What is an Inline 4 Cylinder Engine?
An inline 4 cylinder engine is a type of internal combustion engine. It has four cylinders arranged in a straight line. These cylinders are positioned vertically or slightly inclined in one row. This engine layout is compact, making it ideal for smaller vehicles.
The inline 4 cylinder engine operates by converting fuel into mechanical energy. Each cylinder has a piston that moves up and down, creating power. The engine follows a four-stroke cycle: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. These stages occur simultaneously in different cylinders to ensure smooth performance.
This engine configuration is common in cars, motorcycles, and some light trucks. Its popularity comes from its efficiency, reliability, and balanced performance. It is also fuel-efficient, lightweight, and cost-effective to produce.
In summary, the inline 4 cylinder engine is a robust and practical choice. Its simple design and versatility make it widely used across various applications.
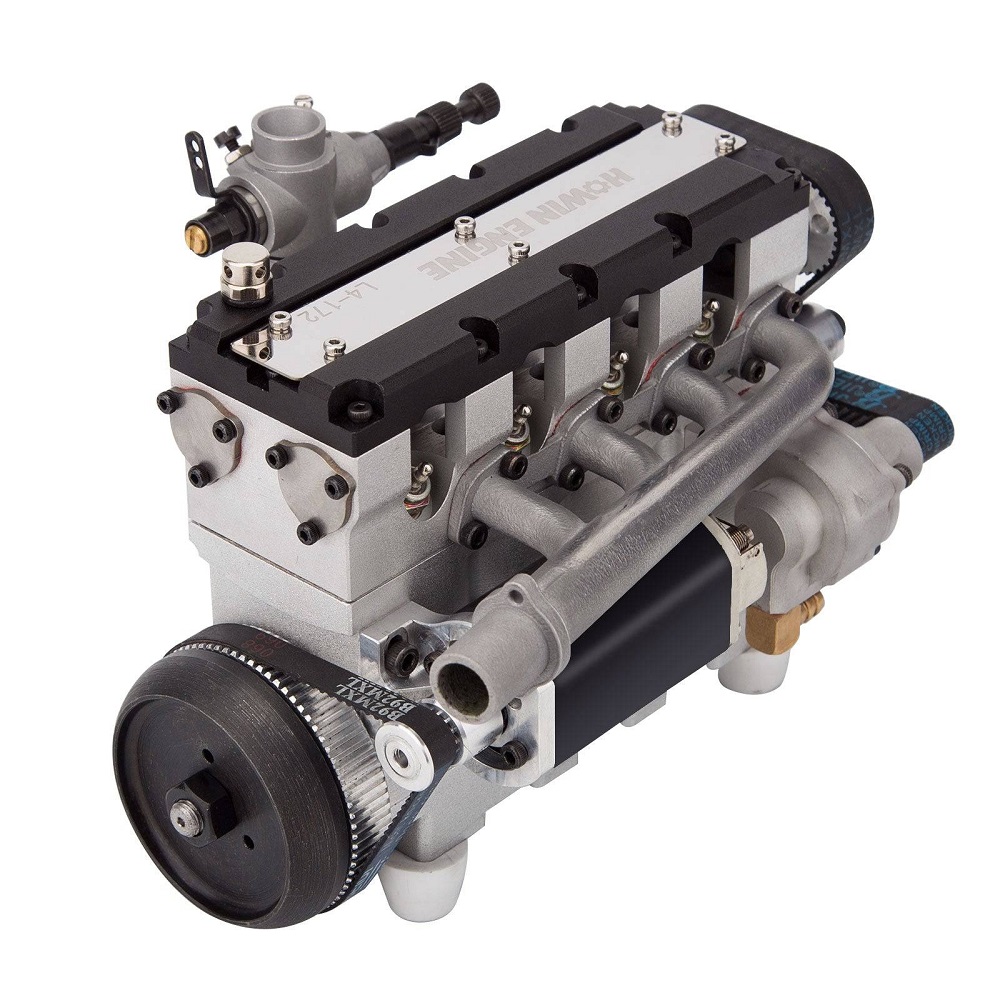

History and Evolution of Inline 4 Cylinder
The inline 4 cylinder engine has a rich history in the automotive world. It emerged in the early 20th century as engineers sought compact, efficient engine designs. The simplicity of its design made it a popular choice compared to more complex engine configurations.
