What is a Four Cylinder Engine?
A four cylinder engine is a type of internal combustion engine. It uses four cylinders arranged in a specific configuration. This engine type is popular in various vehicles due to its balance of power and efficiency.
Overview of Engine Configuration
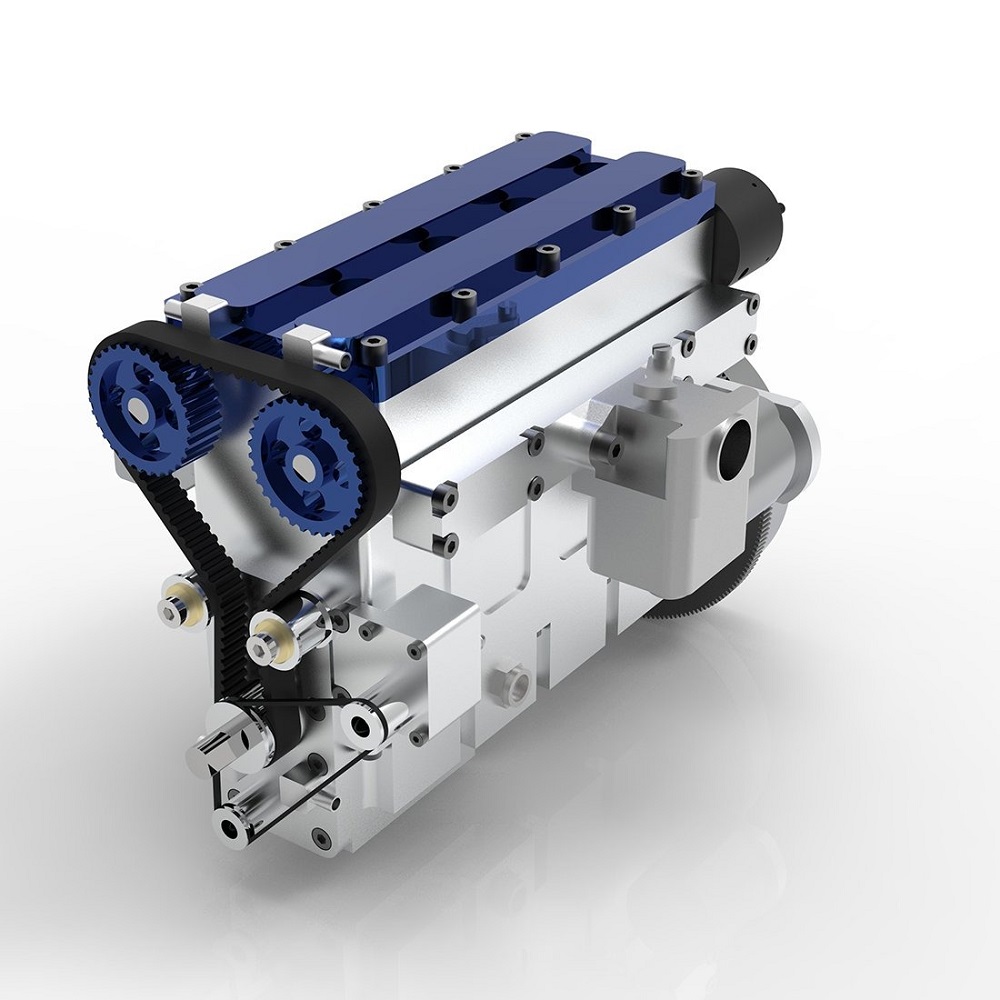
A four cylinder engine is typically configured in an inline layout. In this setup, all four cylinders are aligned in a single row. This arrangement is common because it requires less space and is simple to manufacture. Inline configuration provides smooth operation and reduces vibration.
Another possible configuration is the “flat” or “boxer” layout. Here, the cylinders are placed horizontally in two sets of opposing pairs. This setup offers a lower center of gravity, which enhances handling in vehicles.

Key Components of a Four Cylinder Engine
- Cylinders: The engine’s core consists of four cylinders, where fuel combustion occurs.
- Pistons: Each cylinder contains a piston, which moves up and down as the engine operates.
- Connecting Rods: These rods connect the pistons to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: The crankshaft converts the pistons’ linear motion into rotational motion.
- Camshaft: It controls the timing of the engine’s valves.
- Valves: These open and close to allow air and fuel in and exhaust out.
