What is a Cylinder Head in an Engine?
The cylinder head is a vital component of an engine. It sits above the engine’s cylinders and forms the top of the combustion chamber. It plays critical roles in ensuring cylinder head engine efficiency and functionality.
Definition and Overview
A cylinder head engine is an engine part that encloses the cylinders from the top. It acts as a cover for the engine block and contains important elements required for combustion. Its design ensures proper airflow, fuel delivery, and heat control.
Cylinder heads are usually made from durable materials like aluminum or cast iron. They are designed to withstand high pressure and temperature generated during engine operation. This helps in maintaining optimal performance and engine longevity.
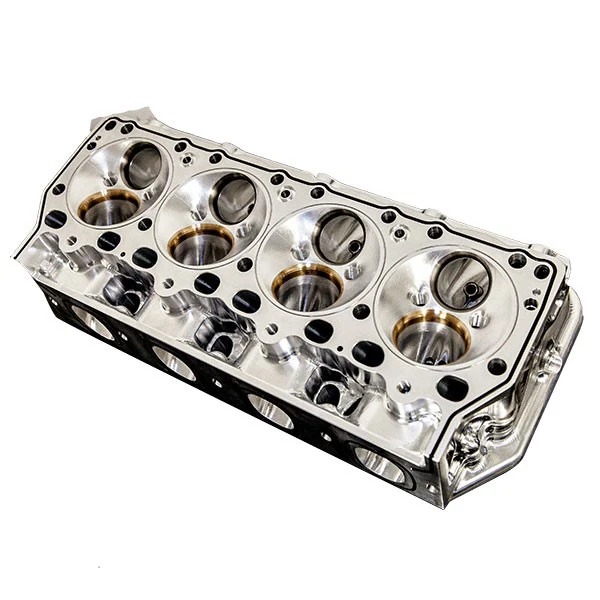

Components of a Cylinder Head
The cylinder head houses several essential components that contribute to engine operation. Here are the key components:
- Combustion Chamber: The area where the air-fuel mixture is burned to produce power.
- Valves: They control the inlet of air and fuel and the outlet of exhaust gases.
- Valve Springs: These ensure the proper closing of valves.
- Rocker Arms: They transfer movement from the camshaft to the valves.
- Spark Plugs: Found in gasoline engines, these ignite the air-fuel mixture.
- Injector Ports: Found in diesel engines, responsible for injecting fuel into the chamber.
- Cooling Channels: They allow coolant to flow and prevent overheating.
- Oil Passages: Used for lubricating moving parts within the cylinder head.
All these components work harmoniously to ensure the engine runs efficiently. Proper maintenance of the cylinder head and its components is crucial for engine performance.
Functions of a Cylinder Head
The cylinder head serves multiple crucial functions in the engine. Its design ensures the proper performance of an engine through its critical operations. Below, we’ll explore the main functions of a cylinder head in detail.
Sealing the Combustion Chamber
The cylinder head seals the combustion chamber to ensure efficient power generation. It forms a tight barrier above the cylinders and prevents fuel or air from escaping during combustion. This sealing is vital for maintaining compression, allowing the engine to produce maximum power. Proper sealing also reduces emissions and improves fuel efficiency.
Facilitating Air and Fuel Mixture Entry
The cylinder head manages the intake of air and fuel into the combustion chamber. It houses the intake valves that open to allow the air and fuel to enter the chamber. This process ensures the mix reaches the cylinder in the correct ratio and contributes to smooth engine operation. The design of the air and fuel channels directly affects engine performance and efficiency.
Heat Dissipation Process
Effective heat management is key to an engine’s longevity. Cylinder heads contain cooling channels to divert heat from the combustion process. The coolant flows through these channels to reduce temperatures in the cylinder head. This process prevents overheating and minimizes the risk of warping or cracking during high-stress conditions.