Initially, inline 4 cylinder engines were used in smaller vehicles and motorcycles. Their lightweight and compact structure provided better efficiency and performance. Over time, automotive technology advanced, improving the durability and power output of these engines.
The 1950s and 1960s marked a significant period for the evolution of inline 4 cylinder engines. Car manufacturers began producing high-performance versions of this engine for sports cars, making them powerhouses on the road. Japanese carmakers, in particular, played a key role by introducing fuel-efficient and reliable inline 4 engines in popular models.
In the 1980s and 1990s, as environmental concerns increased, the demand for fuel-efficient vehicles grew. The inline 4 cylinder engine became even more sought after for its fuel efficiency and lower emissions. It was paired with advanced technologies such as fuel injection systems and turbochargers to improve performance and meet changing regulations.
Today, the inline 4 cylinder engine remains a dominant force in the automotive industry. Modern versions are highly efficient, lightweight, and environmentally friendly. Advances in materials and design have made them even more powerful and reliable. Hybrid and electric powertrains have also incorporated inline 4 cylinder engines as part of their systems.
The history and evolution of the inline 4 cylinder engine showcase its adaptability and enduring relevance. Its journey reflects the automotive industry’s continuous quest for innovation, efficiency, and sustainability.
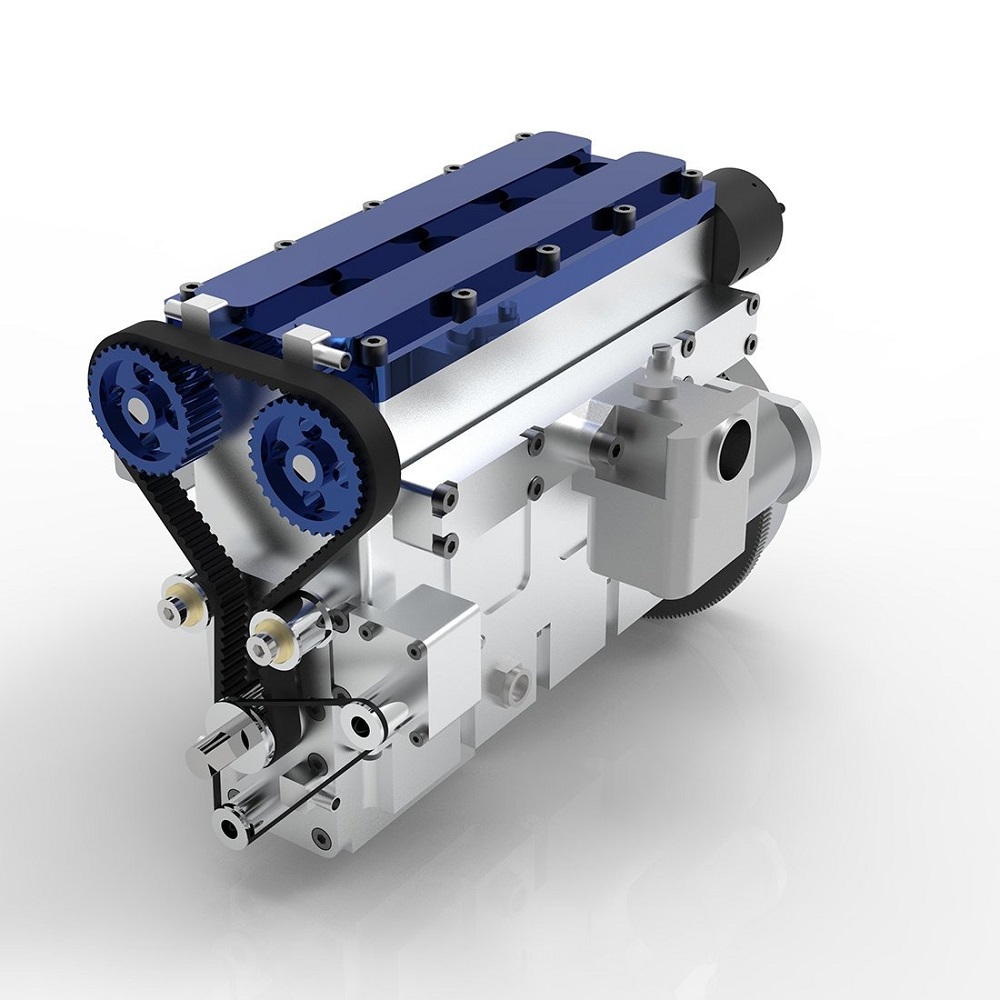
Key Features of Inline 4 Cylinder
The inline 4 cylinder engine is celebrated for its numerous practical features. These attributes make it a preferred choice among small to medium-sized vehicles. Below are the key features that set it apart:
1. Compact Design
The inline 4 cylinder engine has a slim and compact design. Its cylinders are arranged in a straight line, allowing it to fit easily into small engine bays. This makes it a top choice for vehicles with limited space, like compact cars and motorcycles.