- Fuel Injectors: They spray fuel into the combustion chamber for ignition.
- Spark Plugs: These ignite the fuel-air mixture to create combustion.
Each component plays a vital role in the engine’s functionality. Together, they ensure the engine runs smoothly and efficiently.
How Does a Four Cylinder Engine Work?
A four cylinder engine works through a series of precise mechanical processes. Its operation involves converting fuel and air into energy to power a vehicle. The engine cycles through four main strokes: intake, compression, power, and exhaust.
The working principle
- Intake Stroke: The intake valve opens, allowing air and fuel into the cylinder. This creates the mixture needed for combustion.
- Compression Stroke: The piston moves up, compressing the air-fuel mixture. This increases its energy potential for ignition.
- Power Stroke: The compressed mixture is ignited by the spark plug. This creates an explosion that forces the piston down. The force of this motion powers the crankshaft.
- Exhaust Stroke: The exhaust valve opens, allowing the used gases to leave the cylinder. The piston then rises to push the gases out fully. This prepares the cylinder for the next cycle.
These strokes occur in repeated sequences to power the vehicle. The engine’s precision ensures a smooth and efficient operation. Every cylinder contributes to the overall performance of the engine.
Comparison to other engine types
A four cylinder engine differs from other engines, like three-cylinder or six-cylinder ones, in several ways:
- Efficiency: Four cylinder engines provide a balanced mix of power and fuel efficiency. They are more efficient compared to larger engines like six or eight cylinders.
- Size and Weight: Four cylinder engines are compact and lightweight. This makes them ideal for smaller vehicles, unlike heavier six or eight-cylinder engines.
- Cost-effectiveness: Producing and maintaining a four cylinder engine costs less compared to bigger engines. This makes them more affordable for general use.
- Power Output: While sufficient for daily driving, four cylinder engines may not match the power of larger engines. This makes them less suited for high-performance or heavy-duty needs, where a six or eight-cylinder engine excels.
Understanding how four cylinder engines work and their comparisons with others helps in choosing the right fit for specific needs.
Advantages of a Four Cylinder
A four cylinder engine offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for modern vehicles. These benefits highlight its efficiency, compact size, affordability, and practicality.
Fuel efficiency