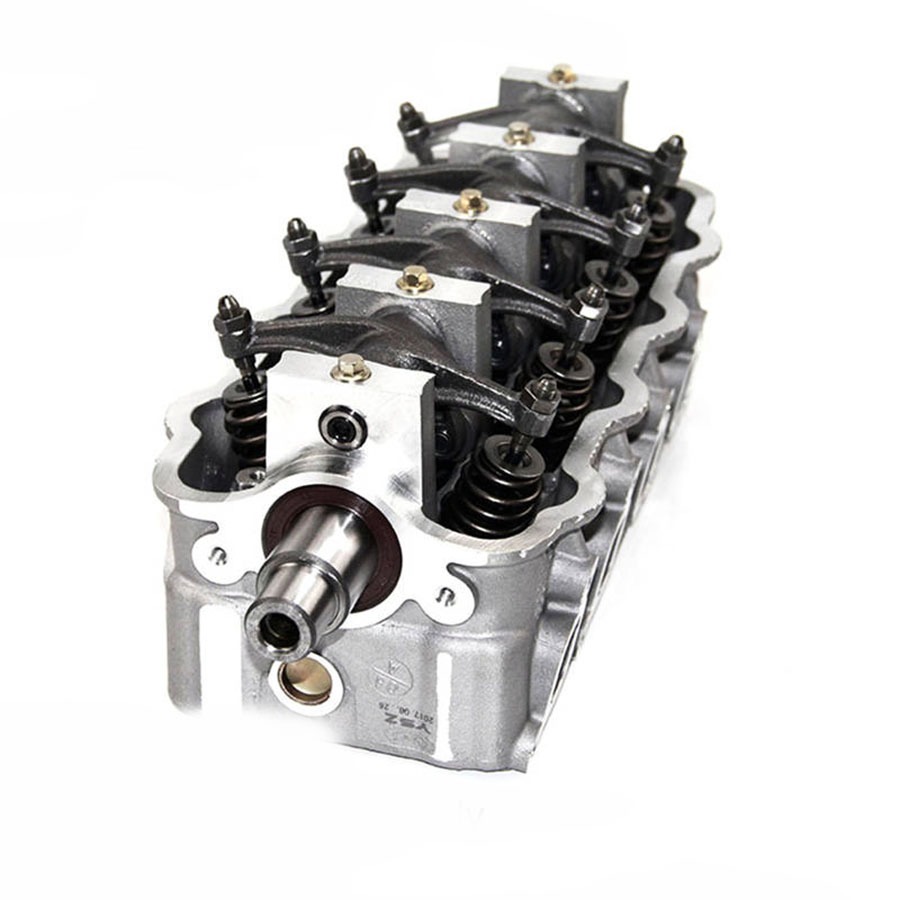

Supporting Valve Mechanism
Another important function of the cylinder head is supporting the valve mechanism. It houses essential components like valves, valve springs, and rocker arms. These parts work together to control the timing of air and fuel intake, as well as the release of exhaust gases. The cylinder head engine ensures the smooth interaction between the camshaft and valves to sustain the engine cycle.
By performing these key roles, the cylinder head contributes significantly to efficient engine operation. Maintaining the cylinder head is crucial for avoiding performance issues and ensuring longer engine life.
Types of Cylinder Heads
Understanding the types of cylinder heads is crucial for assessing engine design and efficiency. Each type offers unique features and advantages based on its setup. Below are the three common types of cylinder heads explained.
Flathead Cylinder Head
Flathead cylinder heads are the simplest type of cylinder head design. They do not contain complicated valve mechanisms overhead. Instead, the valves are positioned beside the cylinders within the engine block.
Key Features:
- Simple construction with fewer parts.
- Easy to manufacture and repair.
- Known for lower cost and compact size.
However, these cylinder heads are less efficient than modern designs. They have restricted airflow and lower power generation. Flathead engines are rarely used in modern vehicles due to these limitations.
Overhead Valve (OHV) Cylinder Head
OHV cylinder heads represent a more advanced design than flathead cylinder heads. Unlike flathead heads, the valves are placed above the cylinders in an OHV engine.
Key Features:
- Improved power and efficiency compared to flathead design.
- Utilizes pushrods to operate the valves.
- Compact design allows fitting into smaller engine spaces.
OHV cylinder heads offer better performance than flatheads. However, they are mechanically more complex and require higher maintenance. They are still popular in various vehicles, especially in trucks and heavy-duty cars.