2. Lightweight Construction
The simple and streamlined layout reduces the overall weight. A lighter engine improves fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. This feature also enhances handling and maneuverability.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
Inline 4 cylinder engines are cheaper to manufacture than more complex configurations. The simple design requires fewer parts, reducing production and maintenance costs. This affordability appeals to both manufacturers and consumers.
4. Fuel Efficiency
These engines are known for their impressive fuel efficiency. Their lightweight design and effective fuel combustion make them better for saving fuel. They are an eco-friendly option for reducing emissions without sacrificing performance.
5. Smooth Operation
The engine provides a balance between power and vibration control. The inline arrangement of the cylinders enables even distribution of power. This leads to a smoother driving experience compared to some other engine types.
6. Adequate Power-to-Size Ratio
Despite their small size, these engines can pack a punch. They deliver a good balance of power and performance for vehicles of all sizes. Innovations like turbocharging have further enhanced their output capabilities.
7. Durability and Reliability
Over decades, this engine type has proven to be dependable. With proper maintenance, it can last for a long time. Modern advancements in engineering and materials ensure better longevity and reduced wear.
In summary, the inline 4 cylinder engine offers a reliable and efficient solution for performance and everyday use. Its thoughtful design and balanced features make it an evergreen choice in the automotive world.
How Does an Inline 4 Cylinder Work?
An inline 4 cylinder engine works by converting fuel into mechanical energy. It uses the four-stroke cycle system: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. These cycles happen continuously in each cylinder to produce power. The engine is compact, efficient, and widely used in vehicles.
To start, the intake stroke draws air and fuel into the cylinder. During the compression stroke, the piston moves upward, compressing the air-fuel mixture. Next, the power stroke ignites this mixture with a spark, causing a small explosion. This pushes the piston downward, creating energy to drive the vehicle. Finally, the exhaust stroke removes waste gases.
All four cylinders work simultaneously but at different stages of the cycle. This coordinated operation ensures smooth and steady power output. Components such as pistons, crankshafts, and valves help in this process. These parts work together to transfer energy to the drive system.
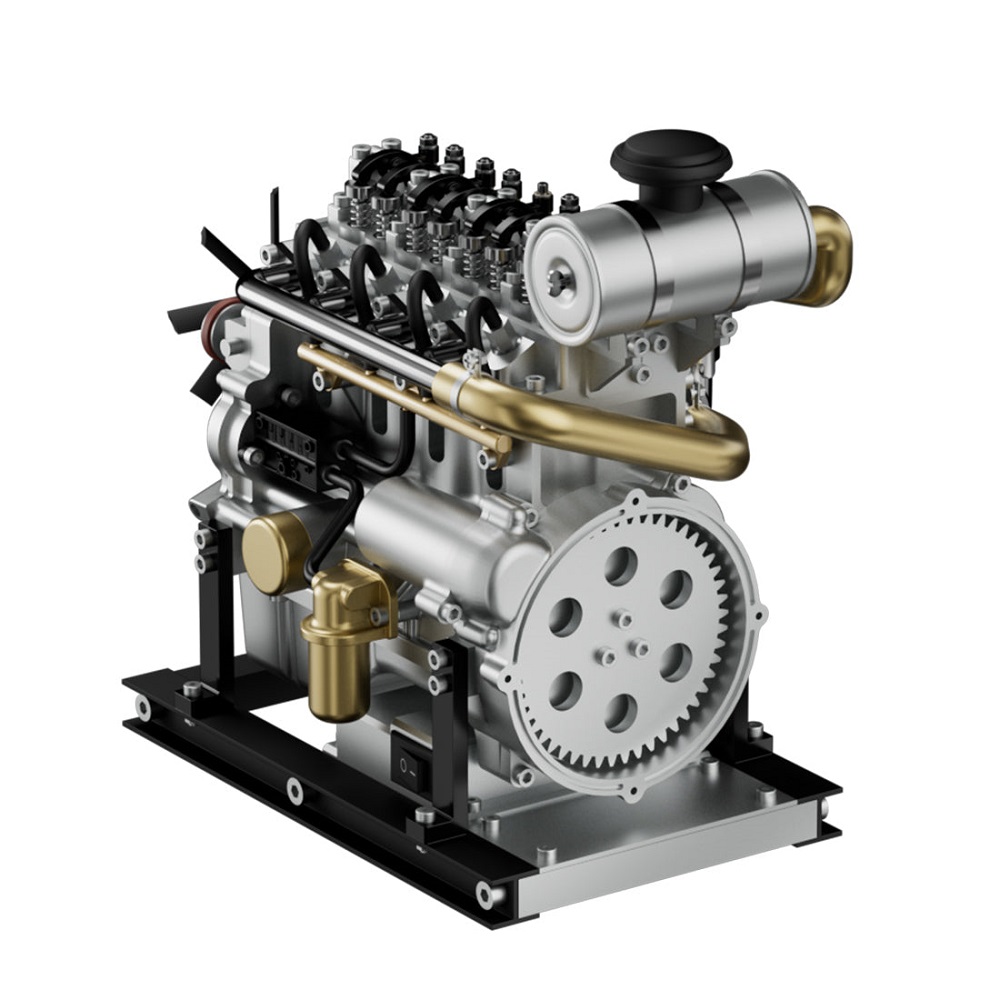
Combustion Process in an Inline 4 Cylinder Engine