Four cylinder engines are known for their fuel efficiency. They consume less fuel compared to larger engines like six or eight cylinders. This efficiency is often due to their smaller size and reduced weight. Engineers design these engines to optimize fuel use, ensuring less waste. For drivers, this means lower fuel costs and fewer trips to the gas station.
Compact design and lightweight
The compact design of a four cylinder engine allows it to fit into small spaces. This is ideal for vehicles with limited room under the hood. Since it is lightweight, it reduces the overall weight of the vehicle. A lighter vehicle improves maneuverability and handling. It also enhances fuel economy, making vehicles more eco-friendly.
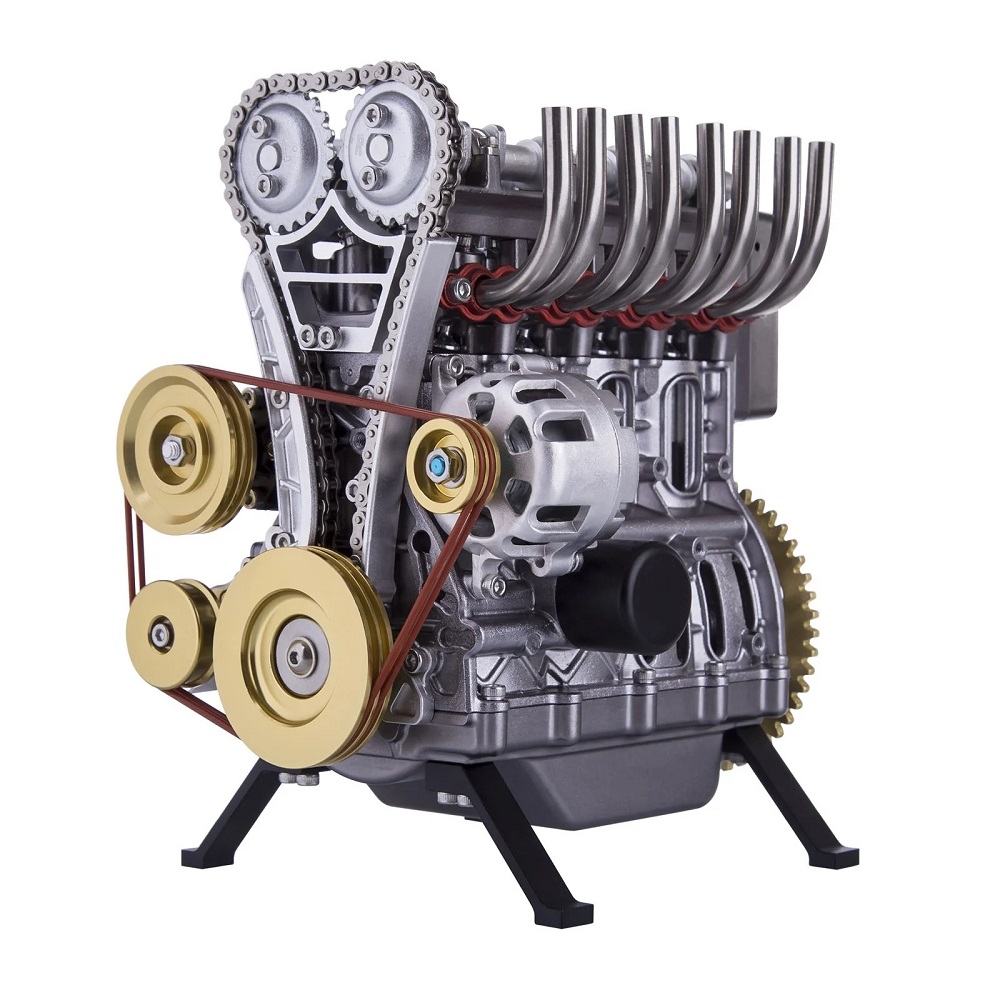

Cost-effectiveness
Four cylinder engines are affordable to produce and maintain. Their simpler design requires fewer materials, cutting manufacturing costs. Repairs and maintenance are also less expensive than with larger engines. Many vehicles equipped with four cylinder engines have a lower upfront cost. This affordability appeals to drivers seeking reliable and budget-friendly options.
These advantages make the four cylinder engine a practical choice for many vehicles. Its combination of efficiency, compact design, and cost-effectiveness supports its widespread use.
Performance Capabilities of Four Cylinder
Understanding the performance capabilities of four cylinder engines helps assess their suitability for various uses. These engines balance power, efficiency, and practicality to meet everyday driving needs and beyond.
Horsepower and torque
Four cylinder engines offer adequate horsepower for most driving situations. Their designs focus on delivering efficiency and steady power. Horsepower typically ranges from 100 to 300, depending on the engine model.
Torque is essential for acceleration and pulling power. Four cylinder engines deliver sufficient torque for commuter cars and small trucks. Advanced designs improve torque output, ensuring smooth performance even in challenging driving conditions. While not matching larger engines’ power levels, these engines perform well under normal use.
Suitability for everyday driving
These engines are ideal for daily driving due to their efficiency and reliability. They power sedans, compact SUVs, and small trucks efficiently, making them popular choices. Their compact design allows better fuel economy, reducing costs for everyday drivers.
Four cylinder engines also excel in urban environments. Their lightweight nature contributes to responsive handling and ease of parking. Combined with good fuel efficiency, they fit well with modern commuting demands.