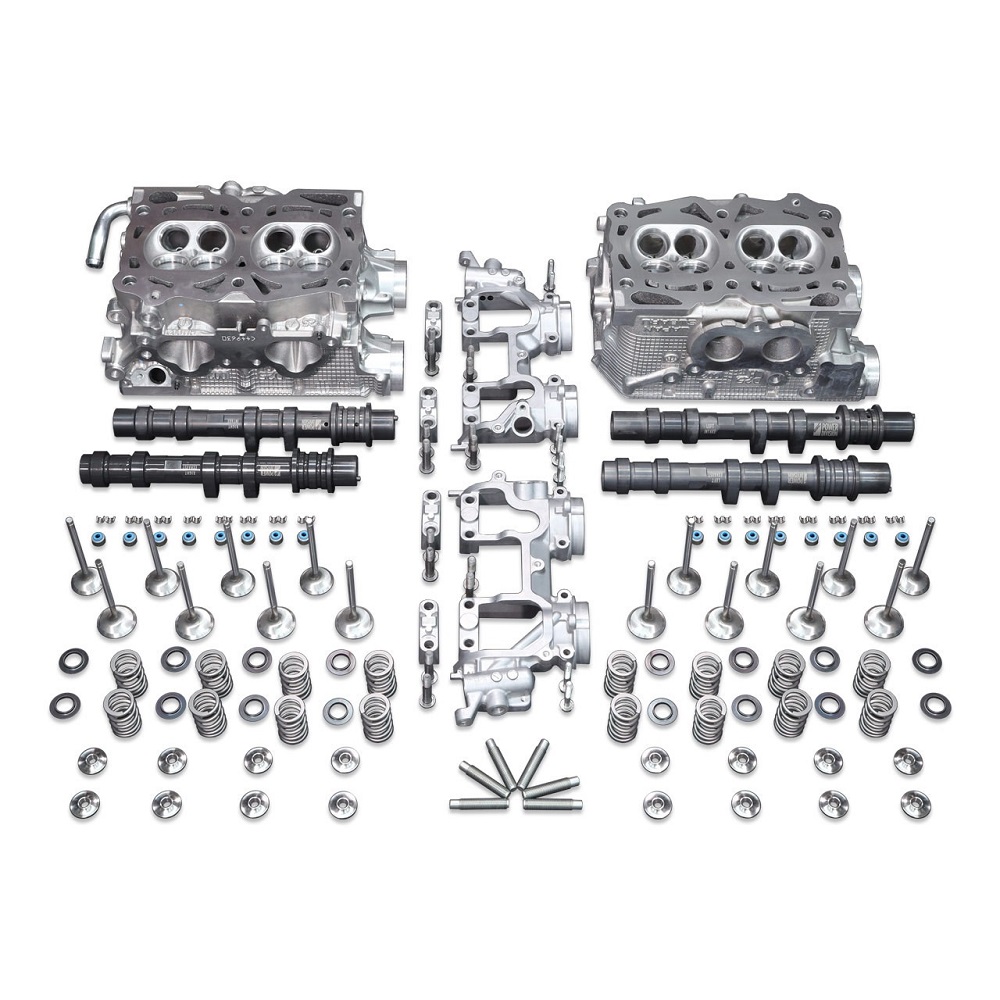
Overhead Camshaft (OHC) Cylinder Head
OHC cylinder heads are regarded as the most efficient and modern type of cylinder head design. They place the camshaft directly above the valves inside the cylinder head.
Key Features:
- Enables direct operation of valves without pushrods.
- Allows higher RPM and better engine performance.
- Suitable for advanced engines needing precision.
OHC heads can be classified into single overhead camshaft (SOHC) or double overhead camshaft (DOHC). DOHC designs provide even finer control over valve operations. They increase engine power and efficiency significantly.
Each of these cylinder head types has distinct advantages and intended uses. Choosing the right cylinder head depends on the engine needs and vehicle purpose.
Material Used in Cylinder Heads
Cylinder heads play a critical role in engine performance and durability. They are typically made from materials that can withstand high stress, pressure, and temperature during operation. Two common materials used for cylinder heads are aluminum and cast iron. Let’s explore their characteristics and compare their benefits to understand their performance better.
Aluminum Cylinder Heads
Aluminum is a lightweight material that is widely used in modern engines. It has excellent thermal conductivity, which helps in quick heat dissipation during engine operation.
Benefits of Aluminum Cylinder Heads:
- Lightweight design improves fuel efficiency.
- Faster heat dissipation prevents overheating.
- Easier manufacturing and shaping processes.
- Resistance to corrosion for prolonged durability.
Aluminum cylinder heads are commonly used in high-performance and modern engines due to their advanced thermal properties and lightweight nature. However, aluminum is softer than cast iron and can be more prone to damage under extreme stress.