The combustion process in an inline 4 cylinder engine begins with the air-fuel mixture. This is ignited by a spark plug inside the cylinder. The ignition creates controlled explosions, producing mechanical energy.
One cylinder goes through the four stages: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. During intake, air and fuel enter the cylinder. Compression increases pressure by squeezing the mixture tightly before ignition.
When ignited, the mixture expands rapidly, forcing the piston down. This movement converts energy into rotational power via the crankshaft. Exhaust gases are then expelled to prepare for the next cycle.
The combustion cycle happens continuously in all four cylinders. Each cylinder fires separately, ensuring stable and balanced output. Engineers optimize this process for maximum performance and fuel efficiency.
Advantages of Inline 4 Cylinder
The inline 4 cylinder engine offers various advantages that make it a popular choice for vehicles. Below are the key benefits:
1. Efficiency and Performance
Inline 4 cylinder engines are highly efficient in power delivery and fuel consumption. Their streamlined design ensures optimized fuel usage, which contributes to lower running costs. They also provide a good balance of power and performance for daily driving needs.
2. Compact and Lightweight Design
The straight alignment of cylinders makes these engines compact and easy to fit in vehicles. Their lightweight construction improves mileage and contributes to better handling. This design is ideal for vehicles requiring agility and speed.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
These engines are economical to produce due to their simple components. The lower manufacturing costs translate into affordability for car buyers. Additionally, repairs and maintenance are less expensive compared to complex engines like V6 or V8.
4. Smooth Operation
Inline 4 engines produce less vibration compared to larger, more complex engines. Their balanced operation ensures smoother rides. This quality enhances driving comfort, especially in urban traffic conditions.
5. Versatility
Due to their adaptability, inline 4 engines can be used in a variety of vehicles. They are found in cars, motorcycles, and even smaller trucks. Their practical nature fits well with diverse automotive applications.
6. Environmental Friendliness
These engines are designed to be fuel-efficient, leading to reduced emissions. Modern technology also incorporates features like turbocharging to maintain performance while lowering environmental impact.
7. Reliability and Longevity
Inline 4 engines have a proven track record of reliability when properly maintained. Their simple design means fewer parts can go wrong. Drivers appreciate their durability, which allows the engine to perform for years.
In summary, inline 4 cylinder engines are practical, efficient, and versatile. These benefits make them a top choice for small to medium-sized vehicles.