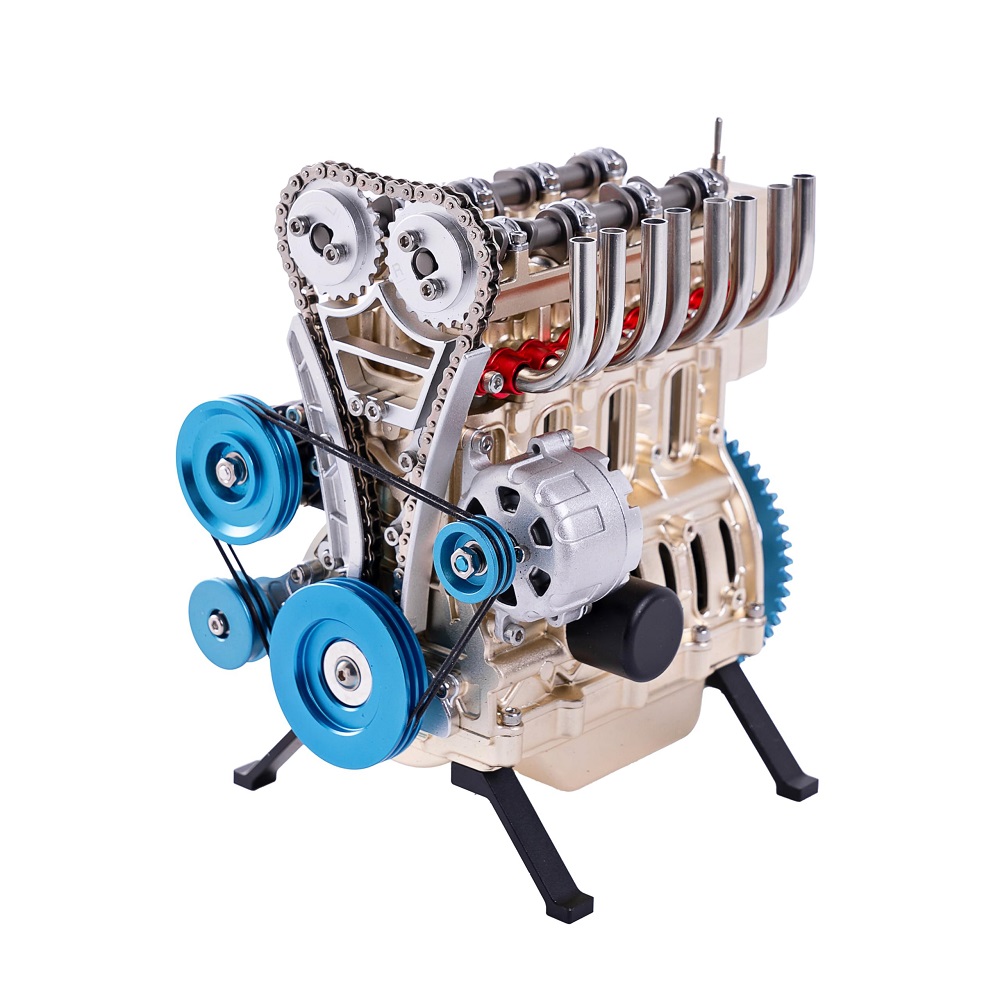

High-performance variations
High-performance four cylinder engines push boundaries with advanced technology. Turbocharging is common, increasing horsepower without needing larger engine sizes. Such engines deliver impressive speeds and acceleration while remaining efficient.
Manufacturers also equip some engines with direct fuel injection systems. These improve power delivery and overall performance while maintaining fuel efficiency. Sports cars or high-end models often feature these advanced versions of four cylinder engines.
In conclusion, four cylinder engines balance horsepower, torque, and efficiency. Their performance capabilities make them versatile for everyday driving and even high-performance needs.
Applications of Four Cylinder
A four cylinder engine is versatile and widely used in various applications. Its compact design, efficiency, and balance of power make it ideal for diverse needs. From vehicles to other industries, this engine type has proven its effectiveness and reliability.
Popular vehicle types using this engine
- Compact Cars: Many sedans and hatchbacks use four cylinder engines. These vehicles prioritize fuel efficiency and city-friendly design.
- Crossover SUVs: Compact and mid-size crossover SUVs often come equipped with four cylinder engines. These engines provide enough power for daily commuting and family trips.
- Small Trucks: Some light-duty trucks use four cylinder engines to balance decent towing capacity and fuel economy.
- Hybrid and Electric Vehicles: Many hybrid cars, and some plug-in vehicles, use four cylinder engines alongside electric motors for added efficiency.
These engines are especially suited for vehicles prioritizing affordability, lower emissions, and mileage.
Other industries and applications
- Marine Vehicles: Four cylinder engines serve as outboard motors for smaller boats and personal watercraft. They ensure efficiency and reliability on water.
- Power Equipment: These engines power devices like generators, pressure washers, and water pumps, offering consistent performance.
- Agricultural Machines: Four cylinder engines are used in small tractors and tillers. They provide steady power for farming needs.
- Construction Equipment: Compact machines such as skid steers and loaders use these engines. They deliver reliable performance with manageable size and weight.
- Motorcycles and ATVs: High-performance motorcycles and all-terrain vehicles (ATVs) frequently use enhanced four cylinder engines.
Given their balance of affordability, efficiency, and practicality, four cylinder engines remain a top choice in both the automotive and non-automotive sectors. They continue to demonstrate their adaptability across a variety of applications.
