery enhance on-road and racing experiences.
- Legacy in Luxury Brands: Renowned manufacturers like Ferrari and Rolls-Royce depend on them for flagship models.
The advantages of 12 cylinder engines go beyond raw power. They epitomize the pinnacle of automotive engineering and luxury.
Challenges and Limitations of 12 Cylinder
Despite the advantages of 12 cylinder engines, they come with certain challenges and limitations. These drawbacks mostly revolve around their fuel consumption, maintenance costs, and physical aspects like size and weight.
Fuel Consumption and Environmental Impact
- High Fuel Usage: 12 cylinder engines consume a lot of fuel due to their size and power output.
- Low Fuel Efficiency: Their designs focus on performance rather than economical fuel use.
- Emissions Concerns: Higher fuel usage leads to increased emissions, contributing to pollution.
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter laws make it harder for these engines to meet modern standards.
Maintenance and Repair Costs
- Complex Systems: 12 cylinder engines are intricate, requiring specialized expertise for repairs.
- Expensive Parts: Replacement parts can be costly due to their premium nature and limited availability.
- Longer Repair Times: Repairs may take longer due to the engine’s complexity.
- Higher Maintenance Frequency: Regular servicing is crucial for these engines to perform smoothly.
Space and Weight Constraints
- Large Size: These engines occupy more space, limiting vehicle design options.
- Heavier Weight: Increased weight affects fuel efficiency and handling.
- Compact vs Practical Designs: While the V-type is more compact, it still poses challenges in smaller vehicles.
- Chassis Compatibility: Additional engineering is required to accommodate their dimensions and weight.
While 12 cylinder engines are an engineering marvel, these limitations make them less practical for everyday use. Manufacturers must address these challenges to ensure their feasibility in modern vehicles.
Popular Cars with 12 Cylinder
12 cylinder engines are often found in prestigious and high-performance cars. Their unique power and smoothness make them ideal for luxury and sports markets. These engines are integral to the identity of several globally recognized car models.
Iconic Sports Cars Featuring 12 Cylinder Engines
- Ferrari Berlinetta models: Ferrari is synonymous with 12 cylinder engines. Models like the Ferrari 812 Superfast showcase immense performance. These cars feature unparalleled speed and precision.
- Lamborghini Aventador: The Lamborghini Aventador uses a V12 engine for power and rapid acceleration. It remains a symbol of extravagant design and performance.
- Jaguar XJ220: This iconic car, while rare, highlights the potential of 12 cylinder engines in sports cars. It dominated the automotive scene for years with remarkable top speeds.
These cars have solidified the role of 12 cylinder engines in delivering peak performance for thrill-seekers.
Luxury Cars with 12 Cylinder Engines
- Rolls-Royce Phantom: The Phantom combines the quiet, smooth operation of a V12 engine with unmatched luxury. It’s a masterpiece in design and performance.
- Bentley Mulsanne: Bentley integrates the raw power of a 12 cylinder engine with top-tier refinement in the Mulsanne. The vehicle represents sheer class and comfort.
- Mercedes-Maybach S-Class: The Maybach series employs these engines to provide opulence and stunning road performance. It delivers balance between craftsmanship and power.
Luxury brands prioritize 12 cylinder engines for their symbolic association with prestige and smoothness.
High-Performance Vehicles in Motorsport
- Formula 1 cars from the past: Early Formula 1 cars used compact 12 cylinder engines. They benefited from excellent power-to-weight ratios.
- Le Mans Prototypes: Many Le Mans race cars feature V12 engines for endurance racing dominance. They showcase the engine’s power and reliability.
- Ferrari Racing Heritage: Ferrari’s history in motorsport highlights the undeniable role of 12 cylinder engines in competitive racing.
12 cylinder engines play a significant role in motorsport, providing unmatched performance for high-stakes scenarios.
These iconic sports cars, luxury vehicles, and motorsport models demonstrate the versatility and dominance of 12 cylinder engines in automotive history.

Future of 12 Cylinder Engines
As technology evolves, the future of 12 cylinder engines faces opportunities and challenges. Manufacturers aim to refine and reinvent these engines while addressing environmental and economic concerns. Some innovations and trends shape the outlook for these engineering marvels.
Innovations in 12 Cylinder Engine Technology
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Engineers focus on making 12 cylinder engines consume less fuel without sacrificing power.
- Hybrid Integration: Combining 12 cylinder engines with electric motors enhances performance and reduces emissions.
- Advanced Materials: Lightweight and durable materials reduce engine weight and improve efficiency.
- Variable Cylinder Activation: This technology allows certain cylinders to deactivate, minimizing fuel consumption when full power isn’t needed.
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Built-in systems monitor performance, helping reduce maintenance needs and increasing reliability.
Innovations aim to extend the lifespan of 12 cylinder engines while meeting modern standards.
Impact of Electric Vehicles on 12 Cylinder Engines
- Electric Vehicle Dominance: The growing popularity of electric cars challenges the relevance of traditional combustion engines.
- Market Shift: Consumers prioritize eco-friendly and cost-saving options, reducing demand for fuel-heavy engines.
- Regulations and Emissions: Stricter laws on emissions favor electric drivetrains over gas-powered systems like 12 cylinders.
- Luxury Electric Alternatives: Brands offering top-tier electric vehicles as luxury alternatives compete directly with traditional 12 cylinder cars.
Electric vehicles limit the appeal of 12 cylinder engines in the shift toward sustainable transportation.
Is There Still a Place for 12 Cylinder Engines in Modern Automobiles?
- Niche Market: These engines continue to thrive in luxury and performance car segments.
- Cultural and Historical Value: Iconic brands maintain them as part of their heritage appeal.
- Unique Driving Experience: Superior power, smoothness, and elegance ensure 12 cylinder engines remain desirable.
- Collector’s Appeal: Enthusiasts invest in vehicles equipped with 12 cylinder engines for rarity and prestige.
- Selective Usage: Certain industries or machines may still favor these engines for specialized purposes.
While challenges exist, 12 cylinder engine may retain a limited but significant role in modern cars. Their legacy lives on through innovation, adaptation, and continued appreciation for their exceptional performance.
Leave a Reply