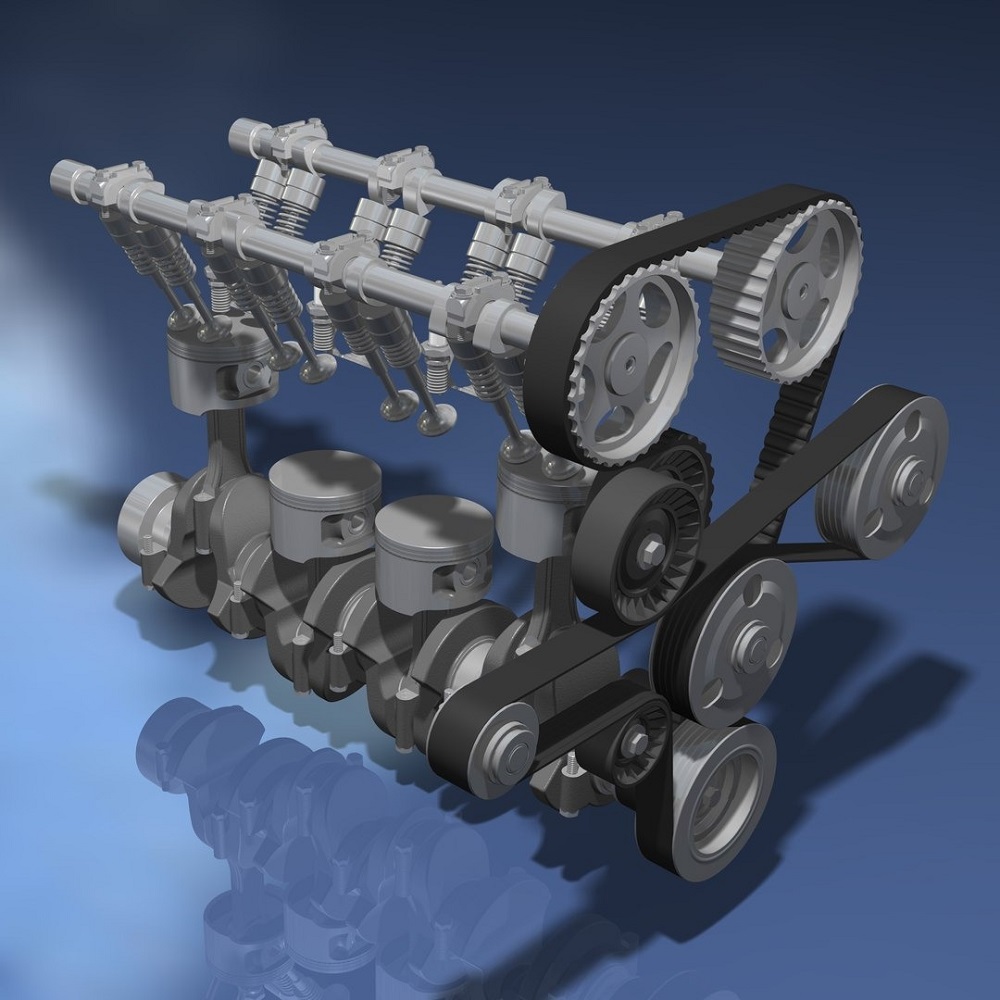
Common Applications of Inline 4 Cylinder
The inline 4 cylinder engine is versatile and widely used across various applications. Its compact size and efficiency make it suitable for different types of vehicles and machines. Below are the common applications where these engines excel:
1. Passenger Cars
Inline 4 cylinder engines are a popular choice for compact and midsize cars. They provide a good balance of fuel efficiency and performance. These engines are found in sedans, hatchbacks, and smaller SUVs. Their compact design allows them to fit into tight engine bays.
2. Motorcycles
Motorcycles are one of the most frequent users of inline 4 cylinder engines. The engine’s lightweight and compact nature ensures optimal speed and agility. Riders benefit from smooth power delivery and better fuel economy.
3. Light Trucks and Vans
Small trucks and vans often use inline 4 cylinder engines. These engines deliver sufficient power for transport and light hauling. They also provide better mileage, making them economical choices for businesses.