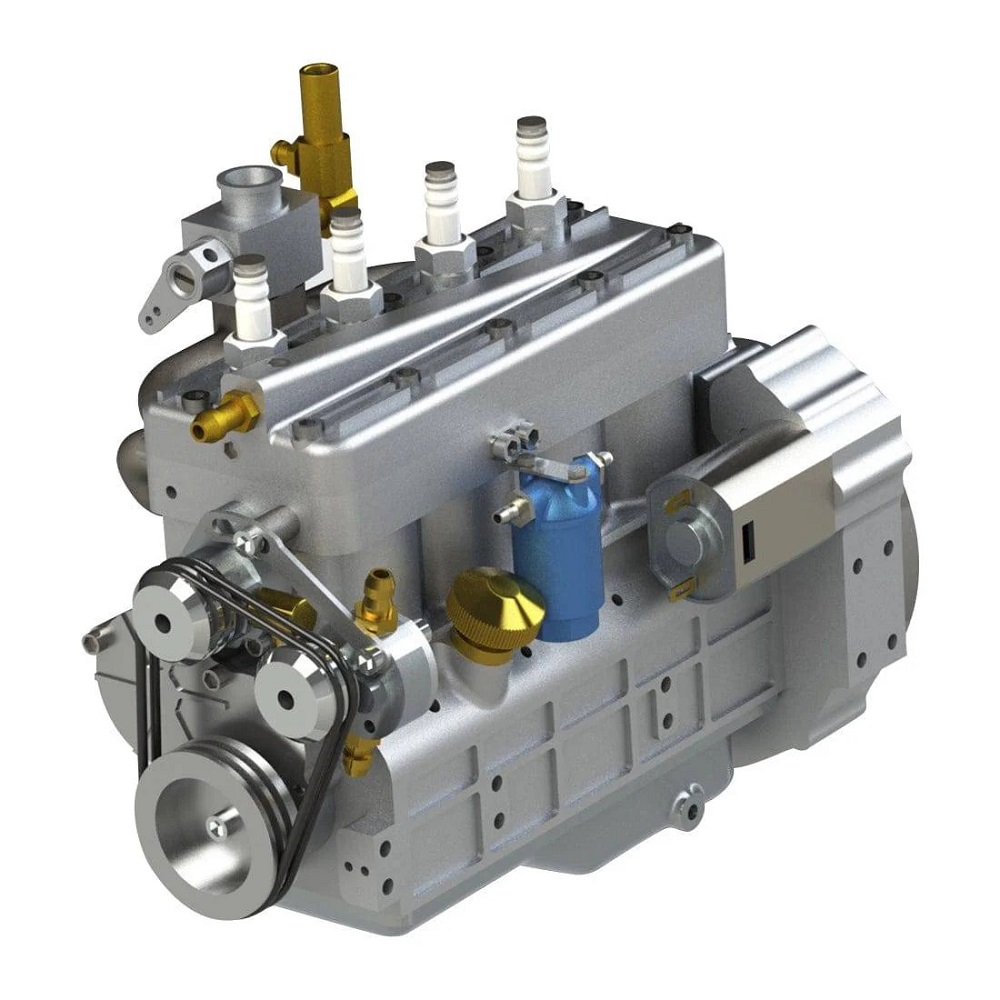

Four Cylinder Engines vs Other Engine Types
Understanding how a four cylinder engine compares to other engine types helps in choosing the right option. These comparisons highlight the strengths and limitations of different engine configurations for various needs.
Comparison with three-cylinder engines
- Power and Performance: Four cylinder engines produce more power than three-cylinder engines. They are better suited for faster speeds and greater acceleration.
- Smoothness: They operate more smoothly, with less vibration. Three-cylinder engines often feel rougher due to their configuration.
- Fuel Efficiency: While three-cylinder engines are lighter and often more fuel-efficient, the difference is not significant.
- Cost and Maintenance: Three-cylinder engines are slightly cheaper to produce and maintain. This is because they have fewer parts, like one less cylinder.
In summary, a three-cylinder engine is ideal for small, city-centric vehicles aiming for top fuel economy. However, the four cylinder engine delivers a better balance of power and smoothness for varied driving conditions.
Comparison with six and eight-cylinder engines
- Size and Weight: Four cylinder engines are smaller and lighter, making them ideal for compact vehicles. Six and eight-cylinder engines are heavier and take up more space.