Cast Iron Cylinder Heads
Cast iron has been a popular choice for cylinder heads in older and heavy-duty engines. It is durable and able to bear high stress without deforming.
Benefits of Cast Iron Cylinder Heads:
- Tough and durable material.
- Better resistance to stresses caused by high compression.
- Longevity under extreme operating conditions.
- Lower manufacturing costs compared to aluminum.
Cast iron cylinder heads are more robust but heavier. They are commonly found in large trucks and heavy-duty machinery engines where longevity and stress resistance are critical.
Comparison of Materials
Choosing the right material depends on the vehicle’s purpose and engine requirements.
Both materials have unique advantages based on the engine type and workload. Aluminum is better suited for modern and high-speed engines, while cast iron is preferred for heavy-duty tasks. The choice of material directly impacts engine performance, lifespan, and maintenance needs.
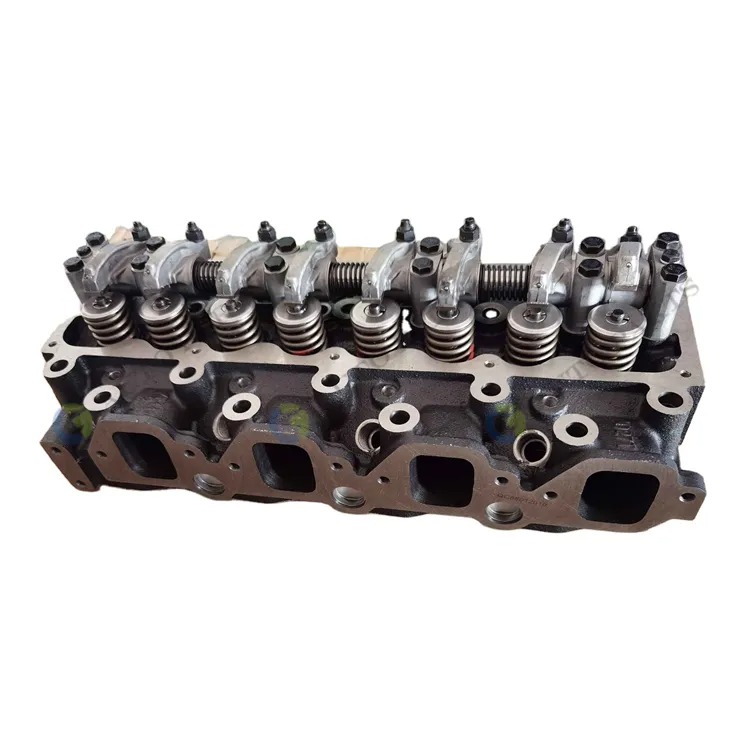

Common Problems with Cylinder Heads
Cylinder heads are vital for engine efficiency, but they can face several problems over time. Identifying these issues early can save you from costly repairs. Below are the most common problems with cylinder heads.
Cracking Issues
Cracks in cylinder heads are a major concern. These often occur due to excessive heat or stress. Overheating is a common cause of cylinder head cracking. Extreme temperature changes can also lead to cracks. Cracks result in coolant leaks or reduced engine compression. This can significantly impact engine performance.
To prevent cracking, ensure proper coolant levels and maintain the cooling system. Always monitor the engine temperature to avoid overheating. Use good-quality cylinder heads made of durable materials like aluminum or cast iron.
Warping and Overheating
Warping occurs when the cylinder head loses its flat shape. It usually happens due to overheating. A warped cylinder head can cause an improper seal with the engine block. This can result in poor combustion and reduced engine efficiency. Overheating the engine is a key factor leading to warping.
To avoid warping, ensure the cooling system functions properly. Check the radiator, thermostat, and coolant levels regularly. Immediate attention to an overheating engine can save the cylinder head from warping. Proper maintenance is key to avoiding this issue.
Leakage in Cylinder Heads
Leakage in cylinder heads is another common problem. Leaks can occur in the cooling channels or the combustion chamber. Coolant or oil leaks are frequent symptoms of a damaged cylinder head. Such leaks can reduce engine performance and cause overheating.
To detect leaks, inspect the cylinder head and its gaskets regularly. Use quality gaskets to maintain a strong seal. Address any leaks promptly to prevent major engine damage. Regular maintenance and inspections can minimize leakage risks.