4. Sports Cars
Many sports cars utilize high-performance versions of inline 4 cylinder engines. Turbocharged models produce impressive power despite their smaller size. This makes them ideal for achieving speed and agility without extra weight.
5. Construction and Agricultural Equipment
Compact utility machines, including mini excavators and small tractors, use these engines. Their efficiency and reliability ensure long operational hours and lower fuel consumption.
6. Marine Engines
Smaller boats and watercraft often use inline 4 cylinder engines. These engines offer sufficient power for smaller vessels while remaining fuel-efficient.
7. Generators
Inline 4 cylinder engines also power portable and backup generators. Their reliability and efficiency ensure continuous performance during power outages.
In summary, the broad applications of the inline 4 cylinder engine highlight its utility and adaptability. From passenger cars to industrial equipment, they deliver reliable power and efficiency.
Comparison: Inline 4 Cylinder Engine vs Other Engine Configurations
Comparing engine configurations is crucial to understand their strengths and weaknesses. The inline 4 cylinder engine is often compared to other layouts like V6, V8, and inline 6 engines. Below are key points that differentiate them:
1. Design and Layout
Inline 4 cylinder engines have a straightforward design. All four cylinders are aligned in one row. This layout is compact and lightweight.
V6 engines feature six cylinders arranged in a V-shape. This design allows more cylinders in a smaller space, providing greater power output.
Inline 6 engines place six cylinders in a straight line, similar to inline 4s. However, they are longer and heavier, requiring more space.
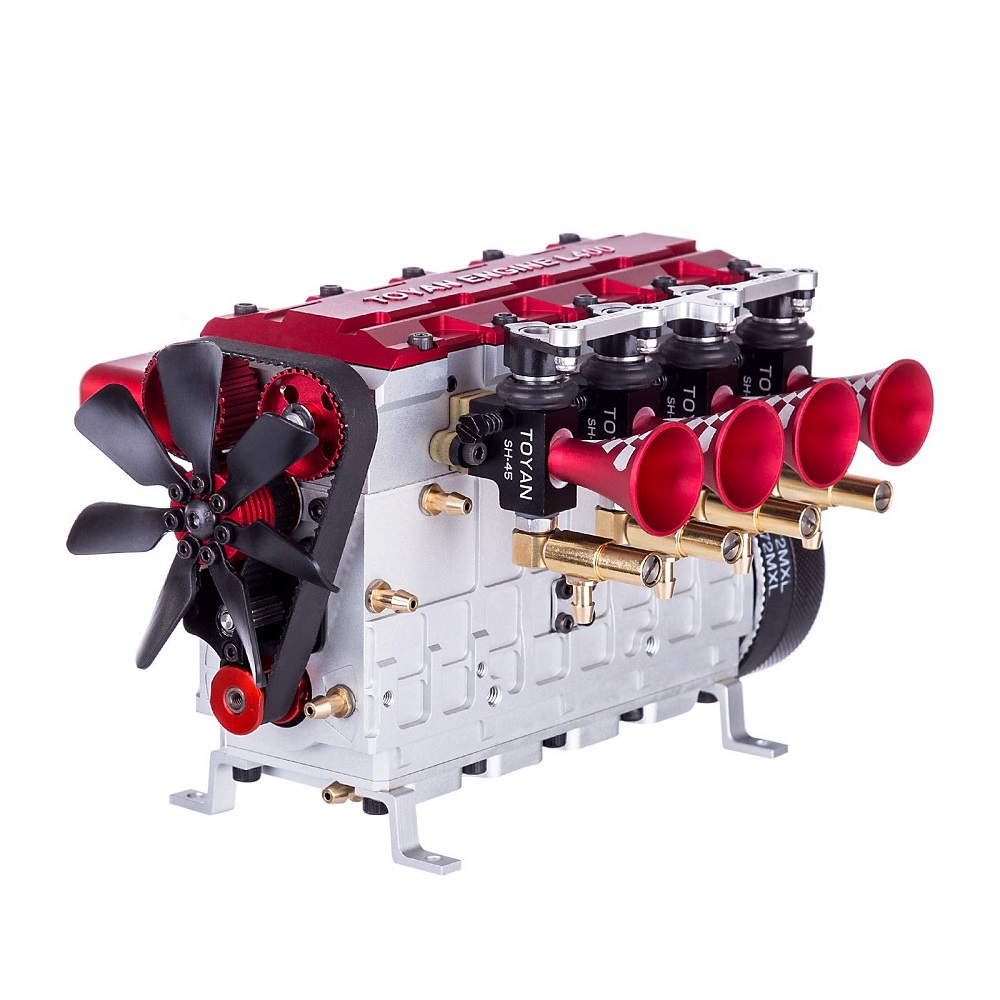

2. Performance and Power
Inline 4 engines are known for balanced performance and fuel efficiency. They are ideal for everyday vehicles and lighter applications.