- Fuel Efficiency: Four cylinder engines consume less fuel than six or eight-cylinder engines. This makes them more economical and eco-friendly.
- Power Output: Larger engines deliver greater power and torque, suitable for high-performance or heavy-duty tasks.
- Cost: Four cylinder engines are cheaper to produce and maintain. Six and eight-cylinder engines have higher upfront and maintenance costs.
- Versatility: Four cylinder engines suit everyday vehicles. Larger engines excel in sports cars, trucks, and powerful SUVs.
In conclusion, the four cylinder engine strikes a balance between power and efficiency compared to its counterparts. It is an excellent choice for commuters and urban drivers. Meanwhile, those seeking extreme performance or towing capacity might opt for six or eight-cylinder options.
Maintenance Tips for Four Cylinder
Regular maintenance keeps a four cylinder engine running smoothly. Let’s explore common issues and preventive practices.
Common issues to watch for
- Oil leaks: Inspect for leaks around the oil pan and valve cover. Replace seals if necessary.
- Overheating: Ensure the cooling system works efficiently. Check the thermostat and coolant level regularly.
- Worn-out spark plugs: Faulty spark plugs can reduce engine performance. Replace them as per the recommended schedule.
- Timing belt wear: A worn timing belt can cause engine damage. Inspect and replace it when required.
- Clogged fuel injectors: Dirty injectors reduce engine efficiency. Clean them or use fuel additives to prevent clogging.
- Low compression: This issue can reduce engine power. Perform regular compression tests to monitor it.
- Check engine light: Pay attention when this light comes on. Diagnose the issue promptly to avoid further problems.
By addressing these issues early, you can save on costly repairs in the future.
Preventive maintenance practices
- Regular oil changes: Replace the engine oil every 5,000-7,500 miles. Use high-quality oil recommended by the manufacturer.
- Replace air filters: Change air filters yearly or as specified. Clean filters improve engine airflow and performance.
- Monitor coolant levels: Check and top off the coolant regularly. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Inspect belts and hoses: Look for cracks or wear. Replace them to prevent breakdowns.
- Keep the fuel system clean: Use quality gasoline and clean injectors. This ensures optimal performance and fuel efficiency.
- Check battery health: Test and clean battery terminals. Replace the battery if needed for consistent starts.
- Follow the maintenance schedule: Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for all engine checks and replacements.
By following these maintenance tips, you can prolong the life and efficiency of your four cylinder engine. Regular care ensures optimal performance and reduces the chances of major breakdowns.
Future of Four Cylinder Engines
The future of four cylinder engines is promising, with innovations and environmental considerations shaping their development.
Innovations and Developments
Recent innovations are transforming the potential of four cylinder engines. Manufacturers are focusing on improving performance while maintaining efficiency. Turbocharging is becoming more common, boosting horsepower without increasing engine size. Direct fuel injection is another key advancement. It ensures better fuel distribution, improving power and efficiency.
Hybrid technology is also enhancing four cylinder engines. These hybrids combine traditional engines with electric motors. They provide better mileage and reduce emissions. Advances in lightweight materials further enhance engine performance. High-strength alloys and composites reduce engine weight, improving fuel economy.
Moreover, Variable Valve Timing (VVT) technology plays a big role. VVT adjusts valve operation for optimal performance at different speeds. It improves fuel efficiency and reduces harmful emissions. Auto manufacturers are continually researching ways to refine these innovations. The focus remains on creating engines that are powerful, economical, and eco-friendly.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Four cylinder engine have a positive impact on sustainability. Their smaller size consumes less fuel, reducing carbon emissions. Engineers are working to make them even more eco-friendly. The development of hybrid four cylinder engines reduces dependency on fossil fuels. They use a combination of gasoline and electric power. This transition supports environmentally conscious driving.
Moreover, advancements in cleaner combustion technologies help minimize pollutants from fuel burning. Continuous research on alternative fuels also promotes sustainability. Biofuels and synthetic fuels offer renewable, lower-emission options for these engines.
Electric vehicles pose a challenge to traditional internal combustion engines, including four cylinders. But, hybrid designs ensure four cylinder engines remain part of this transition. Their adaptability allows them to align with new automotive trends.
In conclusion, four cylinder engine adapt well to future needs. Their ongoing innovations and sustainability actions promise a stable role in modern transportation.
Leave a Reply