By understanding these common problems, you can take steps to maintain your cylinder head. Proper care will ensure efficient engine performance and a longer lifespan for the cylinder head engine.
Maintenance and Care for Cylinder Heads
Proper maintenance of the cylinder head ensures optimal engine performance and a longer lifespan. Proactive care prevents common issues and costly repairs. Following key steps can help you maintain your cylinder head efficiently.
Regular Inspection and Cleaning
Inspect the cylinder head regularly to catch signs of wear or damage. Look for cracks, leaks, or discoloration. Frequent checks protect the engine from larger issues.
Clean the cylinder head to prevent buildup of carbon deposits. Carbon buildup can block airflow and reduce combustion efficiency. Remove debris using appropriate cleaning tools and solutions.
Inspect the cooling channels and oil passages. Ensure they are free of blockages to maintain proper heat dissipation and lubrication. Regular cleaning reduces overheating risk and boosts engine efficiency.

Importance of Tightening Bolts Properly
Bolts play a key role in securing the cylinder head to the engine block. Improper bolt tightening can cause leakage or loss of compression. This affects engine performance and increases wear.
Use a torque wrench to tighten bolts evenly. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended specifications for bolt torque. Avoid overtightening, as this can warp the cylinder head or damage threads.
Loose bolts can lead to poor sealing and combustion issues. Recheck bolt tightness during regular vehicle maintenance. Correct tightening ensures a secure seal and improves engine efficiency.
Recognizing Signs of Damage
Recognizing damage early can save your engine from expensive repairs. Common signs include coolant or oil leaks near the cylinder head. Frequent overheating or loss of compression are also red flags.
Monitor exhaust smoke. White smoke could indicate coolant leaks, while blue smoke suggests oil leaks. Watch for engine misfires or loss of power, which may point to cylinder head issues.
Address these signs immediately by visiting a mechanic for diagnosis. Identifying problems early ensures timely repairs and protects the engine from further damage.
By following these maintenance steps, you can keep your cylinder head engine in excellent shape. Regular care ensures optimal performance, reliability, and longer lifespan for your vehicle.
Replacement and Repair of Cylinder Heads
Cylinder heads are vital for engine operation. Over time, they may require replacement or repairs. Understanding when to replace or repair them ensures your engine operates efficiently. Regular maintenance helps minimize repair needs, but knowing these processes is crucial.
When Should a Cylinder Head be Replaced?
Cylinder head replacement is necessary in specific situations. Below are the common indicators for replacement:
- Severe Cracking: If cracks are extensive, repairing becomes impossible. Replacement ensures safety and performance.
- Warping Beyond Repair: Excessive warping can affect sealing. When machining cannot restore the surface, replacement is required.
- Repeated Leaks: Continuous oil or coolant leaks despite repairs indicate a need for replacement.
- Corroded Material: Significant corrosion weakens the structure. When corrosion spreads, replacement prevents engine failure.
- Aging Cylinder Head: An old cylinder head may develop multiple issues. Replacement ensures engine reliability.
Recognizing these signs early lowers repair costs and prevents further engine damage. Always consult a professional mechanic for accurate diagnosis.
Process of Cylinder Head Repair
Repairing a cylinder head engine requires precise steps. Skilled mechanics typically follow these steps to ensure a proper fix:
- Diagnosis: Mechanics inspect for cracks, warping, or leaks. Pressure tests identify hidden faults.
- Disassembly: The damaged cylinder head is removed. Other components like gaskets and bolts are checked.
- Cleaning: The cylinder head is cleaned thoroughly. This removes carbon buildup, dirt, and debris.
- Machining: Warped cylinder heads undergo machining. A flat surface ensures proper sealing and functionality.
- Crack Repair: Epoxy sealants or welding repair cracks. This process restores the cylinder head.
- Replacement of Worn Parts: Damaged valves, springs, or seals are replaced. This ensures smooth operation.
- Reassembly: Mechanics carefully reassemble the cylinder head engine. Proper bolt tightening ensures a secure fit.
- Testing: The repaired cylinder head engine is tested for leaks and pressure performance.
While repair restores efficiency, it’s not always possible. If repairs fail to provide lasting solutions, replacement becomes the best option. Regular maintenance and timely checks prevent extensive damage to your cylinder head engine.

Leave a Reply