V6 engines deliver more power and smoother operation. They suit larger vehicles needing extra torque and acceleration.
Inline 6 engines are often praised for their smoothness and higher power output. They are preferred for performance-oriented and luxury vehicles.
3. Cost and Manufacturing
Inline 4 engines are cheaper to manufacture due to their simple structure. They contain fewer parts, leading to lower production costs.
V6 engines, with a more complex design, are pricier to produce and maintain.
Inline 6 engines are expensive to build and require larger vehicles to accommodate their design.
4. Fuel Efficiency
Inline 4 cylinder engines lead in fuel efficiency. Their lightweight design optimizes fuel consumption. This makes them eco-friendly and cost-effective.
V6 engines provide more power but consume more fuel compared to inline 4s.
Inline 6 engines deliver significant power but tend to exhibit higher fuel consumption.
5. Applications
Inline 4 engines are highly versatile. They are found in cars, motorcycles, and small trucks.
V6 engines are commonly used in SUVs, pickups, and some sports cars. They strike a balance between power and size.
Inline 6 engines are seen in performance cars, heavy-duty trucks, and luxury vehicles. They prioritize power and smoothness over compactness.
Summary
The inline 4 cylinder engine is unmatched for efficiency, affordability, and versatility. While other configurations like V6 and inline 6 excel in power and smoothness, they are usually less fuel-efficient and costlier to produce. Choosing the right engine depends on the vehicle’s intended use and required performance. Inline 4 cylinder engines remain the go-to choice for practical applications like daily driving and lightweight vehicles.
Maintenance Tips for Inline 4 Cylinder Engines
Proper maintenance is crucial to keep an inline 4 cylinder engine running smoothly. It extends the engine’s lifespan and enhances performance. Follow these tips for effective maintenance:
1. Regular Oil Changes
Change engine oil every 3,000 to 5,000 miles or as per manufacturer recommendations. Fresh oil helps lubricate moving parts and prevents engine wear. Use the oil type specified in your vehicle’s manual.
2. Replace Air Filters
Check and replace the air filter regularly. A clean filter ensures proper air circulation and improves efficiency. Dirty filters can restrict airflow and affect fuel economy.
3. Inspect and Replace Spark Plugs
Inspect spark plugs every 30,000 miles, or as recommended. Worn spark plugs reduce combustion efficiency and performance. Replace damaged or worn plugs for smooth engine operation.
4. Monitor Coolant Levels
Maintain adequate coolant levels to prevent overheating. Flush and replace coolant as specified by the manufacturer. Overheating can cause serious internal damage to the engine.
5. Keep the Engine Clean
Regularly clean the engine to remove dirt and debris. This prevents blockages and ensures optimal performance. Use a soft cloth and a mild cleaner to avoid damage.
6. Inspect Belts and Hoses
Check for any cracks or fraying in belts and hoses. Replace damaged parts to avoid breakdowns. Belts and hoses ensure proper functioning of various engine components.
7. Check the Battery
Keep the battery terminals clean and secure. Test the battery regularly to ensure it holds a charge. A failing battery can cause engine starting issues.
8. Pay Attention to Warning Signs
Listen for unusual noises such as knocking or ticking. Watch out for warning lights on your dashboard. Address potential issues immediately to prevent larger problems.
9. Ensure Proper Tire Maintenance
Maintain proper tire pressure and alignment for optimal engine performance. Misaligned tires can increase engine workload and fuel consumption.
10. Schedule Regular Inspections
Schedule professional inspections as per your vehicle’s maintenance schedule. Regular check-ups catch minor issues before they become severe.
Following these tips will keep your inline 4 cylinder engine in top condition. Regular care ensures reliability, better performance, and a longer lifetime for your engine.

Leave a Reply